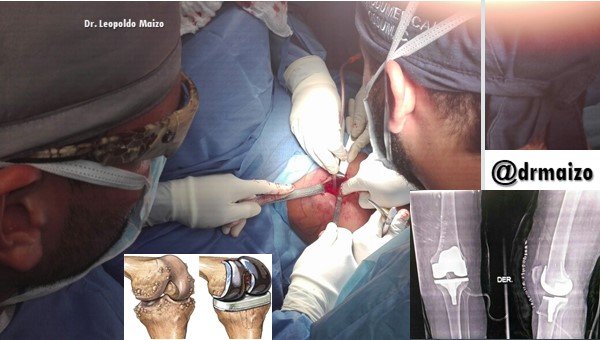
Joint Replacement
One of the most complex surgeries in the world of orthopedic surgery are those of joint replacement and placement of prostheses, being the most common at the level of the hip and knee. Although they are surgeries that require many hours of work, they are justified by the benefit they provide to patients who recover through these surgical interventions.
Today we will talk about knee replacement surgery.

What are the benefits of a total knee prosthesis?
The greatest benefit is the disappearance of pain. Some patients notice some discomfort in the operated joint after the intervention. This discomfort is due to the surgery and to the fact that the muscles surrounding the joint are weakened by inactivity. This discomfort may last for a few weeks or months. As for muscle strength, it usually recovers once the pain fades. Mobility improves and recovery depends on how stiff the joint was before the operation.
Risks
As in any surgical procedure, there are risks in the placement of the knee prosthesis. We recommend the patient to inform the doctor of any problem or health situation to be taken into account at the time of surgery. In order to determine the surgical risk as accurately as possible and prevent possible complications, blood tests, a chest X-ray and an electrocardiogram are performed. These tests are evaluated by the clinician and anesthesiologist when interviewing the patient. The anesthesiologist will report on the type of anesthesia and the risks involved.

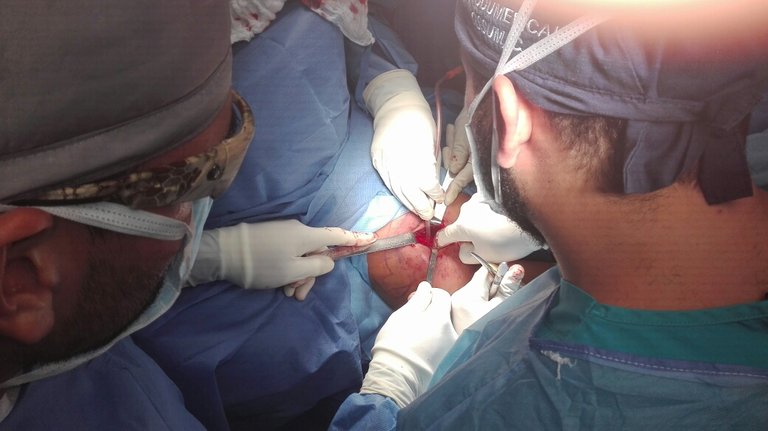
Possible complications
The greatest potential complication of a total knee prosthesis is infection. Its origin may be located right in the wound area or deep around the prosthesis. It can occur during admission to the hospital or once the patient is at home, and even years after the intervention. Superficial wound infections are treated with antibiotics. Deep infections require surgical treatment and removal of the prosthesis.
Sometimes the infection is caused by the spread of an infection located elsewhere in the body. To prevent this type of infection, total knee replacement wearers should take antibiotics before undergoing dental manipulations, urinary catheterizations, or other types of surgery. If an infection occurs, antibiotic treatment is indicated.
There are other complications directly related to the prosthesis:
Loosening: this is the most frequent mechanical problem after implantation of a prosthesis. It causes pain and, if important, it may be necessary to replace the prosthesis with another. The development of new methods of attaching the prosthesis to the bone will minimize or eliminate this problem in the future.
Dislocation of the kneecap: in important osteoarthritis, with large deformities of the knee, another possible complication is that, once the prosthesis is placed, the kneecap dislocates. The patient usually repositions it spontaneously. In some cases, a reintervention will be necessary to solve it.
Wear: it is a slow process. It can contribute to loosening, although it is rarely necessary to reoperate due to isolated wear.
Rupture: rupture of implants is very rare. If it occurs, a new intervention will be necessary.
Nerve injuries: the nerves close to the operated joint are rarely injured. It can occur in cases in which a very important deformity must be corrected. With time, nerve functions usually recover.
Is the total knee prosthesis definitive?
The expectation of most elderly people is that the prosthesis should not be changed for the rest of their lives. It will provide them with years of painless well-being, achievement impossible otherwise. In young and active people it is likely that a new intervention is needed for the prosthetic replacement. Surgical materials and techniques are rapidly improving thanks to the joint work of orthopaedic surgeons, engineers and other scientists. The future is very bright for patients with a total knee prosthesis.

If you need recommendations or help in orthopedic surgery and traumatology do not hesitate to contact me.
Dr. Leopoldo Maizo - Orthopedic Surgeon

If you want to read more I invite you to visit my page:

Firma diseñada por @themonkeyzuelans, contáctalos vía Discord "themonkeyzuelans#9087"
Great projects from the Steemit community:
- My Fundition campaign: https://fundition.io/#!/@drmaizo/6f88ggj8h

.png)
This project is being supported by @Fundition
Fundition is a next-generation, decentralized, peer-to-peer crowdfunding and collaboration platform, built on the Steem blockchain.
https://fundition.io.#upfundition and #fundition tags on Steem represent the projects that are started on
Are You Prepared to Make the World a Better Place too?
Read the full details of Fundition Fund program
Learn more about Fundition by reading our purplepaper
Join a community with heart based giving at its core
I see that knee prosthesis has come a long way in 20 years..
The prosthesis used to be anchored up the femoral shaft and down the tibial bone shaft, or is there a reason for the short anchor in the above?
Less destructive/intrusive?
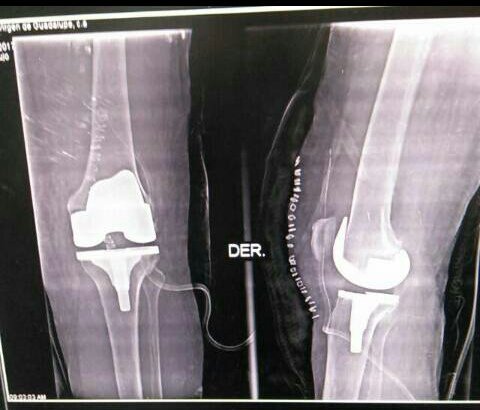
It depends on the cause of the placement of the prosthesis. For example, for chronic infectious processes at bone level and tumor resections, long stems are usually used in the femur shagt and the tibia shaft. When these are placed only by processes of osteoarthritis can be so small that it can even be placed partially. I show you a photo with the two examples:
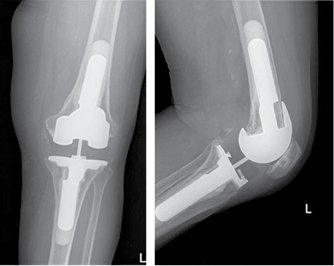
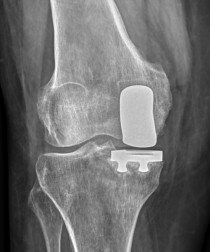
I see. I was unaware of the different types of prosthesis. They are great examples.
Many thanks for the reply.
You are welcome my friend!! :D