Testicular cancer is a cancer that affects the testicles in men, and generally this cancer affects younger men between the
ages of 25 and 30. This cancer is often curable through proper treatment. Treatment options include surgery, radiation
therapy and chemotherapy. If you have been diagnosed with testicular cancer, learn how to treat the cancer stage that is
affecting you.
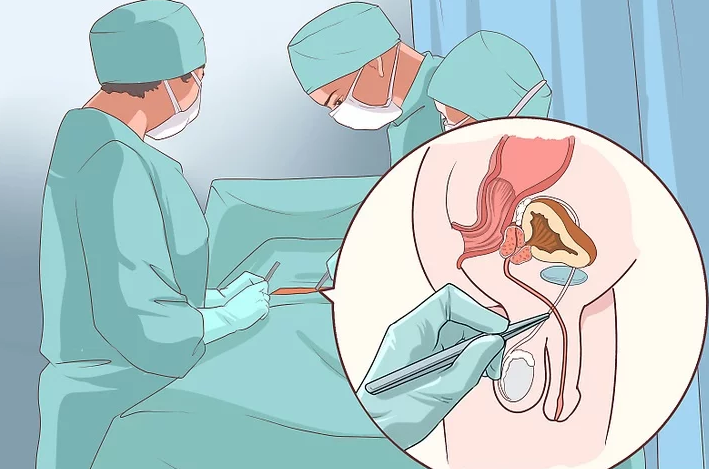
Surgically remove the tumor. Rarely are biopsies performed for testicular cancer because biopsies for this type of cancer in particular increase the risk of cancer spread. If a tumor is detected through a clinical diagnosis, ultrasound, and blood
test, the doctor will remove the tumor in a process called radical inguinal orchiectomy.
In addition to the tumor, the testicle and spermatic cord will also be removed. If you remove the entire testicle, you have
the option of getting a testicular implant
The tumor and other tissues are sent to a laboratory for examination for cancer cells.
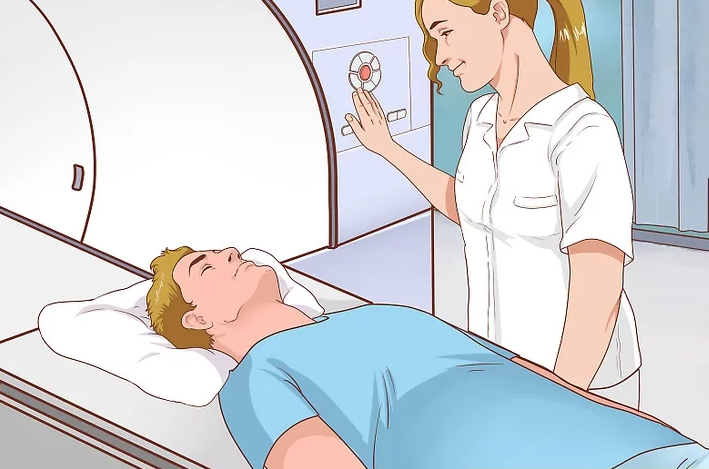
Obtain imaging tests. If the tumor analysis shows there are cancer cells, then your doctor will order imaging tests, such as
an ultrasound (to check for fluid or a solid mass), x-rays, MRI, CT, PET, or bone scans. . The doctor will need images of
your body to determine certain important things about your cancer
Imaging tests will be used to determine if the cancer has spread and where. These tests can help the doctor find out if the
cancer has spread to other areas, such as the lymph nodes or other organs. A CT scan is recommended if metastatic
dissemination is suspected in the pelvis and thorax.
Imaging tests are also used to see if the treatment is working and if the cancer comes back after treatment.
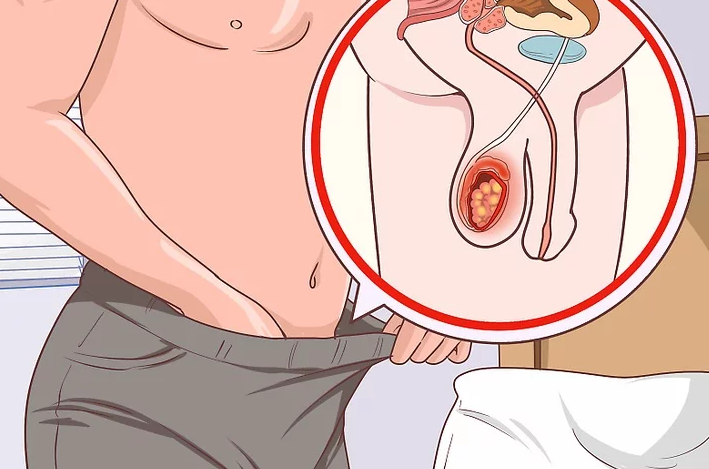
Determine the stage of the cancer. Testicular cancer is divided into stages. The cancer stage refers to the severity of the
cancer. The stage is determined from the examination of the tumor, where the cancer cells are studied in a laboratory. Your
treatment depends on the stage of the cancer, so you will always get cancer by stages when you are diagnosed
Stage 0 testicular cancer occurs when abnormal cells are found in the testicles. The cells can evolve to cancer, but at this
stage they are simply abnormal. This can be something like a testicular scar.
Stage I cancer is discovered after the testicle (s) is removed. Stage I cancer occurs when the cancer is in the testicle or
in the membranes around the testicle. Stage I may also be in the spermatic cord or scrotum. Surgery and close monitoring can be all the treatment needed for stage I. Sometimes chemotherapy or radiation is also used.
Stage II cancer is when the cancer is in the testicle, scrotum, and spermatic cord, along with the lymph nodes in the abdomen. Stage II is often treated with radiation therapy. Sometimes, mild chemotherapy is also used.
Stage III cancer has the same markers as stage II, but it has also spread to lymph nodes beyond the abdomen, to the lungs, or other parts of the body. Surgery is often needed to remove tumors in other parts of the body, along with chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy may involve a combination therapy based on cisplatin with three cycles of bleomycin, etoposide and cisplatin. However, men with compromised lung function should be careful if they receive bleomycin because this chemotherapy can cause lung damage.

Develop your treatment team. You will work with a treatment team when you undergo treatment for testicular cancer. Your equipment will vary depending on the stage of your cancer and your options to treat that stage
You will probably have a urologist, a medical assistant, nurse practitioners and nurses.
If you have radiation therapy, you will have a radiation oncologist. If you undergo chemotherapy, you will have a medical oncologist. You can also have social workers or other mental health professionals, physiotherapists or other professionals.
(THANK YOU FOR READING IF WANT SATISFIED KEEP SUPPORTING THIS TOPIC RELATED ANY QUESTION ASK ME IN COMMENT BELOW )
(DON,T FORGET TO FOLLOW HIM AND SUPPORT ME THANK YOU FOR WATCHING