Once upon a time, there was a molecule X. The molecule X was very stable with all its covalent bonds. But one day it was passing by this protein. The protein grabbed it at broke it into two small molecules. The Twitter of the molecular world went crazy, blaming the proteins as these evil giant molecules, who modify other molecules. In return many other proteins tweeted - #NotAllProtiens. They labelled the proteins responsible for modifying other molecules as 'Enzymes'.
Image created using fake twitter message generator
Proteins vs enzymes
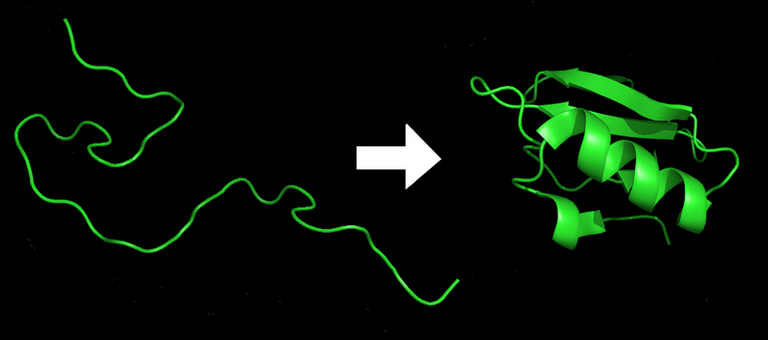
A public domain image
And, this is exactly where the difference lies. Proteins are just a long chain of amino acids, which fold onto itself to form a certain 3D structure. This 3D structures are just simple molecular machines, that does different functions to keep the cell or an organism alive. However, just because all proteins are made of amino acids that doesn't mean they do the same thing.
There are 20 amino acids that join together in different permutation and combinations. What a protein will fold as and function as depends of sequential arrangement of these amino acids.
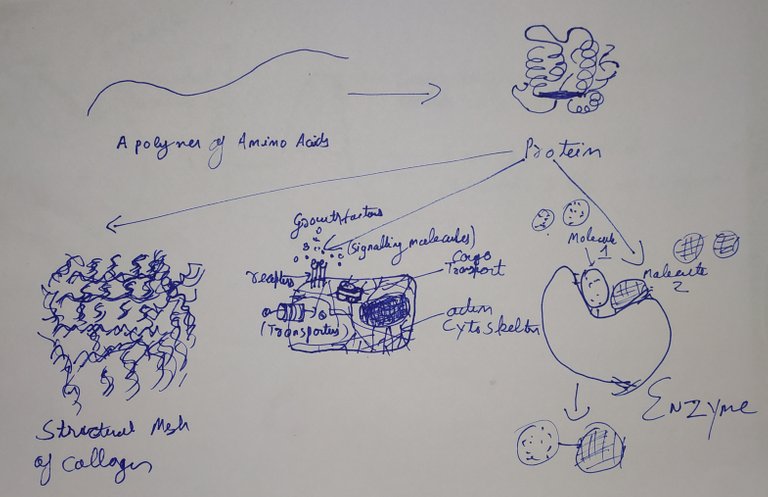
@scienceblocks
For instance, collagen protein in the tissue can be thought of as a mesh of iron rods supporting the structure of the tissue. Then there are these proteins on the surface of the cells which are always sensing the environment - such as growth factor receptors. And then the growth factors themselves are proteins which acts as signals. Then there are scaffold proteins which keeps the other proteins which need to remain in proximity, close by. Then there are proteins which act like transporters taking cargo on road of cytoskelton proteins. Finally, there are proteins that regulate the gene expression known as transcription factors.
But, all these elegant functions they do will be impossible without enzymes. There are chemical reactions that need to occur in the cells. For instance you need to derive energy by breaking down the glucose molecule. But rate at which the glucose will breakdown by itself is very low for it to be useful for a living cell. So there are these set of proteins which bind to glucose and acts as catalyst easing the rate of reaction.
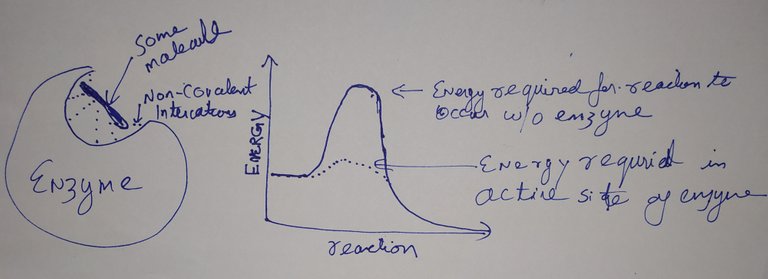
@scienceblocks
The enzymes confine the molecule in a small pocket called active site. It also forms all kinds of bonds with it such as Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and hydrophobic interactions. What confinement and bonding ends up achieving is - 1) it increases the probability of collision between two or more molecules when required when two or more molecules need to combine with each other. It decrease the minimum amount of energy required to break the bonds and start the reaction, aka the activation energy. (If you are thermodynamically inclined, then it makes sure for the reaction change in Gibbs free energy < 0).
The catalysis is required not only to break glucose, or for synthesis of essential compounds like amino acids, DNA bases, and lipids, but also for many non enzymatic proteins described above. For example, body may need to break some proteins at times. Enzymes may modify them by adding a phosphate group or acetyl group on the surface of other proteins, which may act as molecular switch to turn some proteins on and off.
The protein that replicates the DNA and assures that the life goes on - DNA polymerase- is an enzyme that eases the formation of phosphodieaster bond. I mean that is not a joke - you have to bring two highly negatively charged molecules of DNA bases with phosphate groups together, and make them form a covalent bond. The protein that reads the DNA and copy its message to mRNA, is an enzyme called RNA polymerase. Well, mRNA is just a molecule carrying the message of DNA to ribosomes, where this message is read and translated into a protein.
RNA is no saint either!
A public domain image from rfam database
You thought only proteins can be enzymes? Have you thought about RNA. No you only think about yourself!
To make a protein you need to put amino acids together by forming a peptide bond. The catalytic activity for formation of this bond is not provided by protein but rather via ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Just like proteins RNA is also capable to fold onto itself and form 3D structures. Hence, it is not surprising that RNA can also have catalytic activity. Though, I am sure it was surprising back in 1980s, when Thomas Chec and Altman got a Nobel Prize for showing catalytic activity of RNA in 1989. The fact that RNA is a molecule that can store genetic information and as well as catalyze reaction it made many wonder that what if RNA molecules we're indeed the first men to inhibit the earth! Well that's the RNA world hypothesis for origin of life - where RNA is the genetic code and at the same time an enzyme / a polymerase that makes its own copies.
Anyway, in a nutshell a protein is polymer of amino acids, polymerized via peptide bonds. But enzymes are any polymers - be it Protein or even RNA that are capable to act as catalysts. So neither all proteins are enzymes, nor all enzymes are proteins.
StemQ Notice: This post was originally submitted on StemQ.io, a Q&A application for STEM subjects powered by the Steem blockchain.
Thanks for contributing to great content on StemQ.
I'm delighted to see that this question has triggered various interesting answers.
Hi @scienceblocks!
Your post was upvoted by Utopian.io in cooperation with @steemstem - supporting knowledge, innovation and technological advancement on the Steem Blockchain.
Contribute to Open Source with utopian.io
Learn how to contribute on our website and join the new open source economy.
Want to chat? Join the Utopian Community on Discord https://discord.gg/h52nFrV
For some reason it took me forever to learn that ribozymes were RNA strands that functioned as enzymes. It's a super cool, but rather complicated branch of biochemistry.
It's damn interesting. Especially, I find RNA catalyzed RNA polymerization quite intriguing.
This post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team and voting trail in collaboration with @utopian-io and @curie.
If you appreciate the work we are doing then consider voting all three projects for witness by selecting stem.witness, utopian-io and curie!
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!
Hi @scienceblocks!
Your UA account score is currently 3.403 which ranks you at #7001 across all Steem accounts.
Your rank has improved 9 places in the last three days (old rank 7010).Your post was upvoted by @steem-ua, new Steem dApp, using UserAuthority for algorithmic post curation!
In our last Algorithmic Curation Round, consisting of 276 contributions, your post is ranked at #127.
Evaluation of your UA score:
Feel free to join our @steem-ua Discord server
Congratulations,
you just received a 12.70% upvote from @steemhq - Community Bot!
Wanna join and receive free upvotes yourself?

Vote for
steemhq.witnesson Steemit or directly on SteemConnect and join the Community Witness.This service was brought to you by SteemHQ.com
Congratulations @scienceblocks! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click here to view your Board of Honor
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP