The nail is a convex structure of the skin located in the distal regions of the limbs. The nail of the animals is called claw or hoof according to its form.
The nails are formed mainly by dead cells that are keratin, a fibrous protein that produces body naturally. The greatest contribution of keratin to dead cells comes from the bones.
The rate of nail growth varies from one finger to another and from one person to another. The nails grow at an average speed of 0.1 mm / day (1 cm every 100 days or about 4 mm per month) .1 It takes 6 to 8 months for the nails to fully regrow. The toenails take a long time to grow back completely from 12 to 18 months. The exact rhythm depends on the age, the season, the amount of calcium, the factors made and the hereditary factors.
If they are not cut, the nails can reach a considerable length. The nails of the hands grow four times faster than those of the feet.
Anatomy
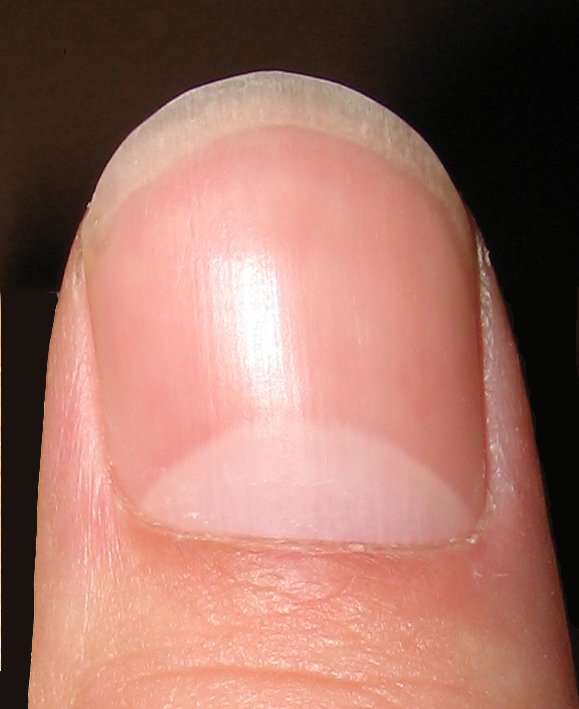
The nails of the hands and feet are composed of:
Nail body: It is the horny structure that we usually know as a nail; the hard and translucent portion composed of keratin.
Matrix or root: It is the part where the ungueal body originates, located under the skin in its lower part.
Lunula: It is the whitish part in the shape of a crescent that is almost always seen at the base of the nail. The lunula is the end of the matrix and, therefore, the visible part of the living nail, although it is not seen in all the fingers. The rest of the nail body is composed of dead cells.
Nail bed: It is the adherent connective tissue that lies under the nail and connects with the finger.
Hiponiquio: It is the tissue located below the free edge of the nail body. It is a waterproof seal that protects the nail bed from infections.
Paronychia: It is the narrow strip of the fold of the skin on the sides of the nail body.
Eponychium: It is the narrow strip of the fold of the skin that seems to end at the base of the nail body. Sometimes the term is confused with cuticle or stepfather. The first term refers to the set of cells that make up external coatings of an organism, among others those of the eponychium. The second term, is equivalent to skin, and is reserved to refer to a small piece of skin that rises from the flesh immediately to the fingernails.
Functions
The nails preserve the sensitive skin they have under them helping balance when walking in the case of the feet.
One function of the nail plate is permeability: the loss of water through the nail is as high as through the palm of the hand. The nail along with the adjacent tissue and the fingertips constitute a functional unit as an organ of touch and prehensile organ that enables functions as important for the life of the human being as scratching and tickling, becoming, in this way, a emotional resource.
It is advisable that, before doing any activity or function with the nails, they are subject to extreme care for good hygiene. It has taken the habit of biting the nails in times of stress.
Another important use of nails is in music. In many plucked string instruments the nails are used, the difference of the sound being notable with respect to the pick. In these cases the nails are allowed to grow and are given a specific shape.
The nails also serve as a decorative element, covering the surface with synthetic enamels and small artificial fragments.
Health and care
The nails can dry, as well as the skin. The manicure and pedicure are cosmetic treatments to give a good appearance to the nails. This is done with various tools, such as cuticular scissors, nail scissors, nail clippers and files. Putting aside purely aesthetic treatments, when there is a nail problem in the nails you should consult a health specialist, such as a dermatologist, or a podiatrist (if the problem occurs in the toenails). The nails can improve their condition if they are attached or put in contact with minerals which, when in contact with them, can give them a greater hardness and nutrition.
Infections in the toes can come from soiled socks, certain types of strong exercises, walking barefoot and exposing the feet. Nails can lead to a deformity based on bumps and scratches.
