Most of you have probably heard the term mining in relation to Bitcoin before.
I'll try to tell you everything I know about Bitcoin mining.

The Bitcoin network consists of blocks (blockchain), which need to be validated somehow.
Bitcoin is proof of work, which means that there are miners who validate the blocks by providing computing power.

These Bitcoin miners get a reward in Bitcoin for every block they validated. These bitcoins are born out of nowhere. So there are more and more Bitcoins.
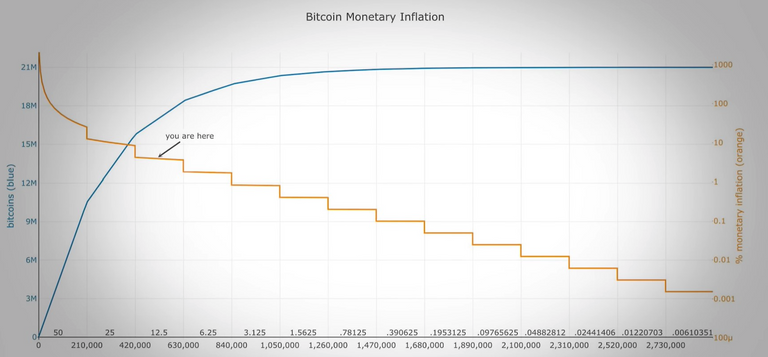
The code is programmed that there will never be more than 21,000,000 Bitcoins and that every 4 years the mining reward is halved. (the process is called halving).
Because of this process, it will take over 100 years until the last bitcoin of the 21.000.000 is mined.
Bitcoin is becoming less and less inflationary.
Bitcoin has moved very cyclically based on its halvings.
After each bear market, we had an accumulation until the next halving and from there a rise to a new all-time high.
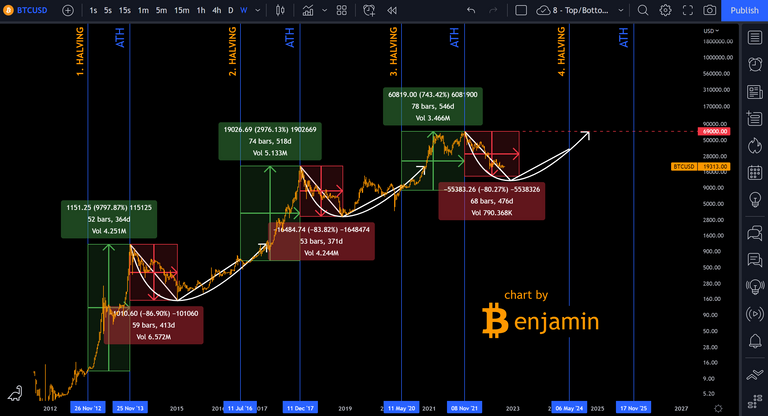
The overall growth is exponential -> the chart is logarythmic.
Each cycle we see less % than in the previous one.
bull markets
2012-13 = +10000%
2016-17 = +3000%
2020-21 = +1000%
bear markets
2014-15 = -87%
2018-19 = -84%
2022-23 = ...

Usually, miners hold their bitcoins for a long time and sell them as soon as the price reaches a new high.
Sometimes miners are forced to sell their coins earlier because they go bankrupt.
For a miner, it is not worthwhile to continue mining if it becomes too difficult to validate the blocks.

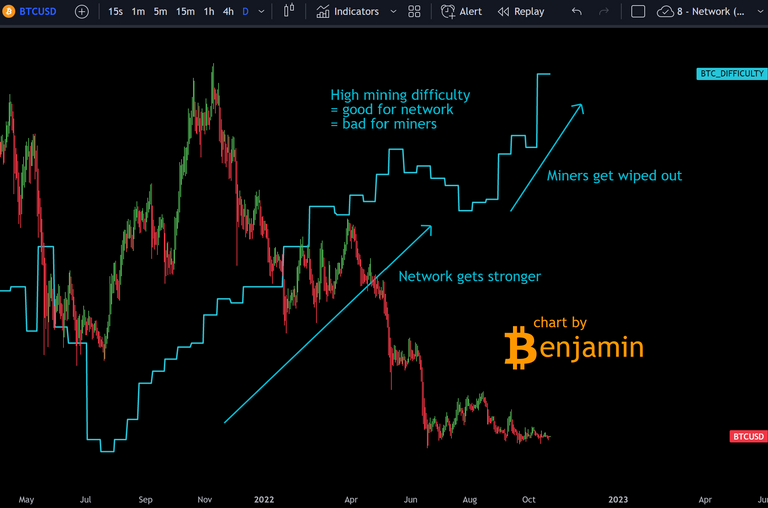
The difficulty of the validation of blocks is called "mining difficulty".
There is the hashrate which makes a statement about how likely it is to find the next block while mining.
If the hashrate increases, the mining difficulty must automatically increase as well in order to maintain balance because otherwise it wouldn't work anymore.
A high hashrate is actually a good sign of a strong network, but it puts miners at a disadvantage.
This is also the case at the moment.
Down below is a picture where the difference between proof of work and proof of stake is explained.
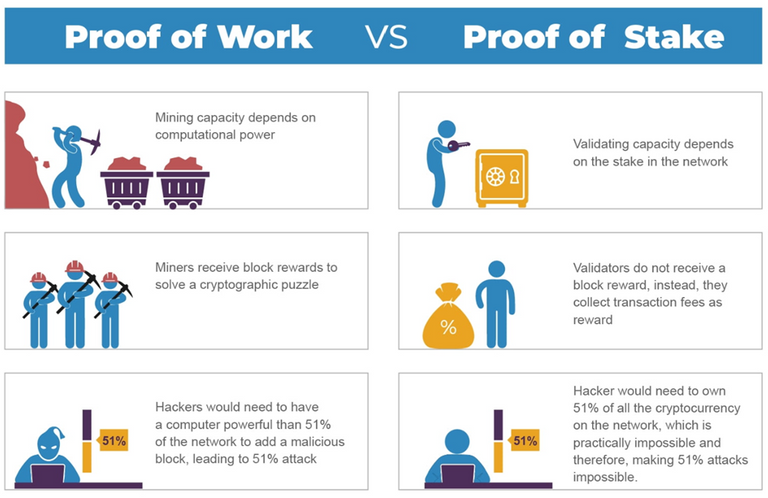
-> In addition to proof of work and proof of stake, there are others, such as proof of history (Solana SOL), and proof of authority (Vetchain VET).
The big players are Ethereum (ETH) and Bitcoin (BTC).

Ethereum is currently in the process of changing from proof of work to proof of stake, in order to be more sustainable than BTC and for some more reasons like scalability.
Mining in and of itself consumes a lot of electricity.

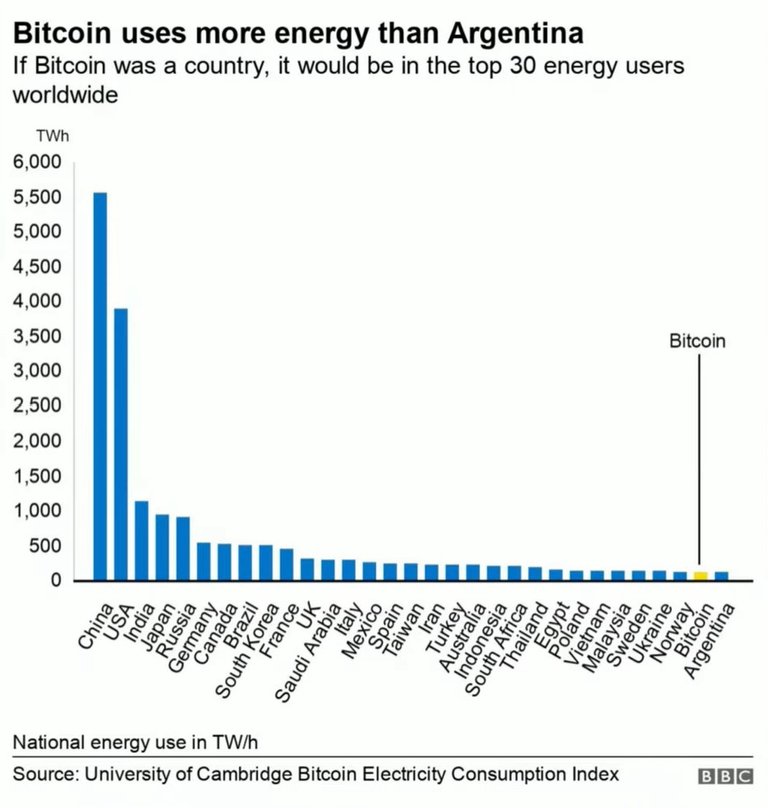
This triggers a lot of criticism and is often used as a reason for the government to go against Bitcoin, even as it uses more and more renewable energy instead of fossil fuel.
It's the same principle as electric cars.
It always depends on how the electricity is generated.
When you mine bitcoins, it happens anonymously, because you don't buy them from anyone.
For this reason, bitcoin mining was banned in China and computing power spread even more to the rest of the world.
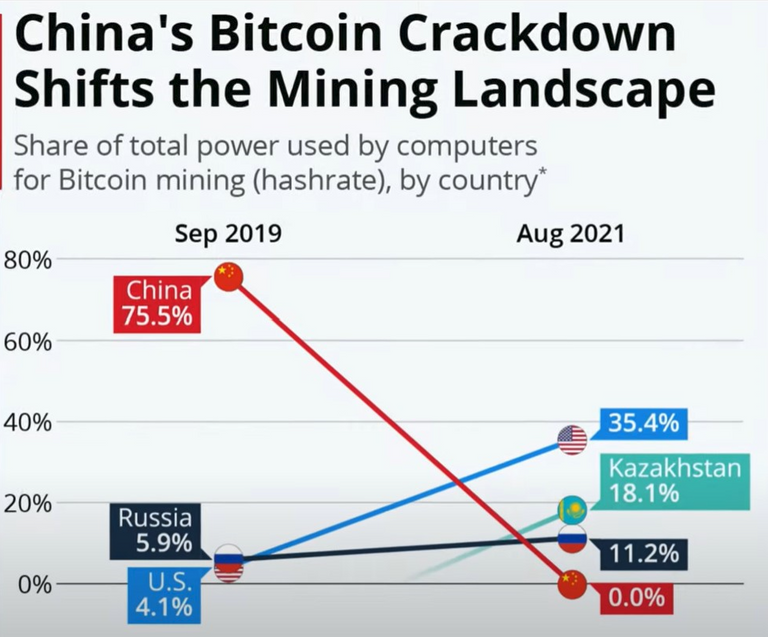
Through this process, bitcoin became more decentralized.
China previously had 75% of the computing power and now they lost their control, which is even better for bitcoin.

Maybe China regrets the ban, but they have never been really convinced of bitcoin anyway.
Most miners that were positioned in China now have their computing power in America, which gives America an advantage over China in terms of bitcoin.

Hopefully i was able to tell you something you didn't know yet.
Feel free to read my other posts:
-> https://ecency.com/@benjammann
Bitcoin - did we see the bottom?
https://ecency.com/bitcoin/@benjammann/bitcoin-did-we-see-the
Bitcoin - misthoughts
https://ecency.com/bitcoin/@benjammann/bitcoin-misthoughts
Bitcoin – is the bear market over?
https://ecency.com/hive-138698/@benjammann/is-the-bear-market-over