INTRODUCTION
Sharing dates back to the creation of the first civilization. In fact, man has been sharing resources as gifts, presents or as a compensation for a job done. This has been termed “The sharing Economy 1.0”. With the broth of the internet and the technology, sharing has been taken to a whole new dimension. This has created a multi-billion-dollar industry and a sharing Economy. The sharing Economy as we have it today is basically, the ability to share used resources with those in need of them in return for money. This has been made possible with the use of the platform business model which in itself powers a whole lot of businesses including popular social media giant like Facebook. The Sharing Economy of today makes use of this platform model to simply connect users in need of a service/product to users with those resources willing to share for a fee. In fact, one of the pioneers of today’s sharing economy Ms. Robin Chase has given the simple formula of idle resources + platform + public participation = sharing economy. The companies (platforms) involved act as an intermediate between these users spelling out terms and conditions of trade and charging a commission for service offering.
Sharing economy might also be termed a collaborative consumption. It saves time, money and maximizes usage of resources in general. The sharing Economy is so diversified having niches within. We have the shared accommodation, shared work-space, shared services, shared transportation, shared Resources, shared knowledge, Shared Medical services and shared education making it 8 major sectors comprising of the global shared economy. Each sector has industry leaders with brands making millions of dollars in revenues annually. Popular among them is Uber and Airbnb which serve the shared transportation and shared accommodation industry respectively.
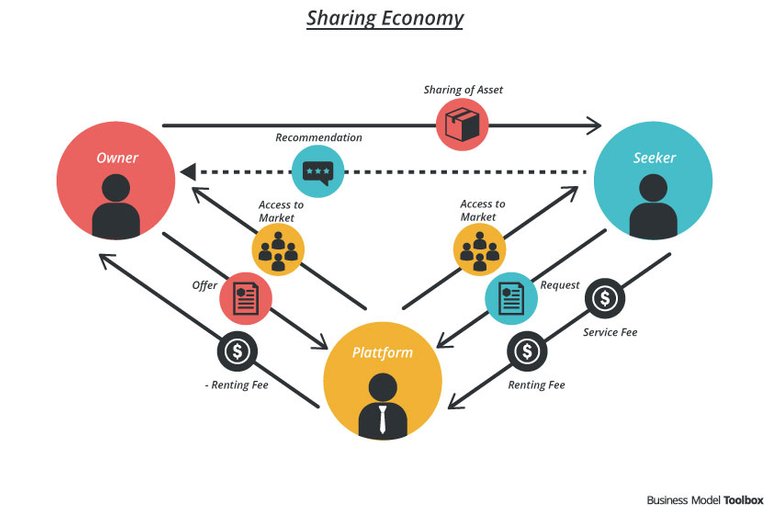
Although the sharing economy has revolutionized the way we live and has had its financial and social impact on our lives positively, it is not without flaws in the current system in place. The problems facing the current system are so numerous but the underlying factor remains that of centralization. In this model of the sharing economy also known as the sharing economy 1.0, intermediaries’ platform facilities the paring of users in need to exchange value and share resources and charge a commission in return for doing so. The current problems facing the sharing economy 1.0 includes but not limited to the following:
- The issue of trust: In a market where transactions are based on mutual understanding and agreement, the issue of trust becomes paramount. The platforms act as intermediaries between customers and suppliers vouching for both parties to facilities transactions. They also help reduce the financial risk involved by collecting collateral from users. This increases the cost involved in the sharing economy.
- Data Leakage and Abuse: Majorities of companies involved in the sharing economy, usual collect users information and data prior to registration. These data collected are stored on servers in centralized locations. Being stored in a single location, these servers are prone to various cyber attacks and hack will have the tendency of leaking the personal information of millions of customers to hackers who have access to the servers. These include credit card details, email addresses, phone numbers, social security numbers etc., which might be sold by these hackers. companies, on the other hand, might abuse the privilege given to them by their prospective customers and become non-compliant with the terms and conditions during registration. The data in itself might be resold to other third parties to make use of which the knowledge of data owners.
- Excessive Transaction cost: like any other company, the platforms behind the shared economy are established to make a profit and sometimes, they do so to the detriment of their customers. Their activities revolve around maximizing profits through commissions charged on shared services on their platforms. This sometimes reaches as high as 50% but it’s usually 20% most times.
The Blockchain Solution to these problems – The Uchain Solution
The Blockchain technology has evolved over time since the introduction of the Bitcoin in 2009. The blockchain is a decentralized open ledger and database that keeps records and track of all transactions and data such as finance contracts, supply chain information and digital assets. The blockchain keeps records of all data and transactions on its network by making use of a chain of records. The blockchain is basically divided into two parts which are the block and the chain. Each block is a sequence of individual transaction that is encrypted and time stamped and updated on the blockchain network upon completion. The blocks are linked together by links called chain which enable a new block to be created once the former is completed. The reason why the blockchain has seen so many application and adaptability include;
Secured and authenticated: The blockchain is secured and authenticated all transactions carried out on the network thus eliminating fraud and building trust. It does so by making use of a digital signature mechanism for creating and executing transactions. This helps trace and monitor the accountability of processes that took place beforehand.
Splintering: The blockchain allows the sharing of transaction history. Records on the blockchain once executed cannot be reversed or deleted. This makes the blockchain immutable. The blockchain is thus authentic and the more records shared on the network, the stronger the blockchain becomes.
Peer to Peer: The blockchain enables one to carry out a transaction in a peer to peer model eliminating the influence of third parties and of middlemen. This creates transparency on the network and eliminates the need for Trust.

Uchain is a blockchain platform that disrupts the sharing economy as we have it today. The Uchain platform revolutionizes the sharing economy 1.0 and births the new model of the sharing economy 2.0 which is focused on value creation. The Uchain solutions to the problems of present sharing economy include:
- Security of User’s data: With the problem of data leakage and abuse created by using central servers, uchain adopts the blockchain technology to decentralized data storage and access. This makes it extremely difficult for security breaches on the Uchain network and help provides an extra layer of security on the data of customers.
- User credit passport: The blockchain as I have earlier described is a distrusted ledger and immutable. Have transaction records on the blockchain permanently and also traceable creating a chain of trust. The Uchain solution is to adopt this chain of trust in creating a credit passport mechanism which will be used by sharing service providers to track users behavior and in identity verification. This eliminates the need for intermediaries to vouch for users and its associated financial risks involved.
- Expensive Transactions cost: By making use of the peer to peer feature of the blockchain technology, uchain aims to reduce the cost associated with sharing service by as much as 20%. In connecting users and service providers, the need for intermediaries and the high charges with commissions will be greatly reduced. The Uchain token will enable instant and real-time settlement of transactions enabling a faster and secure solution to the traditional sharing Economy. Uchain cuts out intermediaries giving the benefits of the sharing economy back to the users.
The Uchain Ecosystem
The uchain ecosystem is basically comprised of the users and developers. Uchain users can be categorized into the service users, independent service providers, and enterprise service providers. These categories of persons use and/or provide the uchain sharing services. The developers on the other hand are the set of persons keeping the uchain ecosystem up and running. They might be independent developers or uchain foundation developers.
The Uchain product offerings.
Uchain has been in works to revolutionize and disrupt the sharing economy 1.0 as we have it today. The team has various products and services already in place to facilitate this disruption. Some of its products of the Uchain group holdings so far are listed below:
- U-bicycle (Fourth largest bike sharing platform in the world.)
- X-Bike (also known as Campus Bike, a frontier brand for sharing bicycles in Chinese Colleges).
- LocalKing (The Taiwanese transport sharing market leader)
- GrabCycle (holds shares in Grab’s Southeast Asia bike sharing brand)
- U-park (Pioneering brand for Smart parking services.
- U-car (Innovations brand for Car sharing services.)
More details about the products are described in the Whitepaper.
The Uchain token.
There two type of tokens in the Uchain ecosystem. The UCN and UCP.
UCN is the native currency of the Uchain economy and it’s a basis for the interaction with the platform.UCN is an ERC20 token based on the ethereum blockchain. Users who wish to join or leave the platform must buy or sell the UCN. The UCP is just UCN with voting power. It grants holders the ability to receive incentives for holding UCN for a long time. The UCP, however, is not tradeable.
MEET THE TEAM
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
ROADMAP
.png)
Global Partnership
.png)
ICO DETAILS
Token UCN
Price 1 ETH = 5,000 UCN
Accepting ETH
Hard cap 42,000 ETH
Pre-Sale: 06/20/2018 midnight - 06/23/2018 midnight
Token Sale 07/10/2018 midnight - Unspecified
USEFUL LINKS
Website
Whitepaper
Telegram
Twitter
Authors Details
Bitcointalk Username: Romeoetin
Bitcointalk: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=2093652