Hi Steemians its Geofrey again, as i mentioned in my introduction i am thrilled and fanatic about this whole concept of blockchain and all its benefits. So i prepared this to add to your knowledge about blockchain, if you're a banker you will appreciate the great competitor you now have.
What is a block chain?
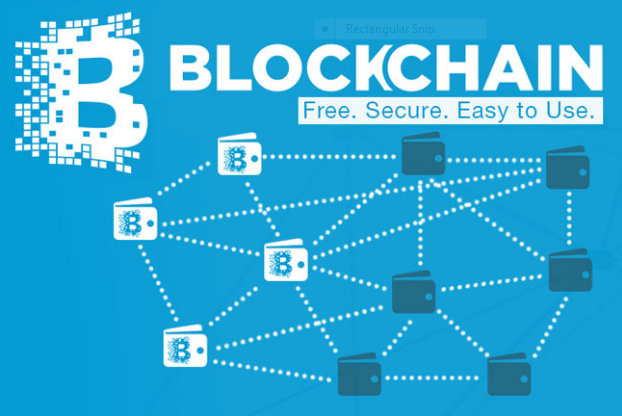
A block chain is a type of distributed ledger or database that puts a number of digitally recorded data transactions into data packages called blocks. These blocks of data are recorded and stored together in a linear chain. Each block is chained to another block using the cryptographic signature. It’s because of this complied data of transactions in the block chain that makes it a ledger.
Block-chain also verifies and authenticates transactions using what we call consensus (or in bitcoin language, it’s called Mining). Most people when they think of block-chain they think of bitcoin but block-chain is more than just bitcoin. This technology plus the full distributed ledger technology will do more than what internet has to information.
In his published article in 2008, the anonymous inventor of block-chain and bitcoin wanted to create a system that facilitate a peer to peer transaction without any financial intermediary. Literally, this technology has the potential to bypass banks, Money transfer agents like western union, Money gram, express money and other related third parties. This is has been successfully achieved through the bitcoin Cryptocurrency and other cryptocurrencies out there. You can easily transfer money in form of bitcoin to your relative anywhere in the world as long as he/she is registered on the bitcoin block chain at 0.0001btc or $0.29 transfer fee and the transaction will only take 10 minutes to be confirmed.
Distributed ledger technology.
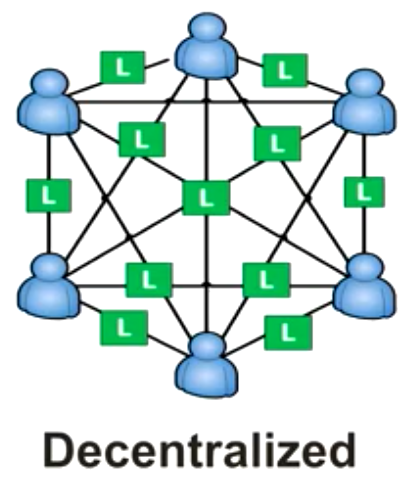
A block chain is a decentralized, public and a trusted Ledger.
In a decentralized block chain, ledgers are not kept solely for a single entity or user. Transactions recorded are secured and maintained in servers called nodes (in case of bitcoin ‘Mining nodes) all over the world. So in the process of creating a transaction e.g a bitcoin transaction, different nodes/miners use energy intensive super computers to solve a mathematical algorithm that will produce a single bitcoin transaction. This process is competitive with over 6000 computers throughout the world trying to update the same ledger by adding a block of a transaction. Once one node finds the solution, the transaction is then broadcasted to the network of miners for authentication and when 50% of nodes confirm that the algorithm is solved( reach a consensus) , a block of that transaction is then added to the block chain. This is done from all different parts of the world (decentralized) and publicly registered on the block chain ledger. This usually takes only 10 minutes to update the ledger. However, with new and faster block chain it can take even a minute to confirm and publish a transaction. It is secure, decentralized, public and trusted. That’s how bitcoin and cryptocurrencies work. You trust the block chain, every detail is public, sending and receiving money is cheap and takes only 10 minutes. Its transparent, audited and Trusted.
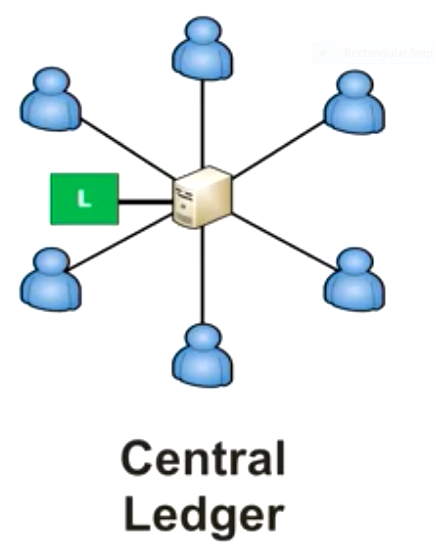
How do our banks work?
Banks use a centralized system. You put all your trust in the bank. Banks keep a ledger just like bitcoin. However, their ledger is closed to the public and therefore they are your trusted third party. Each time you deposit in your account they credit it and debit it whenever you withdraw. You don’t have access to what is transpiring in the banking system, you also need permission to withdraw or receive some amount through your account.
Banks need to change the outdated banking system and adopt a block chain distributed ledger technology.
Let’s consider what happens when you want to send Money from your country to another county. Banks use what’s called corresponding banking to swift your money to your desired receivers account. Corresponding banking is expensive and inefficient especially in this fast economy.
If A wants to send money from Lets say Crane bank Uganda to receiver B in NAB Australia, Sender A will request for a swift which will be initiated by his bank to go to another bank in UK (corresponding bank) this process will include changing Uganda shillings into Euros charges will apply. While in that process, receiver B will be anxiously waiting to receive the money in his account which wont happen any sooner until another step is undertaken. You assured him that you sent the money two days ago and your bank A confirmed it but he hasn’t received the money. Where is the money? So, UK bank (corresponding bank) will swift the money to NAB bank (receivers bank) which will also require exchange rate charges from Euro to AUD. Finally, after 3 to 5 working days money is received in Receiver B bank account.
In that illustration we did not consider the amount you spend in transfer charges, we only looked and the effect of time in business.
What does a decentralized system offer?
Just imagine what would happen if all banking institutions were registered on the same block chain enabling faster and cheap transfer of funds throughout the world without any need for corresponding banking and lots of paper work. A block chain will authenticate, audit and update the ledger for all banking transfers. It will also minimize hacking and security concerns “distributed ledgers are inherently harder to attack because instead of a single database, there are multiple shared copies of the same database, so a cyber-attack would have to attack all the copies simultaneously to be successful. The technology is also resistant to unauthorized change or malicious tampering, in that the participants in the network will immediately spot a change to one part of the ledger. Added to this, the methods by which information is secured and updated mean that participants can share data and be confident that all copies of the ledger at any one time match each other.”
Alternatively, each bank or a few banks can decide to run their own block chain, it will still serve the same purpose. Another benefit of this is; when one bank gets to the verge of collapsing due to under capitalization, it would be very easy and faster to get funding/investors from other banks on the same block chain because each banks historical performance is publicly recorded on a distributed ledger.
So, where is your trust? In banks, PayPal, Okpay? They keep your ledger and charge you tremendously. Or will you trust the block chain, pay less and access your money any time you want?
This is just an introduction to block chain and a simple illustration of its applicability in banking systems. Block chain can be applied in many fields and sectors including, smart contracts, voting, data storage, governance, protection of intellectual property, e-tax, e-business, supply chain auditing, Internet of things, cryptocurrencies and all form of digital money and many more. So many articles related to above areas will be published, so look out for our next article on Block chain and smart contracts.
Geofrey Kafeero.

Banks had made a whole lots of money from us already. Transfer charges, ATM charges and so on. Its time for us to benefit ourselves. Thank you for the post.
You're welcome my friend.
good post, agree with good future for blockchain and all crypto technologies.
This is a very thorough, EZ-to-understand article - thank you for sharing @geofreykafeero good sir ! I jumped on the PayPal bandwagon long ago but couldn't agree more as I have watched them jack the fees. I am hopeful the crypto goes worldwide viral in a way that supplants the central bankers' present noose 'round our necks.