
It is a fact: the transactions currently conducted on the Bitcoin network are slow and costly. However, as we told you in this article, the Lightning Network could provide a solution to these problems as early as next year.
But what is Lightning Network? In this article, we will give you a simple explanation of how it works.
This is the translation of an article from CoinTelegraph. Please click here to access it.
1. What's the problem?
Blocks are slow.
And therefore expensive. If an individual were to send you Bitcoins, you would receive them after several hours, and the individual would have to pay a high transaction fee. With such limitations, how will the Blockchains ever be able to become inescapable?
We therefore understand the value of an idea that could make it possible to overcome these difficulties. The Lightning Network is one of those ideas.
But before we understand the solution, we need to start by understanding the problem it addresses.
2. Why are Blockchain networks so slow?
Imagine that a Blockchain is a register.
And this register contains several pages (blocks). Transactions are recorded on each of these pages. As soon as there is no more room on a page for registering new transactions, it must be added to the registry before you can start registering transactions on a new page.
Before a page (a block) can be added to the register (the blockchain), a process must be performed to ensure that network participants have agreed on what is contained on that page. This process takes about 10 minutes (on the Bitcoin Blockchain) for each block.
Imagine: you send 1 Bitcoin to your friend Joe. The transaction will look like something like this:
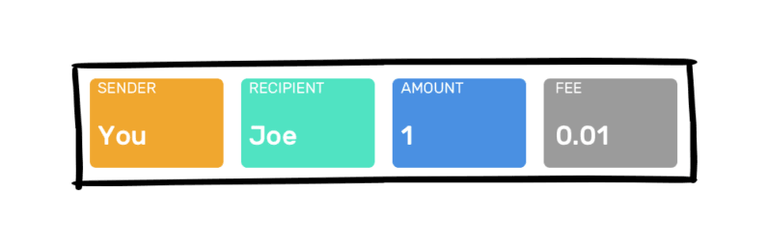
A transaction contains, among other things, information about the sender, information about the beneficiary, the amount involved and the transaction costs associated with it.
3. Wait a minute... transaction fees?
Yes, there may be additional transaction fees provided by the shipper.
This gives you the opportunity to financially encourage minors to include your transaction in a block as soon as possible.
There is no fixed price in advance, and it is up to you to decide how much you are willing to pay in order to speed up the processing of the transaction. The higher the fees you pay, the faster your transaction will be processed.
At a moment, several transactions are waiting to be recorded on the current page (the block).
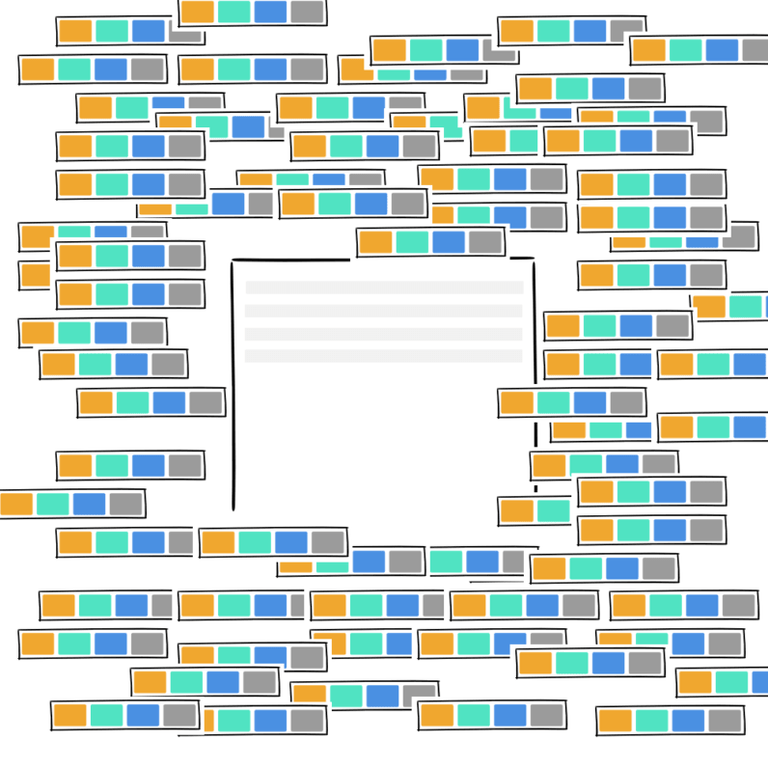

Minors - in other words, the computers working on the Blockchain network - must decide which of the available transactions will be added to the current block. To help them make their decision, they will look at the transactions that offer the greatest rewards.
Therefore, transactions with the highest fees will be processed first.
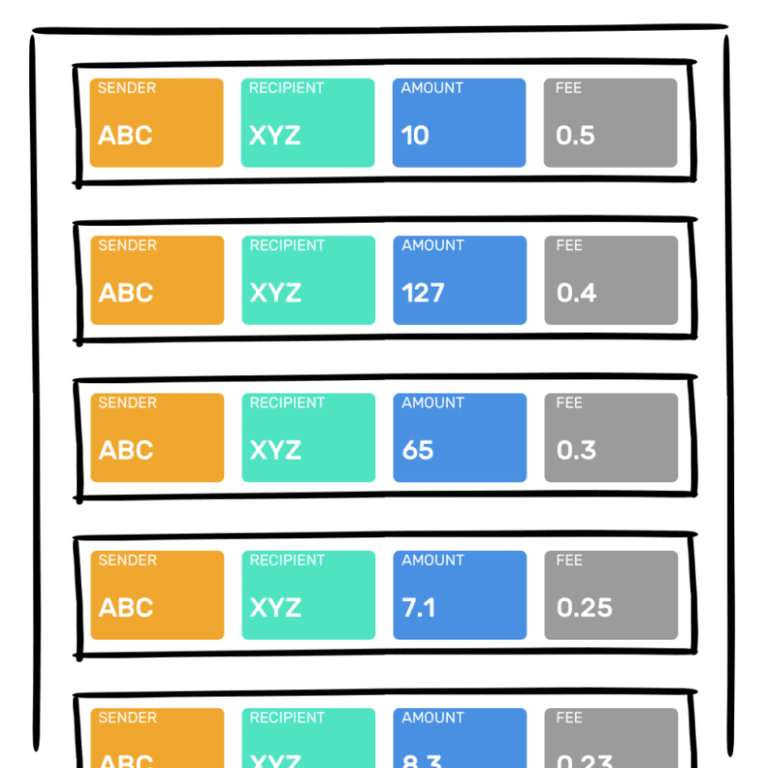
If there are enough transactions with more fees than yours to fill the next block, then your transaction will have to wait in a queue. The waiting time is very variable: it can last a few minutes, several hours, and sometimes even several days.
But the rule is intangible: the more you agree to pay high fees, the faster your transaction will be processed.
That's why the Blockchains are so slow, and they carry significant costs for those who want to use them. In an ideal world, the democratization of this technology would lead to an uninterrupted increase in the number of transactions.... but as the number of transactions increases, the network slows down, which is a barrier to adoption.
But the Lightning Network aims to remedy this problem.
4. What is the Lightning Network?
The idea behind the Lightning Network is that not all transactions need to be recorded on the Blockchain.
Imagine that you and I are conducting several transactions between us. In such a case, we could avoid recording all these transactions on the Blockchain, and move them "out of the chain".
Simply put, here's how it works:
We will both open what is called a payment channel, and we will record its opening on the Blockchain. We now have the ability to conduct as many transactions as we wish through this payment channel - and it can remain open for hours, days, weeks or even decades.
The only time we will interact with the Blockchain is when we want to close this channel. We will then simply enter the final balance of the transactions that took place on it.
Thanks to this idea, we will be able to create a network of payment channels, which rarely need to induce registrations on the Blockchain.
Imagine three individuals: Xan, Yelena and Zeke.
If on the one hand Xan and Yelena have opened up a payment channel between themselves, and on the other hand Yelena and Zeke have done the same, then Xan will be able to send money to Zeke based on Yelena.
Imagine Xan wants to send 2BTC to Zeke. Yelena will be able to send these 2 BTCs to Zeke, and Xan will then reimburse Yelena by sending 2 BTCs.
That's the idea behind the Lightning Network. Insofar as this will make it possible to avoid frequent use of the Blockchain, transactions can take place "at lightning speed".
As you must have understood, all the magic happens in these payment channels. Let us look at how they work.
5. How do the payment channels of the Lightning Network work?
These payment channels function like safes. Two people will put the same amount of money in one of these boxes, and then put their padlocks in them.
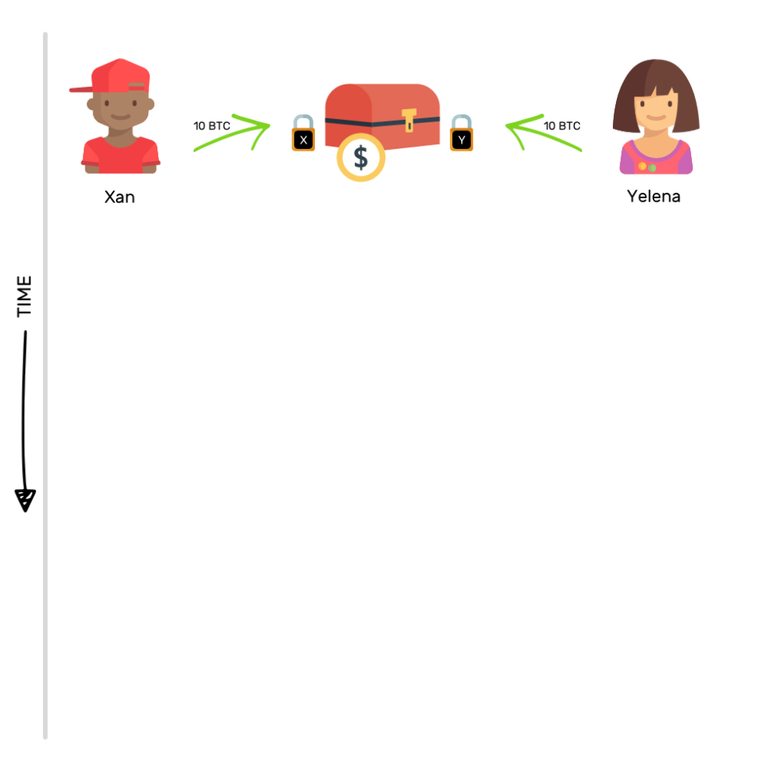
Depositing an equal amount of money in this "Common Box" is recorded on the Blockchain as an "Open Transaction". A payment channel has just been created between these two individuals.
Why does it have to be necessary to invest money in a safe?
The idea is that no one will be able to use the Bitcoins in this safe without the consent of the other. These are exclusively intended for transactions between the two individuals.
Imagine: Xan and Yelena each place 10 BTC in this common pot. A few hours later, Xan would like to send 2 BTCs to Yelena. How is he going to do that?
He will simply transfer the promise of ownership of 2 of his Bitcoins to Yelena, among the 10 that are housed in the safe. When this one is unlocked, Xan will be able to recover 8 BTCs, while Yelena will be able to get 12 BTCs.
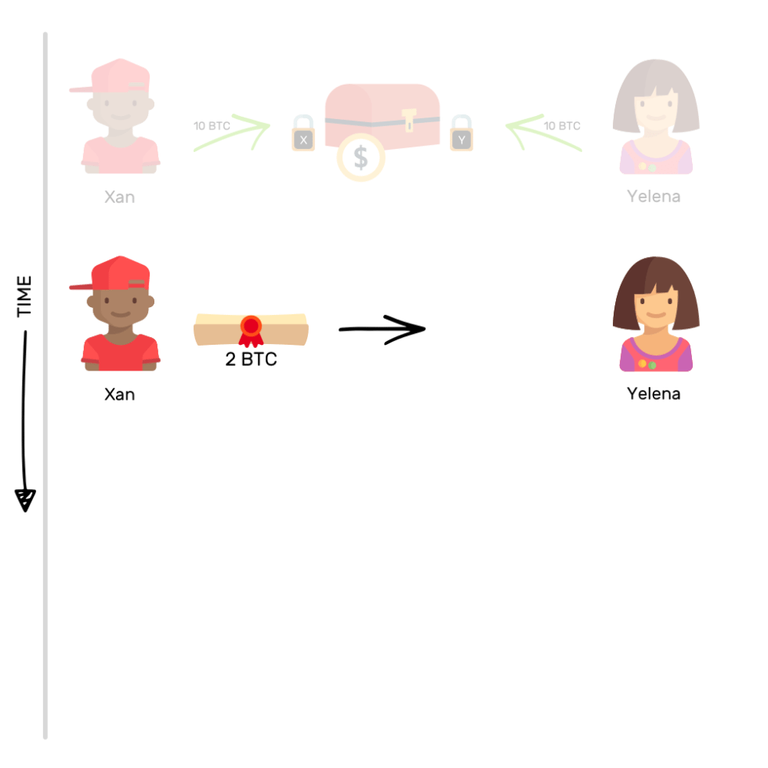
But they are not going to unlock this safe right away: they would like to make more transactions. This is where all the advantages of these payment channels lie.
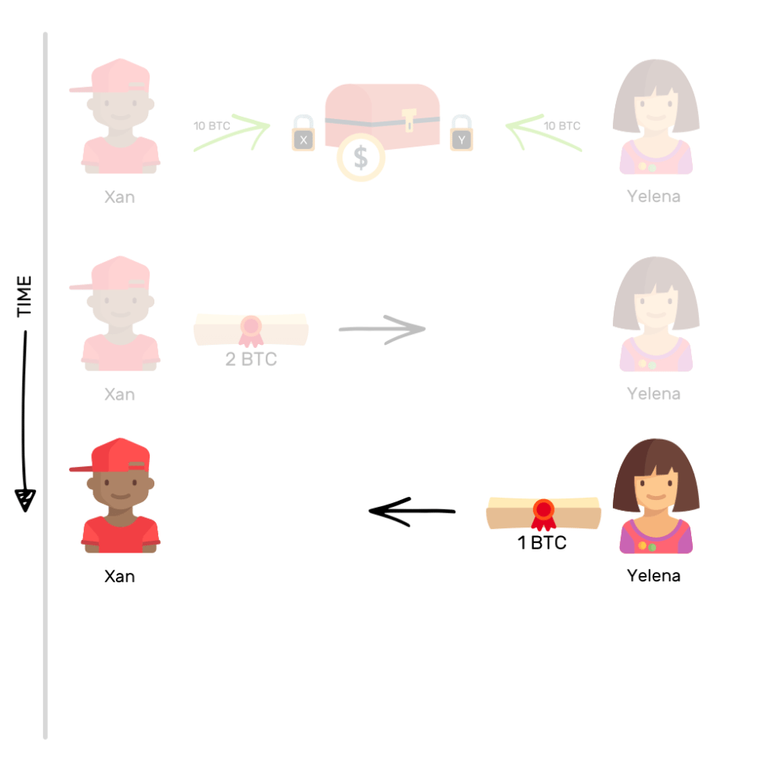
The next day, Yelena wants to send 1 BTC to Xan. She will then only have to do the same thing - transfer the promise of ownership of one of her Bitcoins to Xan. If the safe was opened as a result of these two transactions, Xan could then claim 9 BTCs, and Yelena will get 11 BTCs on her side.
Here's how these off-chain transactions work:
To sum up, a payment channel is nothing more than:
the pooling of Bitcoins by two individuals
transfer of the promise of ownership of these funds through an agreement between the two participants
Xan and Yelena can close this payment channel at any time.
Closing this channel will consist of opening the safe and taking the money it contains. The safe will be opened on the Blockchain, and information about the distribution of these Bitcoins will be recorded there forever.
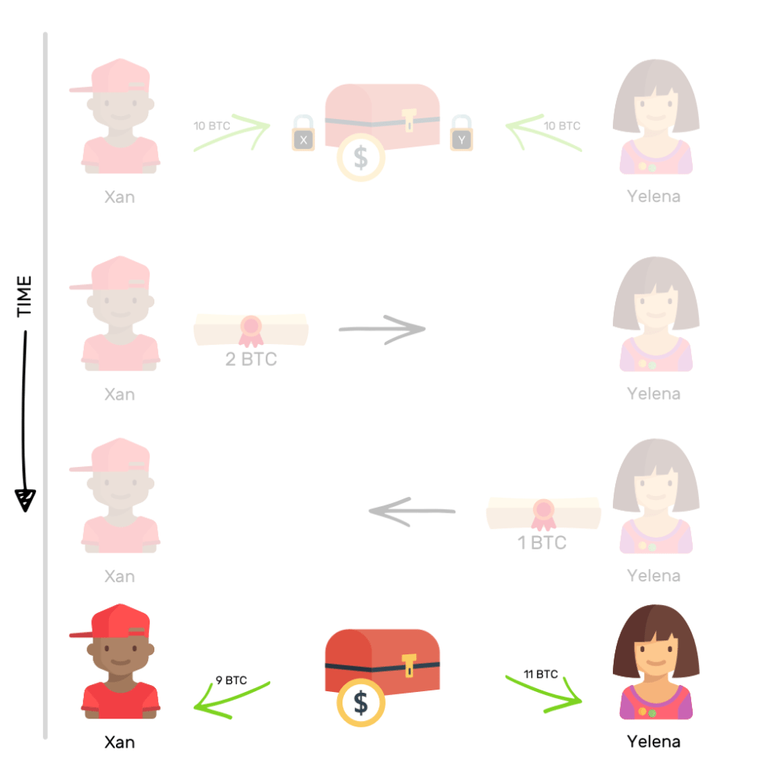
This is how these payment channels work.
But it is not enough to show their real potential. Their true potential is unleashed when several payment channels operate simultaneously to create a network - the Lightning Network.
6. Okay... so how does the Lightning Network work?
The Lightning Network works by transferring value: from holding Bitcoins to the promise of holding Bitcoins.
And that changes everything. We will continue to use an example to illustrate how the Lightning Network works.
Imagine 3 people - Xan, Yelena and Zeke. There is an open payment channel between Xan and Yelena, and another one between Yelena and Zeke.
No payment channels have been opened between Xan and Zeke.
In such a situation, if Xan wishes to transfer 2 BTCs to Zeke, it will be able to rely on the payment channel established between Yelena and Zeke.
What will it look like?
Xan will ask Yelena to transfer the promise of 2 BTC to Zeke, relying on the payment channel Yelena-Zeke. Xan will then refund 2 BTCs to Yelena, using the Xan-Yelena payment channel.
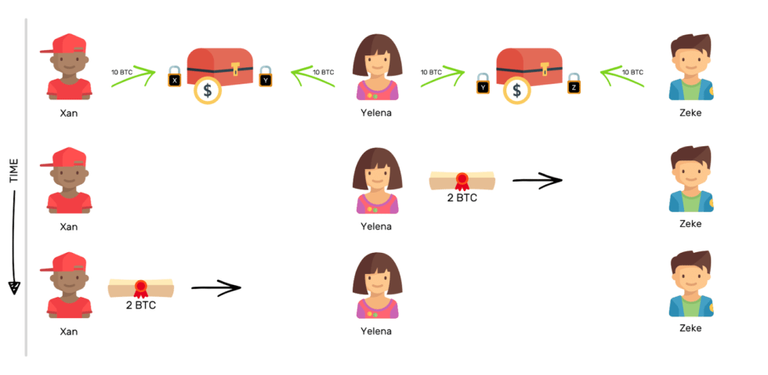
With such a network of payment channels, a large part of the transactions will be able to take place outside the Bitcoin's Blockchain, thus relieving the Bitcoin's congestion.
The Lightning Network will thus be able to help the Bitcoin network manage millions of transactions much faster and at significantly reduced costs.
Also to read: Simple explanation of how Blockchain technology works
Reference: CoinTelegraph
Fantastic post detailing the concept behind this exciting advance in blockchain usability. I'd heard of the lightning network, but you're the first who has taken the time to break it down... and done very well. Thanks!