
Hardcap: $25 M
Token: ERC20
Token Symbol: PAI
Total Supply: 2.1 billion
Website: https://pchain.org/index
Whitepaper: https://pchain.org/js/generic/web/viewer.html
Telegram: https://t.me/pchain_org
What is P Chain?
- A native multichain platform that supports EVM
- It consists of an integrated oracle mechanism that filters out noises in smart contracts and cross chain requests
- Creates a scalable architecture based on mulit-layer transactional sharding in order to speed up process of transactions
- Uses PDBFT based consensus
Architecture
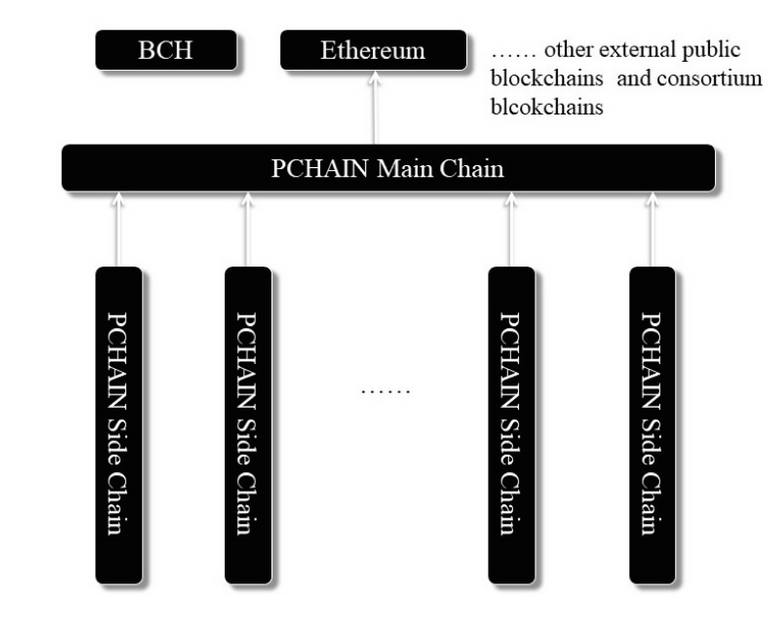
- Architecture consists of a main chain and a child chain
- Main chain contains various account information, transfers digital currency amongst users as well as an interface for interaction with external public or consortium blockchains
- Child chain is a derivative of the main chain where for every new DApp formed a new child chain is created. It holds the records of data specific to the smart contract.
Features
Consensus
- Currently all chains run in POS based mechanism in the initialisation by default
- Users can choose which chain to participate in consensus
- Incentivised mechanism is implemented to ensure equal users participate across different chains (users are prompt to participate in blocks with more pending transactions)
- When there are enough users expressing the need for consensus on a certain chain- they form a set of nodes
- A randomly allocated node will be the masternode
- BFT protocol is used to generate and broadcast block across the network
Sharding
PChain acheives sharding in 2 ways:
Hierarchal structure of the main and child chains
- Since every DApp will have its own (child) chain, it reduces operation pressure on the main chain as well as reducing service interference from other DApp seen in single chains.
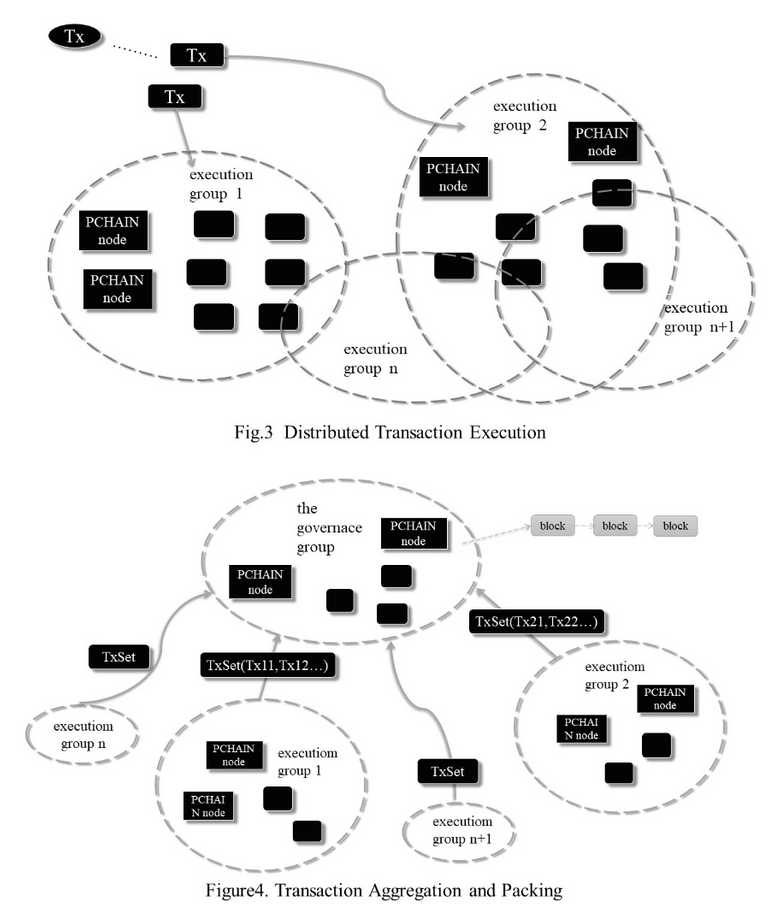
Transactional Sharding
- used in (child) chains with more nodes and a lot of transactions
- Nodes are randomly divided to make an execution group same as qualified nodes are separated into governance group
- Incoming transactions are verified internally by the execution group and reaches consensus on transaction level
- Execution group packages all the verified transactions to be sent to the governance group who collects transaction lists from different execution group to reach consensus on a block level
- Once new block is formed, it is broadcast across the network
Smart Data Oracle
- Knowledge graph module that integrates blockchain data and external data as smart data
- Smart contracts can invoke services of the knowledge graph to get relevant information
- Can be an intermediate layer for combining blockchain and artificial intelligence as well as integrating blockchain technology with external big data
Problems they solve
Scaleability
- architechture allows increased TPS without congestion
Less Calculation Power
- POS based consensus does not consume a lot of calculation power
Effective Oracle Method
- Knowledge graph makes it easier to encapsulate smart contracts
- W3C compliant smart data effectively addresses the issue of nonintelligence in smart contracts
Supports Smart Contract upgrade
- allows both original smart contract and updated smart contract to run if allowed or deprecates the old smart contract
- upgrade only allows addition of storage field and new methods but cannot reduce them
Token Distribution
- 15% Target sale
- 20% Crowd sale
- 25% Team and early contributors
- 25% Community Building
- 15% POS mining
Token use
- PAI tokens are used as payement in accessing smart contracts and as form of incentives when nodes participate in consensus.
Advantages
- Good Team with extensive background and network in tech
- Good partnerships
- Very hyped up ICO with 16k telegram members and 4.3k followers on twitter
- First blockchain to support smart data
- only platform that supports smart contract upgrade
- support cross chain transactions from non native tokens
- DApp has its own blockchain which increases efficiency in browsing and restoring transactions
- supports EVM
- POS based consensus makes parallel computation
- High fault tolerance (if error occurs in one child chain, main chain and other chains are not affected)
- Testnet live with 32 nodes
Comparison and Competition
Quarkchain
- both supports smart contract in EVM running in solidity
- both supports cross chain transactions between blockchains
- different consensus, quarkchain runs in POW
- both successfully implemented sharding in their MVP
- Quarkchain has 5 nodes on their prototype while P chain has 32 nodes
- Quarkchain does not have a smart data feature
- Quarkchain has a simple account managment feature for cross sharding transactions
- Quarkchain does not have patents ( PChain has patents filed with IBM)
- PChain only support transactional sharding while Quarkchain supports both transactional and state sharding
Zilliqa
- Both implemented sharding in their MVPs
- Both support transactional sharding
-Zilliqa's consensus protocol is pBFT - Zilliqa implements multi-sig to improve pBFT limit of 20–50 nodes while PChain uses a novel improved consensus of pBFT — PDBFT
- Zilliqa does not support smart contract in EVM
- Smart contract language for PChain is Turing complete solidity while Zilliqa is non- Turing complete scilla- (smart contracts written in solidity can possibly be converted to scilla)
- Zilliqa has no smart data feature
Aelf
- Both multichain blockchain
- Does not have sharding technology
- Similar architechture with Pchain having a main chain and side chains
- both support cross chain
- Aelf's side chains has a customisable consensus
- No MVP released for Aelf
- Does not support smart contracts running in EVM
- Aelf does not have smart data feature
Team



Partnerships

Conclusion
PChain provides a POS based consensus multichain as a scaleability solution. Like Quarkchain, it has gained a lot of hype especially after CEO, Jeff Cao, launched their testnet. Prototypes are great indication as to whether an ICO will be successful. MVPs show the project's feasibility as well as the team's expertise. On PChain's live demo, it ran with an impressive 32 nodes on the main chain and 16 nodes on the child chain showing smart contract and smart data running successfully. The testnet also exhibited how to debug a smart contract and how the smart contract uses smart data to obtain results.
One of PChain novel breakthrough is their consensus, PDBFT, which is a more efficient version of PBFT. It allows thousands of nodes to be used in the consensus algorithm as it reduces communication scaling cost from n-squared to n and even log(n), this bypasses the normal limit of PBFT which can only support up to 20-50 nodes. Although this novel consensus was not properly explained in their whitepaper and cross chain capabilities of PChain was not shown in their demo, their prototype surely displayed how solid their project is. Definitely one to watch out for!