The term ecosystem is quite popular within the context of nature based fields of study such as biology, natural science and biogeography.
In biology, an ecosystem is defined as ‘a distinct, self- supporting system of organisms interacting with each other and with their physical environment’ according to Oxford.
Perceived both as an interdependent collection of plants/animals and a structured system/ community governed by general rules with tangled species interactions and abiotic mechanisms , an ecosystem’s extensive network of functionality involving both micro and macro organisms in an inter-connected fashion is a critical component of the environment as it ensures biodiversity and the survival of organisms.
Many will automatically think of biological ecosystems when the term ‘ecosystem’ is within their eye sight as a visual stimuli. However, with the emergence of technology within the past half-century, another ecosystem is gaining popularity. It is none other than the technological or digital ecosystems.
With technology overtaking daily life with the exaggerated use, technological platforms are rising into existence with a wide variety of uses to offer.
Inspired by natural ecosystems, the nature of an ecosystem in application to technology was coined by palm to describe app vendors and the accessories. Furthermore, the financial times of London described a technology ecosystem as “product platforms defined by core components made by the platform owner and complemented by applications made by autonomous companies in the periphery…These ecosystems offer solutions comprising a larger system of use than the original platform owner created to solve important technical problems within an industry. In successful technology ecosystems, it is easy to connect to or build upon the core solution in order to expand the system of use and allow new and even anticipated end uses. The core firm’s product has important but limited value when used alone but substantially increases in value when used with the complementary applications…Technology ecosystems include well known smart phones platforms such as Apple and Android, but are also common in gaming consuls and social media platforms. They exist in industrial sectors, where core products in software, manufacturing or scientific machinery nourish an extended community of service organizations that operate as semi-autonomous, value-added re-sellers.”
According to Gartner (2017), “A digital ecosystem is an interdependent group of enterprises, people and/or things that share standardized digital platforms for a mutually beneficial purpose (such as commercial gain, innovation or common interest). Digital ecosystems enable you to interact with customers, partners, adjacent industries – even your competition.”
The most interesting technology-based ecosystem in current times is decentralized ecosystems, a transformation made possible by the block chain technology.
Listed as the most important invention since the internet by Marc Adreessen, the doyen of Silicon Valley’s capitalist, the block chain technology facilitates the move from a centralized to a decentralized distributed system which coordinates transactions without the third party verification, high cost association and the lack of transparency. Tied to crypto currencies, block chain based decentralized ecosystems are an industry of rapid growth.
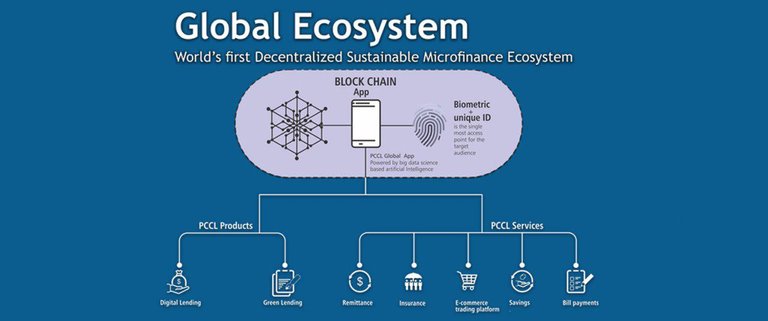
Recognised as the world’s first decentralised sustainable microfinance ecosystem due to its unique features which creates a majestic compatibility, the PCCL global ecosystem is a decentralised platform for microfinance applications based on Ethereum. The project has given rise to a wide variety of applications such as crowd funding and investment platforms, remittance and payments, insurance and E-commerce trading and decentralised lending platforms.
The ecosystem directs its services and products into building four groups of people, the target audience. Within the target audience are two major groups- 1.3 billion poor people & 2.4 billion unbanked people. Poor people and unbanked people worldwide makes up to a total of 3.7 billion which is 2 ½ of the world population. The number is big and so is the effect. Reducing the credit gap by financial inclusion is a prime objective in microfinance.
Though it is unknown to many, unbanked and poor populations are a main contributor to an enhanced credit gap. Financially empowering poor people through financial inclusion and serving the unbanked is a popular technique practiced worldwide to reduce the credit gap and eliminate the poverty line. Inclusive finance is a pre-requirement for fast-tracking growth and minimizing income disparity and poverty. Access to safe, convenient and affordable financial services by the poor and vulnerable groups, is generally considered financial inclusion. Conclusively, financial inclusive augments lives socially and economically improving living standards and the overall quality of life. A paper by a development research group of the World Bank concludes that an estimated 24% of adults in the sub-saharan region of Africa and 18% in the Middle East & North Africa have normal bank accounts. The remaining are unbanked, unserved people.
Upon the base of big data science, block chain technology and AI (Artificial intelligence) for scoring, PCCL’s digital platform is accessible through the PCCL app.As a microfinance centred ecosystem which is both sustainable and decentralised, the PCCL global ecosystem is composed of a total of three principal tiers which function in ultimate cooperation in an ascending order to complete the functionality of the ecosystem. As ecosystems rely on connections, each part is equally important.
By Indrachapa Sandeepani Jayasundera