
Blockchain, the ledger, is basically a data ledger that is designed to manage digital money without the need for an umpire, regulator or central administrator. In 2008 Satoshi Nakamoto devised this system to support his electronic cash system (Bitcoin) and used a mechanism that has today changed the very fabric of accounting of multiple stakeholders’ data.
The Blockchain can also be defined, technically, as a Distributed Ledger Technology or DLT. This technology is the basis of all digital transactions happening on the Cryptocurrency network and in many ways also being adopted in public and private organizations to reduce the burden of building a trust-based consensus.
The Multiple Ledger Conundrum
Millions of business transactions are happening around the world and being recorded every second on ledgers which account for each transaction. However, there could be multiple participants in the transactions e.g. customer, supplier, manufacturer, wholesaler and within each entity, there are numerous stakeholders who have to maintain their own ledger.
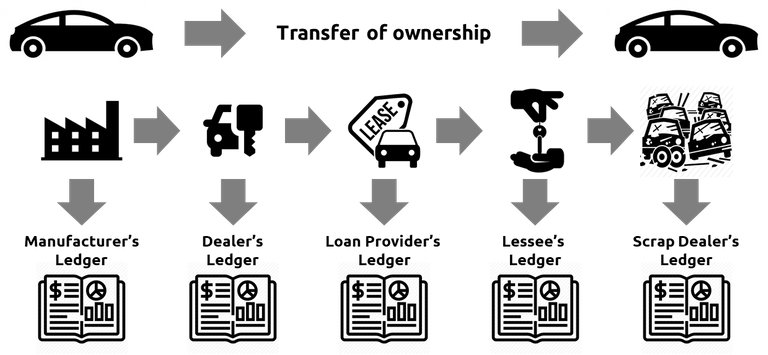
This is a big vulnerability in the global accounting system. It is very difficult to reconcile a large set of ledgers. Moreover, even auditors or managers who have the ability to reconcile such transactions result in a complex, time-consuming and inefficient process.
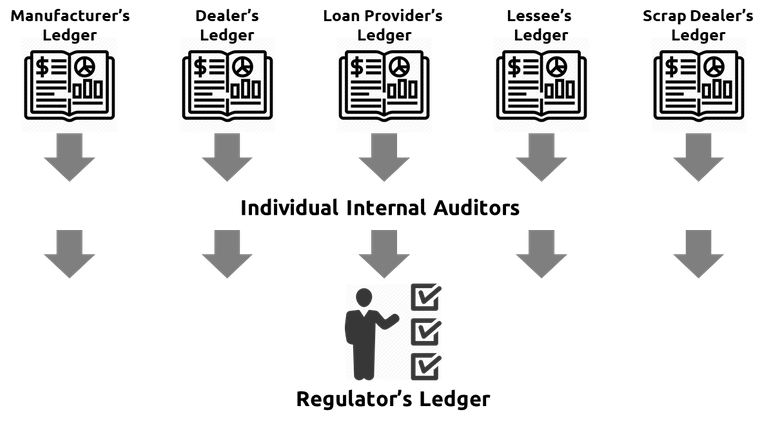
Now here is the bitter truth – each participant ledger of transactions is prone to errors, inefficiencies, and frauds. There is no way to develop a consensus on which ledger is correct and ascertain whom one can Trust!
Birth of the One True Ledger
When Bitcoin originated, it brought along with it a technological shift in the accounting standards around the world. In an earlier article, it was explained that the bitcoin transactions are collected sequentially in an online, public, and a widely distributed Shared ledger called the Blockchain.
This means that irrespective of the number of participants and their individual transactions, there is only one true ledger accessible to one and all. This ledger cannot be changed, edited, modified, deleted or predated in any way, thus making it the one truth ledger among all transactions.
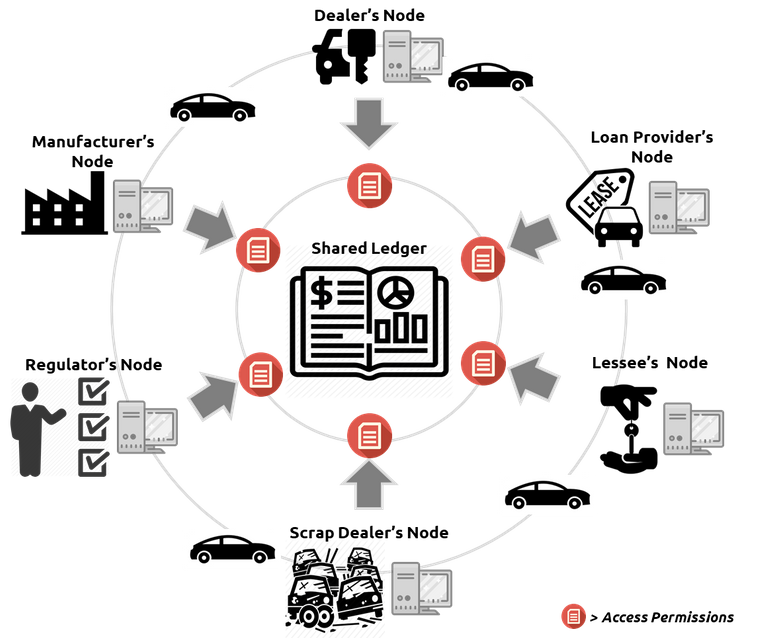
Moreover, the shared ledger is not present as a single copy, but multiple synced copies on the entire network of nodes.
How Does it get done
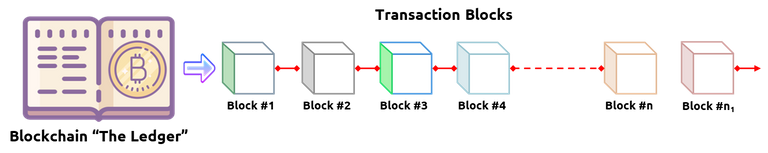
The transaction on this ledger is collected in Blocks – sequentially and with the consensus of all the nodes in the network. These blocks are then encrypted and made immutable, which means the transactions have been made permanent and cannot be changed.
A sequence of such blocks of transactions is called the BLOCKCHAIN, which forms the omnipresent ledger.
What Does It Solve
The central problem that the blockchain ledger solves is the issue of Double Spend. Electronic money is simply – data. Hence, nothing physically stops a holder of currency to spend it twice on the same or different network. In order to stop this from happening, a digital authority would be needed at all times to oversee transactions and identity and stop double-spends.
What Is It Not
The blockchain is not a general-purpose database of transactions. Neither is it a “trust machine” – i.e. something which removes the trust from a human to a machine. It is in fact just a data storage mechanism that uses consensus from all the participating nodes to build the sequential ledger of transactions. The consensus is also only for obtaining the order of transaction entries in the blocks.
Advantages of Blockchain
The advantages which Blockchain enjoys over other ledger systems are:
- Cost-effective*: The shared system of a blockchain ledger eliminates the need for any kind of intermediaries.
- Efficient: The transaction data needs to be recorded only once and is made available to all stakeholders through a distributed network of nodes.
- Safe: The shared ledger is tamper-proof and immutable i.e. it cannot change due to the encryption locking system.
- Secure: The complete ledger is present not as one copy but multiple synced copies of the same ledger on a large network of computers. Hence, it is practically impossible to tamper or hack the complete ledger or even one transaction.
One Last time – ‘A’ Ledger and ‘The’ Blockchain
Ledger: A ledger is a complete record of any economic activity; it is mostly created to track monetary transactions, transfer of goods and services, transfer of ownership of assets. The records in a ledger can be of two types:
- Tangible: e.g. motor vehicles, house
- Intangible: e.g. stock certificates, money, digital rights
Blockchain: Blockchain is can be defined as a single, tamper-proof and shared digital ledger which records all transactions in a decentralized peer-to-peer network. The recording of assets exchange transactions is said to be permanent.
Congratulations @shantanush! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDo not miss the last post from @steemitboard: