In Development Inside Kubernetes Part 2: Traefik Dashboard Setup I showed how to
- Setup Traefik
- View the Traefik Dashboard
- Create an
IngressRoutefor the Traefik Dashboard - Install
cert-manager - Setup a self-signed certificate issuer
- Create a self-signed certificate
- Add SSL to the Traefik Dashboard
IngressRoute
This time, I will show how to get a free SSL certificate from Let's Encrypt and apply that to our existing IngressRoute.
AWS Route 53
For more information about Route 53 certificates, look at the cert-manager information on it.
cert-manager will need to access my Route 53 information through the AWS API. I need to setup an IAM role for cert-manager to assume. I created one in AWS. I am not going to go through it here, but here is the policy I applied to the role that allows the role to access Route 53.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "route53:GetChange",
"Resource": "arn:aws:route53:::change/*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"route53:ChangeResourceRecordSets",
"route53:ListResourceRecordSets"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:route53:::hostedzone/*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "route53:ListHostedZonesByName",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Let's Encrypt Staging Certificate Issuer
Let's Encrypt heavily restricts and rate-limits requests. I want to avoid requesting a certificate until I have a completed configuration. Let's Encrypt gives us a staging server to help us setup our configuration. I get an invalid SSL certificate, but the real benefit is testing the configuration which includes the Route 53 solver. That is the big one. I want to be able to test out that my Route 53 access is configured properly before requesting a real certificate.
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-staging
spec:
acme:
# You must replace this email address with your own.
# Let's Encrypt will use this to contact you about expiring
# certificates, and issues related to your account.
email: [email protected]
server: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
privateKeySecretRef:
# Secret resource that will be used to store the account's private key.
name: letsencrypt-staging
# Add a single challenge solver, HTTP01 using nginx
solvers:
- selector:
dnsZones:
- "thelastpri.me"
dns01:
route53:
region: us-west-1
hostedZoneID: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
accessKeyID: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
secretAccessKeySecretRef:
name: aws-creds
key: secret-access-key
# you can also assume a role with these credentials
role: arn:aws:iam::XXXXXXXXXX:role/cert-manager
I install this with
kubectl create -f letsencrypt-staging.yaml
Staging Certificate Request
To request a certificate, I have created a Certificate resource.
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: local-acme-staging
namespace: kube-system
spec:
commonName: "*.local.thelastpri.me"
dnsNames:
- "local.thelastpri.me"
- "*.local.thelastpri.me"
issuerRef:
kind: ClusterIssuer
name: letsencrypt-staging
secretName: local-acme-staging-crt
I install this with
kubectl create -f dashboard-certificate-staging.yaml
Update IngressRoute
Once my certificate is available, I will need to update my IngressRoute. Here, I add my secretName near the bottom for local-acme-staging-crt. Also, I no longer need sslip.io because I am using Route 53.
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: IngressRoute
metadata:
name: traefik-dashboard-secure
namespace: kube-system
spec:
entryPoints:
- websecure
routes:
- kind: Rule
match: Host("dashboard-traefik.local.thelastpri.me")
services:
- kind: TraefikService
name: api@internal
middlewares:
- name: dashboard-rewrite
- kind: Rule
match: Host("dashboard-traefik.local.thelastpri.me") && PathPrefix("/api")
services:
- kind: TraefikService
name: api@internal
tls:
secretName: local-acme-staging-crt
I install the changes with
kubectl delete ingressroute traefik-dashboard-secure -n kube-system
kubectl create -f ingress.yaml
I can test with
curl -ksiv https://dashboard-traefik.local.thelastpri.me
It should be able to see and verify my certificate information.
Switch from Staging to Live
staging in the domain. This is the Let's Encrypt live environment. Besides the url, the privateKeySecretRef is also different from staging.Now that it has been verified that staging is ok, I can now switch to the live environment. First, I need to start with a new issuer. Notice that the server is https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory and does not have
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-prod
spec:
acme:
# You must replace this email address with your own.
# Let's Encrypt will use this to contact you about expiring
# certificates, and issues related to your account.
email: [email protected]
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
privateKeySecretRef:
# Secret resource that will be used to store the account's private key.
name: letsencrypt-prod
# Add a single challenge solver, HTTP01 using nginx
solvers:
- selector:
dnsZones:
- "thelastpri.me"
dns01:
route53:
region: us-west-1
hostedZoneID: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
accessKeyID: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
secretAccessKeySecretRef:
name: aws-creds
key: secret-access-key
# you can also assume a role with these credentials
role: arn:aws:iam::XXXXXXXXXX:role/cert-manager
Now we have an issuer that will get a real and valid SSL certificate.
I install with
kubectl create -f letsencrypt-prod.yaml
Now that there is a live environment certificate issuer, all that is left is requesting a certificate. This is no different than the staging certificate except that the issuerRef points to letsencrypt instead of letsencrypt-staging and the secretName is local-acme-crt.
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: local-acme
namespace: kube-system
spec:
commonName: "*.local.thelastpri.me"
dnsNames:
- "local.thelastpri.me"
- "*.local.thelastpri.me"
issuerRef:
kind: ClusterIssuer
name: letsencrypt
secretName: local-acme-crt
I install with
kubectl create -f dashboard-certificate.yaml
Once you complete the kubectl command, you can monitor from the dashboard in Rancher Desktop the request.

It will also create a challenge. This challenge is where the AWS Route 53 solver is used to verify the domain.
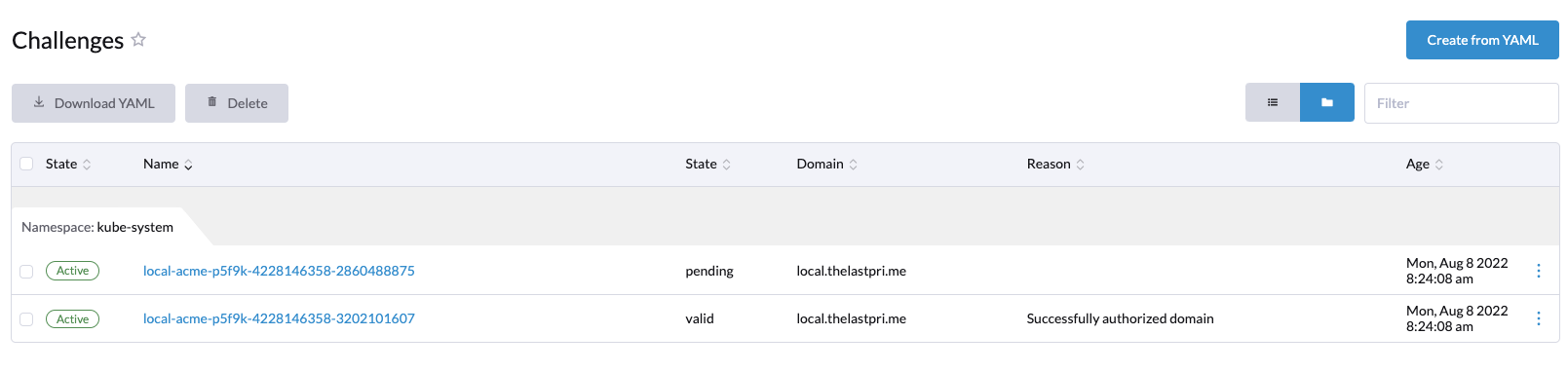
After the challenge is complete, an order is placed.
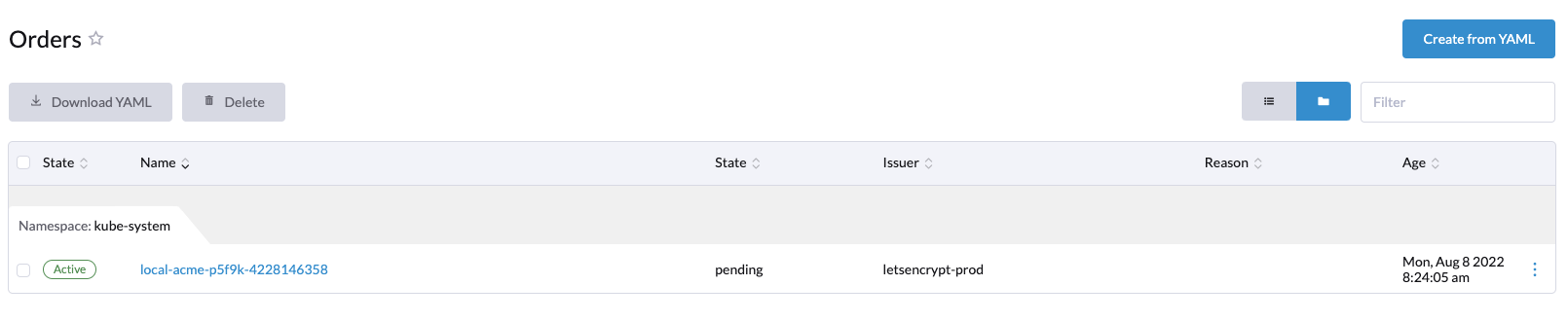
The certificate will remain pending until the order completes.

Final update to IngressRoute
When we finally have a valid certificate, all that is left is to update the IngressRoute. Here I replace local-acme-staging-crt to local-acme-crt.
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: IngressRoute
metadata:
name: traefik-dashboard-secure
namespace: kube-system
spec:
entryPoints:
- websecure
routes:
- kind: Rule
match: Host("dashboard-traefik.local.thelastpri.me")
services:
- kind: TraefikService
name: api@internal
middlewares:
- name: dashboard-rewrite
- kind: Rule
match: Host("dashboard-traefik.local.thelastpri.me") && PathPrefix("/api")
services:
- kind: TraefikService
name: api@internal
tls:
secretName: local-acme-crt
I install the changes with
kubectl delete ingressroute traefik-dashboard-secure -n kube-system
kubectl create -f ingress.yaml
We can test our new certificate with
curl -si https://dashboard-traefik.local.thelastpri.me | head -1
This should return a status 200 with our new certificate information. If I browse to the URL in my browser, I'll see the site is locked and secure.