Types of Bonds in Brick Masonry Wall Construction :
The most commonly used types of bonds in brick masonry are:
- Stretcher bond
- Header bond
- English bond and
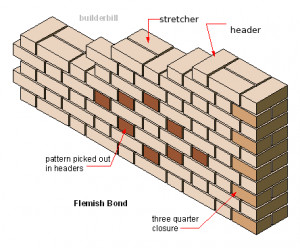
- Flemish bond
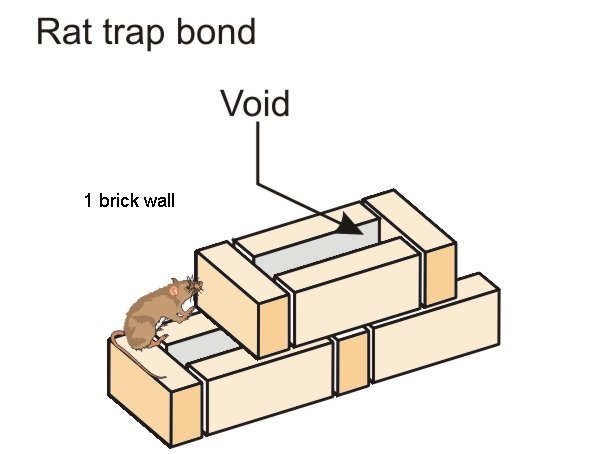
Other Types of bonds are: - Facing bond
- Dutch bond
- English cross bond
- Brick on edge bond
- Raking bond
- Zigzag bond
- Garden wall bond
- Stretcher bond
Longer narrow face of the brick is called as stretcher as shown in the elevation of figure below. Stretcher bond, also called as running bond, is created when bricks are laid with only their stretchers showing, overlapping midway with the courses of bricks below and above.
Stretcher bond in the brick is the simplest repeating pattern. But the limitation of stretcher bond is that it cannot make effective bonding with adjacent bricks in full width thick brick walls. They are suitably used only for one-half brick thick walls such as for the construction half brick thick partition wall.
Walls constructed with stretcher bonds are not stable enough to stand alone in case of longer span and height. Thus they Then need supporting structure such as brick masonry columns at regular intervals.
Stretcher bonds are commonly used in the steel or reinforced concrete framed structures as the outer facing. These are also used as the outer facing of cavity walls. Other common applications of such walls are the boundary walls, gardens etc.
- Header bond
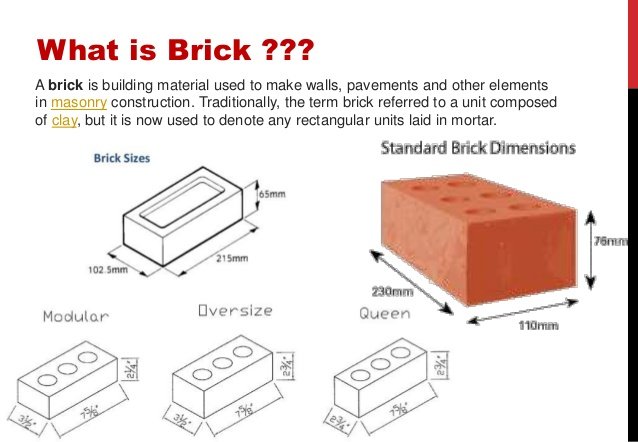
Header is the shorter square face of the brick which measures 9cm x 9cm. Header bond is also known as heading bond. In header bonds, all bricks in each course are placed as headers on the faces of the walls. While Stretcher bond is used for the construction of walls of half brick thickness whereas header bond is used for the construction of walls with full brick thickness which measures 18cm. In header bonds, the overlap is kept equal to half width of the brick. To achieve this, three quarter brick bats are used in alternate courses as quoins.
- English Bond
English bond in brick masonry has one course of stretcher only and a course of header above it, i.e. it has two alternating courses of stretchers and headers. Headers are laid centered on the stretchers in course below and each alternate row is vertically aligned.
To break the continuity of vertical joints, quoin closer is used in the beginning and end of a wall after first header. A quoin close is a brick cut lengthwise into two halves and used at corners in brick walls.
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://theconstructor.org/building/types-bonds-brick-masonry-flemish-english-wall/11616/