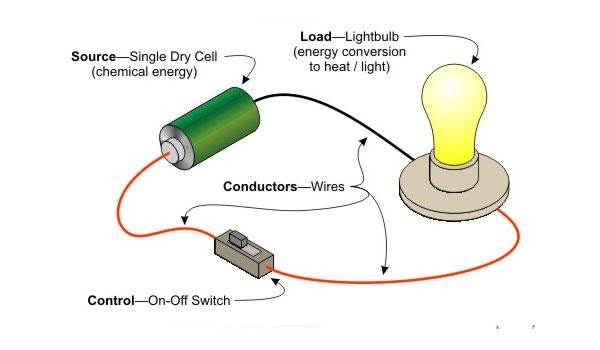
Electric Voltage
Voltage, potential difference, is the energy required to move a unit charge through an element, measured in volts (V).
Basic Concept
To move the electron in a conductor in a particular direction requires some work or energy transfer. This work is performed by an external electromotive force (emf). This emf is also known as voltage or potential difference.
The voltage between two points a and b in an electric circuit is the energy (or work) needed to move a unit charge from a to b; mathematically,
where, w is energy in joules (J) and
q is charge in coulombs (C).
Unit of Electric voltage
Voltage is measured in volts(V) in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Antonio Volta (1745–1827), who invented the first voltaic battery.
A voltage, potential difference, of 1 volt (V) exists between two points if 1 joule (J) of energy is exchanged in moving 1 coulomb (C) of charge between the two points.
Type of Electric Voltage
Voltage can be :
- DC voltage
- AC voltage
A dc voltage is a voltage that remains constant with time. A dc voltage is commonly produced by a battery.
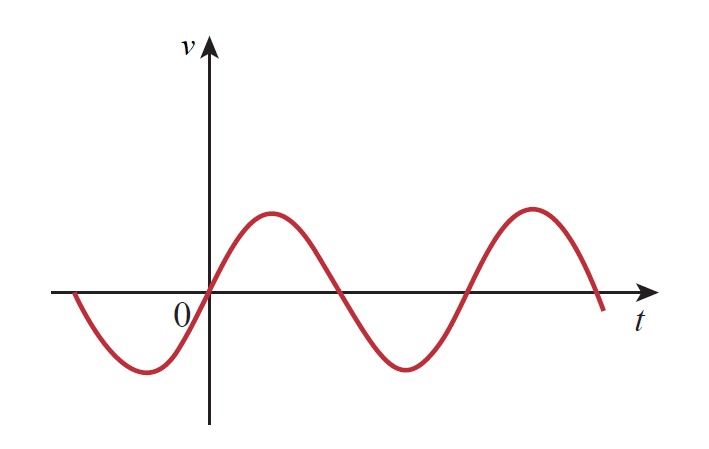
A sinusoidally time-varying voltage is called an ac voltage. ac voltage is produced by an electric generator.
Polarity of Electric Voltage
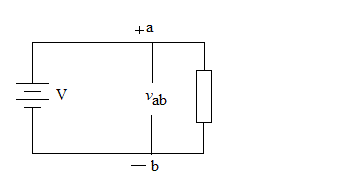
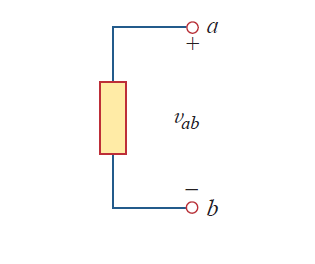
Figure shows the voltage across an element connected to points a and b. The plus and minus signs are used to define reference direction or voltage polarity. The vab can be interpreted in two ways:
- Point a is at a potential of vab volts higher than point b.
- The potential at point a with respect to point b is vab. It follows logically that in general
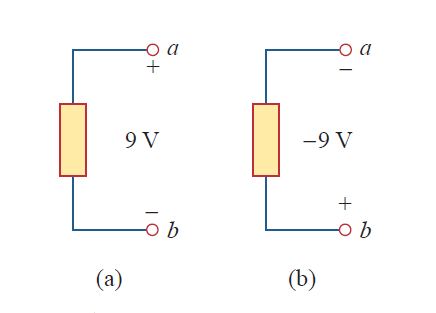
In Fig, we have two representations of the same voltage. In Fig(a), point a is +9V above point b; in Fig(b), point b is -9V above point a. We may say that in Fig(a), there is a 9-V voltage drop from a to b or equivalently a 9-V voltage rise from b to a. In other words, a voltage drop from a to b is equivalent to a voltage b rise from b to a.