The History of Islam
In the seventh century, Hazrat Muhammad (SM:) claimed the angel Gibriel visited to him. During these angelic visitations, which continued for about 23 years until Muhammad's death, the angel purportedly revealed to Muhammad the words of Allah (the Arabic word
for “God” used by Muslims). These dictated revelations compose the Qur'an, Islam's holy book. Islam means “submission,” deriving from a root word that means “Peace.” The word Muslim means “one who submits to Allah.”
The Doctrine of Islam
Muslims summarize their doctrine in six articles of faith:
Belief in one Allah: Muslims believe (Allah Is One), eternal, creator, and sovereign.
Belief in the angels: Muslims believe in the angels.
Belief in the prophets: The prophets include the biblical prophets but end with (Hazrat Muhammad(SM:) as Allah’s final prophet.
Belief in the revelations of Allah: Muslims accept certain portions of the Bible, such as the Torah and the Gospels. They believe the Quran is the preexistent, perfect word of Allah.
Belief in the last day of judgment and the hereafter: Everyone will be resurrected for judgment into either paradise or hell.
Belief in predestination: Muslims believe Allah has decreed everything that will happen. Muslims testify to Allah’s sovereignty with their frequent phrase, (Inshah Allah meaning), “if Allah wills.”
The Five Pillars of Islam
These five tenets compose the framework of obedience for Muslims:
The testimony of faith (Shahada): Shahada is a declaration of faith and trust that professes that thereis only one
God (Allah) and that Muhammad is God's messenger. It is a set statement normally recited in Arabic: la ʾilaha ʾilla-llahu muḥammadun rasulu-llah (لَا إِلٰهَ إِلَّا الله مُحَمَّدٌ رَسُولُ الله) "There is no god but God (and) Muhammad is the messenger of God. " It is essential to utter it to become a Muslim and to convert to Islam. The shahada shows that a Muslim believes in Allah alone as deity and believes that Muhammad reveals Allah.
Prayer (Salat): Salah is the Islamic prayer. Salah consists of five daily prayers according to the Sunna.
The names are according to the prayer times:
Fajr : Prayer is performed before sunrise.
Dhuhr : Is performed in the midday after the sun has surpassed its highest point.
Asr : Is the evening prayer before sunset.
Maghrib : Is the evening prayer after sunset.
Isha : Is the night prayer.
All of these prayers are recited while facing in the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca and form an important aspect of the Muslim Ummah. Muslims must wash before prayer, this washing is called wudu ("Purification"). The prayer is accompanied by a series of set positions including. Bowing with hands on knees, standing, prostrating and sitting in a special position (not on the heels, nor on the buttocks). A Muslim may perform their prayer anywhere, such as in offices, universities, and fields. However, the mosque is the more preferable place for prayers because the mosque allows for fellowship.

3 . Giving (Zakat): Zakat or alms-giving is the practice of charitable giving based on accumulated wealth. The word zakat can be defined as purification and growth because it allows an individual to achieve balance and encourages new growth. The principle of knowing that all things belong to God is essential to purification and growth. Zakat is obligatory for all Muslims who are able to do so. It is the personal responsibility of each Muslim to ease the economic hardship of others and to strive towards eliminating inequality. Zakat consists of spending a portion of one's wealth for the benefit of the poor or needy, like debtors or travelers. A Muslim may also donate more as an act of voluntary charity (sadaqah), rather than to achieve additional divine reward. There are five principles that should be followed when giving the Zakat:
- The giver must declare to God his intention to give the zakat.
- The zakat must be paid on the day that it is due.
- After the offering, the payer must not exaggerate on spending his money more than
usual means. - Payment must be in kind. This means if one is wealthy then he or she needs to pay a portion of their income. If a person does not have much money, then they should compensate for it in different ways, such as good deeds and good behavior toward others.
- The zakat must be distributed in the community from which it was taken.

4 . Fasting (Sawm): Three types of fasting (Siyam) are recognized by the Quran: Ritual fasting, fasting as compensation for repentance (both from sura Al-Baqara), and ascetic fasting (from Al-Ahzab). Ritual fasting is an obligatory act during the month of Ramadan.
Muslims must abstain from food and drink from dawn to dusk during this month, and are to be especially mindful of other sins. Fasting is necessary for every Muslim that has reached puberty (unless he/she suffers from a medical condition which prevents him/her from doing so). The fast is meant to allow Muslims to seek nearness and to look for forgiveness from Allah, to express their gratitude to and dependence on him, atone for their past sins, and to remind them of the needy.
During Ramadan, Muslims are also expected to put more effort into following the teachings of Islam by refraining from violence, anger, envy, greed, lust, profane language, gossip and to try to get along with fellow Muslims better. In addition, all obscene and irreligious sights and sounds are to be avoided. Fasting during Ramadan is obligatory, but is forbidden for several groups for whom it would be very dangerous and excessively problematic.
These include pre-pubescent children, those with a medical condition such as diabetes, elderly people, and pregnant or breastfeeding women. Observing fasts is not permitted for menstruating women. Other individuals for whom it is considered acceptable not to fast are those who are ill or traveling. Missing fasts usually must be made up for soon afterward, although the exact requirements vary according to circumstance.
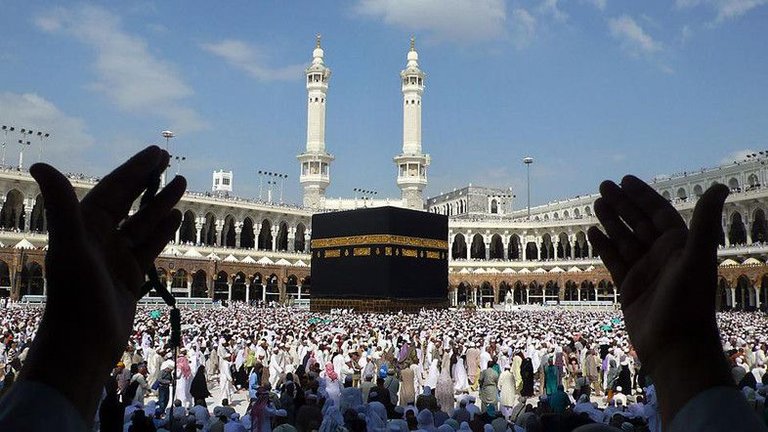
5 . Pilgrimage (Hajj): The Hajj is a pilgrimage that occurs during the Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah to the holy city of Mecca. Every able-bodied Muslim is obliged to make the pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in their life. When the pilgrim is around 10 km (6.2 mi) from Mecca, he/she must dress in Ihram clothing, which consists of two white sheets. Both men and women are required to make the pilgrimage to Mecca. After a Muslim makes the trip to Mecca, he/she is known as a hajj/hajja (one who made the pilgrimage to Mecca). The main rituals of the Hajj include walking seven times around the Kaaba termed Tawaf, touching the Black Stone termed Istilam, traveling seven times between Mount Safa and Mount Marwah termed Sa'yee, and symbolically stoning the Devil in Mina termed Ramee. The pilgrim, or the haji, is honoured in the Muslim community. Islamic teachers say that the Hajj should be an expression of devotion to God, not a means to gain social standing. The believer should be self-aware and examine their intentions in performing the pilgrimage. This should lead to constant striving for self-improvement. A pilgrimage made at any time other than the Hajj season is called an Umrah, and while not mandatory is strongly recommended. Also, they make a pilgrimage to the holy city of Jerusalem in their alms-giving feast.

Hello,
We have found that all or part of the above post may have been copied from: https://www.facebook.com/103058633179787/photos/pb.103058633179787.-2207520000.1481508040./246171992201783/?type=3
Not indicating that the content you post including translations, spun, or re-written articles are not your original work could be seen as plagiarism.
These are some tips on how to share content and add value:
Repeated plagiarized posts are considered spam. Spam is discouraged by the community, and may result in action from the cheetah bot.
If you are actually the original author, please do reply to let us know!
Thank You.
More Info: Abuse Guide - 2017.