Our body is very complex and interesting, it is very good to learn a little more about the
The human anatomy is the science of a practical and morphological character mainly dedicated to the study of the macroscopic structures of the human body; Thus leaving the study of tissue to histology and cells to cytology and cell biology. The human anatomy is a special field within the general (animal) anatomy.
Under a systematic view, the human body - like the bodies of animals - is organized at different levels of hierarchy. Thus, it is composed of apparatuses, these are integrated systems, which in turn are composed of organs, which are composed of tissues, which are formed by cells, which are formed by molecules, etc. Other visions (functional, morphogenetic, clinical, etc.), under other criteria, understand the human body in a slightly different way.
Branches and divisions
Some branches or disciplines such as osteology, myology, arthrology, angiology or neuroanatomy surround the study limits of the human body in a more particular way. Thus, myology performs the specific study of muscles, its characteristics:
Systematic or descriptive anatomy: schematizes the study of the human body by fractionating it in the minimum constituent parts, and organizing them by systems and apparatus.
Topographical, regional or surgical anatomy: organizes the study of the body by regions following various criteria. Regional Anatomy studies each region separately and all aspects of that region are studied at the same time. If the thorax is studied, all its structures are studied: vascularization, muscles, bones, nerves ... 1
Surface anatomy: it is an essential area in the study, since the surface anatomy boxes offer visible and tactile information about the structures that are placed under the skin.
Artistic Anatomy: deals with anatomical issues that directly affect the artistic representation of the human figure. For example, the muscles that appear superficially and their tensions according to the different postures or efforts; The anatomical transformations that occur in function of the age, of the "race" (or rather clina or fisiotipo), of the diseases; The anatomical transformations due to the gesture or the emotions are studied in a subdivision of the artistic human anatomy denominated physiognomy or physiognomic.
Neuroanatomy performs the study of the nervous system extensively.
Clinical Anatomy: Emphasis is placed on the study of structure and function in correlation to medical-clinical (and other health sciences) situations. Here different areas like: the surgical anatomy; Radiological anatomy in relation to diagnostic imaging; The morphogenetic anatomy that is related to congenital diseases of development; Pathology, among others.
There are other anatomical modalities that are applied to the study of the human body as: Comparative anatomy, functional anatomy, etc.
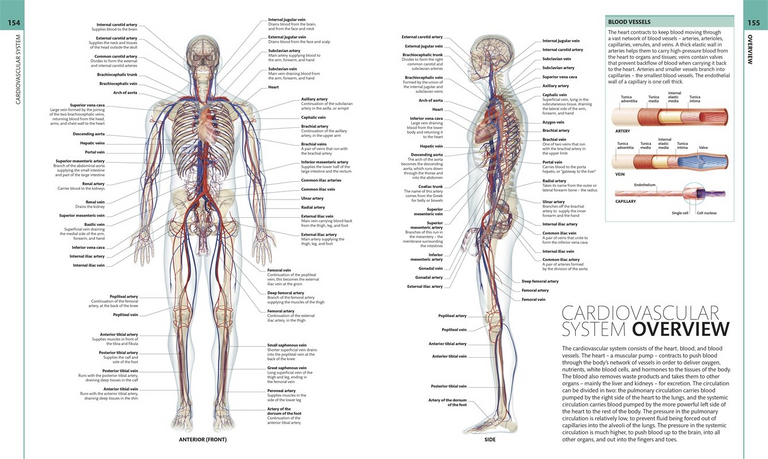
Systems and devices of the human body System
A system is a group of associated organs that concur in a general function and are formed predominantly by the same types of tissues. For example: the skeletal system, the cardiovascular system, the nervous system, etc.
Immune system: defense against agents causing diseases.
The integumentary system: skin, hair and nails.
Nervous system: collection, transfer and processing of information. It consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (nerves of the whole body).
Circulatory system: formed by the heart, arteries, veins and capillaries.
Lymphatic system: formed by capillaries, vessels and lymph nodes, spleen, thymus and bone marrow.
Endocrine system: communication within the body through hormones. It consists of the endocrine glands that synthesize hormones and pass them to the internal environment (blood, lymph, interstitial fluid) such as pituitary, thyroid, thymus, adrenals, pancreas and gonads and secretory cells found in organs that are not properly glands But they secrete hormones like the kidney and heart.
Muscular system: movement of the body.
Bone system: structural support and bone protection.
Joint system: formed by the joints and associated ligaments that join the skeletal system and allows the body movements.
Apparatus
An apparatus is a group of organs that play a common function and their organs do not have predominance of any tissue, for example the digestive system, or they include several systems, like the locomotive apparatus, integrated by the muscular, osseous, articular systems.
Digestive system: food processor, mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestines and glands attached. It allows the conversion of food into assimilable molecules through enzymes.
Excretory or urinary device: removal of toxic substances and wastes from the body through the urine. Organs: kidneys (containing anatomical-functional units called nephrons), ureters, bladder, urethra.
Reproductive system: the sexual organs (male and female)
Respiratory apparatus: are the organs and cavities used for the exchange of respiratory gases: nostrils, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and lungs. Inside the lungs are the alveoli that are the anatomical-functional unit of the system.
Locomotor apparatus: set of skeletal, articular and muscular systems. These systems coordinated by the nervous system allow locomotion.
Cardiovascular system: set of blood vessels (veins, arteries and capillaries) and lymphatics.
This post has received a 1.56 % upvote from @drotto thanks to: @banjo.