
Solving the physical integrity problem
Solving the physical integrity problem
The most important property of money is its physical integrity, and the most important part of that is its ability to avoid being counterfeited.
For something to be useful as money, it should either cost more to counterfeit than its value, or it should be impossible to counterfeit.
This is why we’ve used gold as money in the past. Gold was not used because it was valuable, but because gold coins are difficult to counterfeit. If you want to create a gold coin, you have to mine the gold. Gold mining is so difficult that it cost more than the money was worth.
The real value of money comes from its integrity as data.
Humans form a superorganism (а social unit with division of labor. Individuals are highly specialized and cannot survive on their own for extended periods of time) that we call a society or an economy. This superorganism emerges through the use of money.
Because money is data, any data corruption will lead to the submersion of the economy. An example of data corruption is counterfeiting. Submersion refers to the economy becoming weaker and more disorganized.
Today we are seeing cryptocurrencies that cannot be counterfeited because of the encryption they use. In a good monetary accounting system, we do not want data (money) appearing out of nowhere, disappearing, or in any way becoming corrupted.
When corruption does happen, the monetary system becomes inaccurate, and will prevent people from making efficient decisions.
Imagine a person who shows up with a bag full of cash and offers to buy your house for what seems like a very good price. You sell the house.
As you drive off, you realize that the road is filled with cash, and there’s a helicopter above dropping more.
People are picking it up in wheelbarrows. The bag of cash sitting next to you suddenly doesn’t seem to be as valuable as it seemed a few minutes earlier.
Down the road, when you’re ready to buy a new house, you discover that your bag of cash will no longer even cover a month’s rent!
You made a very bad decision based on bad money. Now multiply this by millions of people.
Physical integrity of money
Let's compare the physical integrity of different types of money.
First let's imagine the worst type of money we could use.
Suppose we decided to use ice cubes for money.
It’s obvious that this would be a terrible mistake because anyone with a freezer could add new money to the system, thus corrupting the accounting. Ice cubes would melt, causing everyone's hard-earned money to disappear. In a short time, everyone would make poor decisions, and poverty would become the norm.
Now compare that to silver coins.
Silver coins make good data (money) because they add physical integrity to a monetary system. However, a monetary system based on silver coins is still not perfect. Although difficult, it is still, like gold, possible to counterfeit silver coins.
A case in point is the historic Spanish Price Revolution that occurred between 1470 and 1650 when silver began to pour into Europe from the New World. This caused a rampant inflation that lasted for over 100 years, with decidedly negative effects.
Wages lagged behind prices. Landowners and the rich - along with anyone with something to sell - benefited from this inflation. But
for most people, the accounting system did not function properly. They made bad decisions and become poorer even though more silver was readily available.
What about paper money?
Paper money is difficult to counterfeit unless you are the central bank and own the printing presses. In this case, it is very easy to increase the supply.
As with silver during the Spanish Price Revolution, this helps the government, the rich, the landowners, and anyone with something to sell.
Paper money has much less physical integrity than a metal currency, and is far from a perfect money.
The integrity of Bitcoin

Now let's take a look at Bitcoin.
You may think that it’s impossible to counterfeit Bitcoin. But, in fact, Bitcoin mining is counterfeiting. Counterfeiting is necessary to make bitcoins work because the operation of the servers that hold the public ledger depends on counterfeiting (mining) to pay for the system’s administrators (miners).
It is also possible to lose Bitcoins. You may work very hard for your Bitcoins and then lose them. And sorry, but you will not be compensated for your lost value. That is not a feature of a good monetary system.
For Bitcoin to work, it is necessary to have a public ledger stored on someone's hard drive that is publicly accessible.
But what if someone accidentally deleted the public ledger?
To prevent this from happening, the public ledger is mirrored (duplicated) on many computers, and anyone can download it and keep a copy of it on their own computer if they choose to. This gives Bitcoin physical integrity because storing duplicate versions of the data on separate computers protects it from loss.
But what if someone were to tamper with the information? They could change the row that represents the total amount of Bitcoin they own and make it bigger. This is where the blockchain comes in. To prevent corruption, every transaction is recorded and encrypted. These encrypted transactions are also encrypted, then added to a chain.
This system requires vast amounts of computer processing power and electricity to encrypt transactions, but it works and it allows for the funding of the physical infrastructure.
Even so, there is still some vulnerability to Bitcoin's physical integrity.
First, Bitcoin requires encryption, and is not quantum safe. When quantum computers become widely available, in a very short time, Bitcoin will become hackable—first by governments, then by common hackers. When this happens, Bitcoin is finished.
The second vulnerability is that the Bitcoin infrastructure is paid for by bitcoin miners. As time goes by, it is becoming harder and harder to make money mining Bitcoin, and this puts the entire infrastructure at risk as fewer people will be able to provide computers to store the public ledger.
Another issue with Bitcoin is that its ledger is growing. Right now, it is 100GB. Who knows, with more accounts and more transactions, we may see it grow to a terabyte in just a few years. If the blockchain is too big to fit on a hard drive, this threatens the physical integrity of the coins.
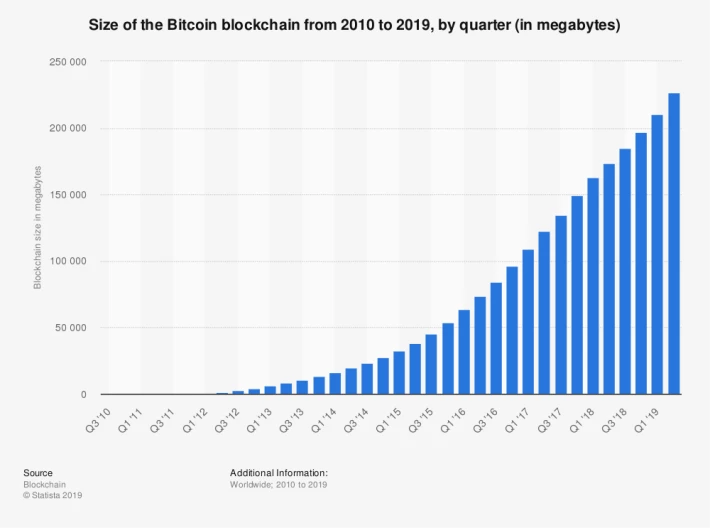
The space demands for storing the Bitcoin blockchain ledger are growing rapidly, and the ledger is becoming more unmanageable every year.
The best way to maintain physical integrity is by not depending on encryption alone, but by utilizing the newest technology: the Cloud.
RAIDA and integrity

Sean H. Worthington: - "I have taught networking and system administration for over seventeen years and, having finished all of the coursework for a doctoral degree, I am all but dissertation (ABD) for my PhD in Computer Information Systems. I can imagine an endless collection of new privacy technologies that could change the world. But I don’t want to write about them, I want to implement them. I have a patent pending on a new cloud-based counterfeit detection system that I call the Redundant Array of Independent Detection Agents, or RAIDA. What is the easiest way to monetize this new technology? By creating a new currency. And that currency is called CloudCoin, because it is based on the cloud. You are likely to see many more inventions from me in the future, but for now, let’s review what RAIDA is..."
RAIDA is a global counterfeit-detection system that is indestructible and cannot be hacked or tampered with. Nuclear bombs, comet strikes, world wars, dictatorships and government hackers cannot not bring down RAIDA.
RAIDA is quantum-safe, self-healing, simple, fast and reliable.
And RAIDA can detect the authenticity of a CloudCoin within milliseconds. That’s right, milliseconds.
Trust
The essence of money is that it can’t be counterfeited.
The purpose of money is to help us economize.
The value of money is based on its physical and logical integrity (trust).
CloudCoin takes our trust in a currency to the highest level yet.
Using the patent-pending RAIDA technologies (with a patent intended to keep just one cloud-based currency), independent system administrators from all around the world can leverage thousands of servers and networks to create an unbreakable system that no single entity or organization can dictate.
Note that the RAIDA does not create, store, transmit, track or broker CloudCoins or any other digital currency. The only function of a RAIDA cloud is to detect the authenticity of a CloudCoin.
Like a blockchain, RAIDA does not have a central administrator.
If I get hit by a bus, the RAIDA keeps going because it doesn’t depend on an individual to run it.
I am sad to say that we had a RAIDA administration (Nick Burges) die during the proof-of-concept test. His death was a great loss to everyone—including CloudCoin. But his death did accomplish one thing that may have a lasting impact on humanity—it showed that the RAIDA technology works, and proved that it is fault tolerant.
Fault tolerance, by the way, is another concept from computer science. Fault-tolerant computing is a key concept in systems design that ensures the system will continue working even in the presence of faults in the hardware.
Not only is RAIDA fault tolerant, but, unlike blockchain technology, the more its popularity and value grow, the more decentralized it becomes. (A blockchain will always move toward becoming more centralized as the associated value goes up.)
The CloudCoin™ structure

A RAIDA network is composed of 25 RAIDA clouds.
A single RAIDA cloud can have up to 32 administrators and one sentinel. The sentinel is responsible for making sure data stays true and available.
Each cloud is a cluster—a group of separate but connected or virtually connected data storage units.
A node is a single machine or group of machines in a cluster.
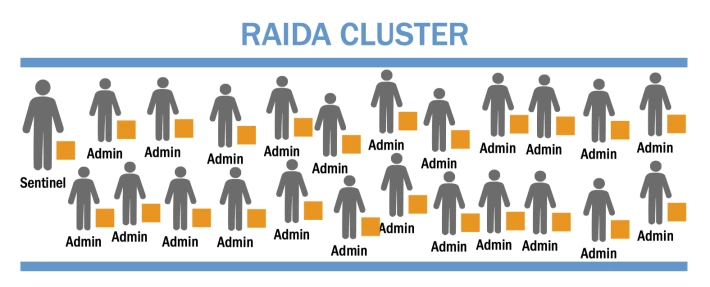
Each cluster has at least one sentinel, and not more than thirty-two admins. In each cluster, the sentinel is responsible for insuring data integrity.
The administrators need to be able to fund their operations. But, unlike Bitcoin, which requires rooms full of servers, the needs of RAIDA are minimal.
In the full 800-node configuration (up to thirty-two admins for each of the twenty-five clusters), each node (single admin) is in charge of only 21,000 CloudCoin notes. This means that the admin only needs 25MB of database storage, a minimal processor, and very little network bandwidth. (Compare this memory usage to the size of the Bitcoin ledger in the previous chapter.)
The system requirements to support RAIDA are so minimal, in fact, that RAIDA can literally run on a Raspberry Pi (A Rasberry Pi is a small, inexpensive computer developed for teaching computer science in schools, and for use in developing countries).
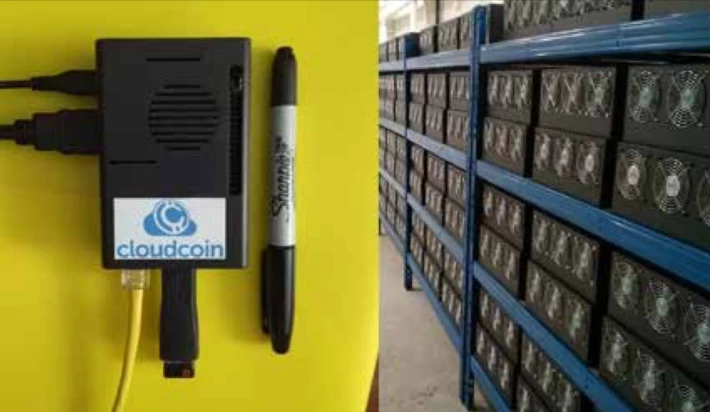

RAIDA node on a Raspberry Pi device on the left. Compare to a blockchain node on the right.
We have one RAIDA that has been running on a Raspberry Pi for months. These little servers are well under $100 each, and you can literally fit one in your pocket!
Unlike the Bitcoin network, it is entirely within the realm of possibility that the RAIDA could be run by volunteers. However, to ensure that there is money to pay the RAIDA admins, these admins are allowed to receive coins for discovering coins that have been otherwise permanently lost—one CloudCoin for every 25 found.
RAIDA clouds

Each RAIDA network is composed of many redundant servers, networks and databases that are interconnected via the Internet. Such arrangements of hardware are often referred to as clouds.
The databases are mirrored in multiple physical locations, with multiple servers to keep the cloud readily available.
Multiple locations also allow for such catastrophic failures as a meteor strike by keeping the system operational, no matter what.
Governments may try to suppress RAIDA servers some day.
It is likely that in time RAIDA clouds would become a target for thousands of highly trained hackers from around the world.
It is also likely that RAIDA would be targeted for Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks (A (DoS) attack is when hackers attempt to block legitimate users from accessing a service, usually by overloading the network or server with invalid communications.) by the worst attackers imaginable.
But with this structure, if some of the components fail or are attacked, the RAIDA system keeps going.
A self-healing system.
A fractured CloudCoin is a CloudCoin that failed authenticity on one or more RAIDA nodes. These nodes can “compare notes,” and in doing so, repair the fractured coin. This process is invisible to the coin owner.
Expanding CloudCoin
When the value of CloudCoin goes up, the entire RAIDA can be cloned multiple times. Each time this happens, the whole system becomes even more fault tolerant than before. If the value were to go up the way Bitcoin has, I can imagine the system growing to 60,000 micro servers—and still remain completely free to use.
What this all means....
RAIDA does everything that a blockchain does, only much faster, more reliably and far more efficiently.
The only thing RAIDA does not do that Bitcoin does is to track your transactions.
RAIDA is scalable. More nodes and networks can be brought on as needed to perform transactions within milliseconds. The work is distributed among more nodes rather than requiring each node to do more work (like blockchain).
Costs are paid through recovery of lost coins, so there are no transaction costs for the user. Every CloudCoin is owned by someone who knows its authenticity numbers (passwords).
However, if no one knows a CloudCoin’s password, it is considered lost. We can identify these lost coins because they have not been re-authenticated in two years.
However, RAIDA itself is only a counterfeit detection system. The data for the money is stored within the CloudCoins themselves.

To be continued..........
Sean H. Worthington PhD ABD for CloudCoin Consortium.
Resources
https://cloudcoin.global/
https://cloudcoinconsortium.org/
https://cloudcoinconsortium.com/use.html
http://www.cloudcoinwiki.com/All_About_CloudCoins
https://raidatech.com/
http://seanworthington.com/
https://t.me/CloudCoinGlobalCommunity
https://www.instagram.com/cloudcoinconsortium/
https://twitter.com/CloudCoinGlobal
https://www.facebook.com/cloudcoinconsortium
https://www.linkedin.com/company/cloudcoin
https://medium.com/cloudcoinconsortium
https://github.com/CloudCoinConsortium
https://www.amazon.com/Beyond-Bitcoin-Future-Digital-Currency-ebook/dp/B076MQCRG6