Have you wondered how a computer works, or want to build one yourself? I did too at one point and now I would like to help fellow beginners understand how a computer works. I have made this as simple and to the point, without missing out on any important details, as possible. I will sometimes refer to a computer colloquially as PC, or personal computer. They both mean the same thing. If you learn anything from this guide or still have any questions, make sure to comment down below. I will to the best of my ability answer each question. This is part one in a series, discussing mainly the basics of how computer work and what each component does, and why it is important. All data transmission in computers is facilitated through electrons going through logic gates, but this is too in depth for this guide. In the future I will make a more in depth guide of how computers work. Thanks for reading my first steemit post!
There are six essential parts that every computer needs. These are the motherboard, processor(cpu), memory (RAM), power supply, storage(hard disk drive) and the case. Each of these are very important in their own right, and a computer needs all of these parts -except for a case- in order to run. Computers also need an operating system, but in this guide I will only cover hardware. I will now explain what each of these parts does, and why it is important to the computer as a whole. To make each component better understandable, I will use a metaphor to compare a computer to a classroom. In the beginning, this metaphor may not make much sense, but as we go on, it should clear up.
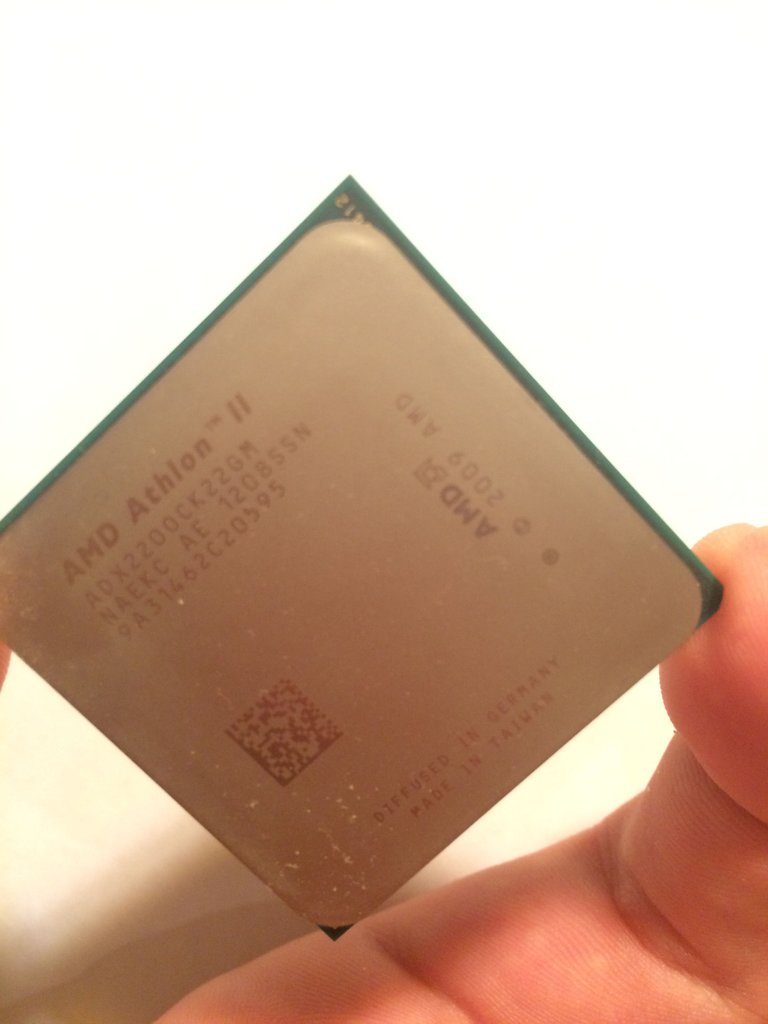
-Processor-
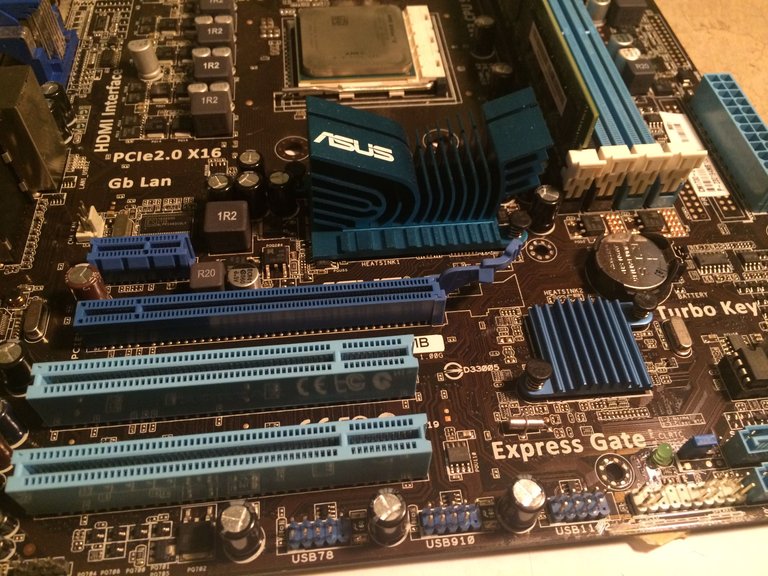
The processor, aka CPU, takes in information from the RAM and interprets the data it receives. In the metaphor, the processor is the teacher or student. It takes data from a book(the storage), copies it to the whiteboard(the RAM), and works on it. If you have a problem in your book that says "4+10= " you could probably do this in your head and wouldn't need to copy this to a white board to solve it. A computer, however, would need to copy this problem from the hard disk drive(HDD) to the ram in order for the processor to work on it. But what if you were asked what the Riemann sum was for a definite integral. You most definitely would need to write this down to solve it. A computer works the same way, just as you copy a problem from a book to a sheet of paper to interpret, a computer copies data from the HDD to the RAM to solve. The CPU connects directly into the motherboard, but it is always covered by a CPU cooler. The CPU cooler is most of the time a heatsink made of of metal with a fan attached to it. The heatsink draws the heat out of the CPU so it doesn't overheat. Remember that data in a computer is sent through electrons, and these electrons build up heat, making the heatsink necessary. The CPU connects to the motherboard through what is called a socket.
-Storage-
This kind of memory storage is called non-volatile storage, and this is because if it loses power, it will never "forget" what it has written on it. Storage originated as magnetic tape in the 1950's, went through a lot of upgrades and now is known as Hard Disk Drives(HDD's), Solid State Drives(SSD's), or Universal Serial Bus (USB) flash drives. In the metaphor, storage is a textbook. You can't directly do anything with a textbook but read it, but if you copy its information to the whiteboard, or a piece of paper, you can now work on it. A computer has to copy the data it finds from the HDD to the RAM in order to work on it similarly. Most non-volatile memory connects to the motherboard through what are called SATA ports. The SATA ports on the motherboard are shown in the following picture. 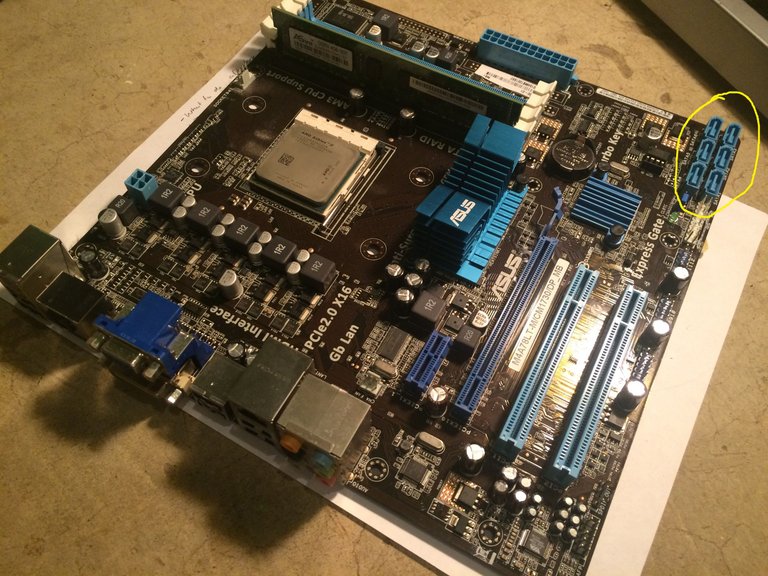
-Memory-
This kind of memory is called volatile storage, for the opposite reason as non-volatile storage. The component that is volatile storage in a computer is called the Random Access Memory, or RAM. In the metaphor, you copy the information from a textbook, to the white board in order to work on it. In a computer, the information is copied from the HDD or SSD, to the RAM for a CPU to interpret it. RAM connects to the motherboard through what are called DIMS.
-Motherboard-
The motherboard is what allows all other components to communicate with each other. The CPU, RAM, power supply, case, and storage all connect to it. In the metaphor, the motherboard is the classroom itself. It is the medium for the students to read the textbook and work problems on sheets of paper.
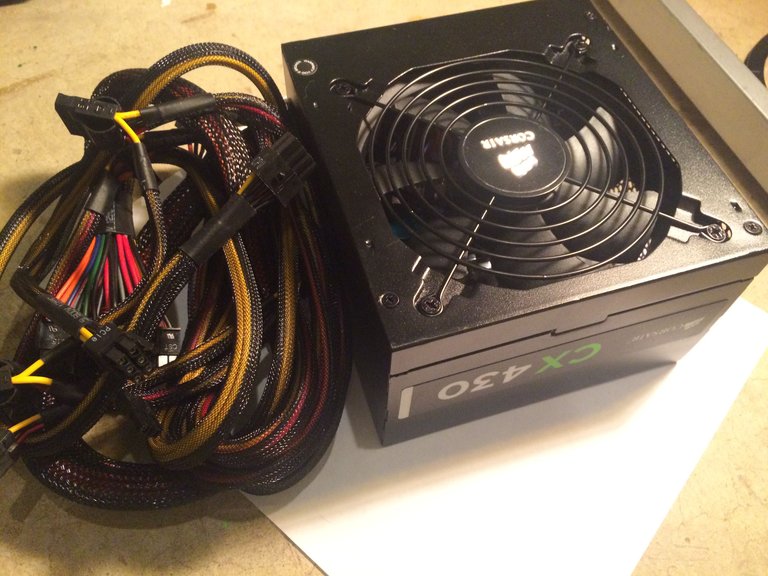
-Power Supply-
The Power Supply Unit(PSU), is what provides power to the rest of your computer. It is important that before you buy one, you calculate how much power you think your PC will consume, and buy a PSU with a power delivery of at least 200 Watts above your calculation. A good website for calculating this is http://www.coolermaster.com/power-supply-calculator/ Cooler Master's own.
-Case-
A computer case is an autological word. Saying the word describes what the word means. A computer case holds and protects all the other components from physical harm and a percentage of dust from getting into the computer. Almost all cases have a front I/O (Input and output). This means they have a power button and some USB ports, as well as a headphone jack. The front I/O also connects to the motherboard, usually along the button edge. In the metaphor, the case is the walls of the classroom.
And those are all the essential parts of a computer! If you enjoyed this guide or learned anything, please tell me about it down below. Thanks for reading my first steemit post!