Public, Permissioned, and Private Blockchains
The Bitcoin Blockchain is the distributed ledger that stores every Bitcoin transactions that have ever transpired in its history. It began with “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” the White Paper written by Satoshi Nakamoto. The code was released as open source in January 2009. The blockchain began shortly afterward when Satoshi Nakamoto “mined” the first Bitcoins. Satoshi Nakamoto disappeared from the public in April 2011.
"A purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash
That would allow online payment
to be sent directly from one party
to another without going through
a financial institution.“-
Satoshi Nakamoto
There are three types of Blockchains:
• Public Blockchain: Bitcoin is the primary example of a Public Blockchain— a large shared network that operates by a common token or coin. They’re open to anyone to join. They have Open-source code that is supported by its network of miners. • Permissioned Blockchain: Ripple is an example of a Permissioned Blockchain— They have closed-source or Proprietary code. All roles within its network are given on a permission basis. They’re also large shared systems that use a common token or coin. • Private blockchains: Private blockchains usually operate on smaller networks and do not use a token or coin. Their association is closely managed. These sorts of blockchains are used by corporate syndicates that have trusted members or company's and trade confidential private data.
Blockchain vs. Banking
We live in a world where banks and governments control every financial decision made. Banks charge a large fee for each transaction. The blockchain is a cheaper and more secure alternative to the current financial systems around the world. It is a completely decentralized and transparent currency. Thus, It does not have any central authority exercising control over it.
Blockchain is more efficient than Banking
Using the Hashcash proof-of-work algorithm blockchain transactions are verified and secured at a lower cost than traditional banking. Bitcoin transactions are recorded by the blockchain miners, and each transaction charges a blockchain fee, also called 'miners' fee. The miner transaction fees, charged to users when performing bitcoin transactions, allows the sender to declare a priority level for the transaction. The lower the blockchain fee, the lower your transaction's priority in the Bitcoin network. Miners collect the fee as a reward for maintaining the Bitcoin network.
What makes Bitcoin safe?
Blockchain solved the "double spending" problem we have with the current financial systems. Each block is securely hashed—meaning it is rendered into a cryptographic hash key. Every transaction creates multiple hash outputs, which are assigned a Transaction Identifier (TXID). _ As every miner has a real-time copy_ of the blockchain at all times and transactions are compared against the latest version before being validated. Miners compare the new TXID with the rest of the blockchain to verify available bitcoin then record the transaction to the blockchain. Hacking it is considered effectively impossible. Everything recorded to the Blockchain is made public and can be viewed on your internet browser via a "Blockcahain Explorer". So, anyone can view any transaction, but no one has the ability to know what accounts belong to who.
Power of the Blockchain
The blockchain is expected to be fast enough to power the internet of things(IoT) and is going head-on with the major financial institutions of the banking world. Blockchains are currently being developed by banks, industries, and governments worldwide. Future blockchain developments will change the way we do almost everything, making the world a more efficient place for everyone.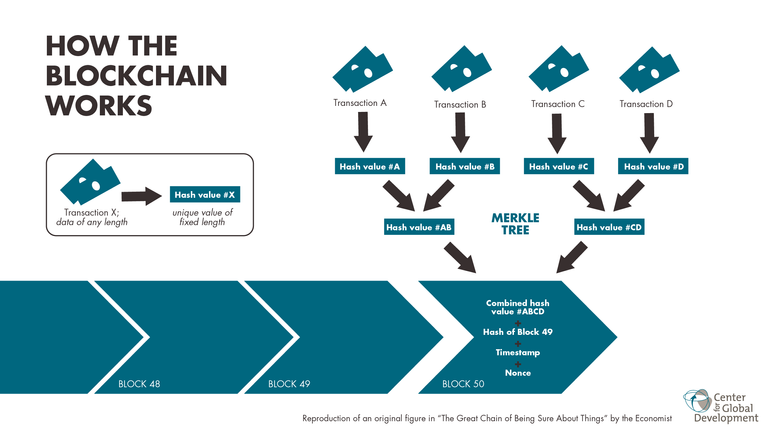
thanks for this i try to understand the blockchain technology !!!
You're Welcome! I have more informative articles ready to be posted, so check back later to learn some more. Thank You!