

1 - INTRODUCTION
''Don’t throw the baby out with the bathwater''. This is considered one of the most popular idioms in the archives of German proverbs, and in my own opinion should be considered as sound wisdom when it comes to dealing with the concept of moving from centralization to decentralization.
With the birth of the blockchain technology and the concept of decentralization came a massive revolution in the financial sector, causing majority of the general populace to see decentralized blockchain technology as the next big thing in the development of 21st century financial operations, thereby causing a massive exodus from the use of centralized financial operations, and abandoning them to the back side of the record books of financial history – a few pages ahead of Trade and Barter system.
Truth be told, the birth of blockchain technology has revolutionized the financial sector and civilization at large, achieving mind boggling feats and delivering on promises made. With respect to financial operations, blockchain technology has conquered problems once thought of as insurmountable, bringing about greater transparency in transactions through its distributed ledger technology, ensuring maximum security of transactions through encryption, improving traceability of goods and services through its audit trail, increasing the speed and efficiency of financial transactions through its single digital ledger system, and finally reducing costs of financial transactions by eliminating the need for middlemen through its smart contract technology.
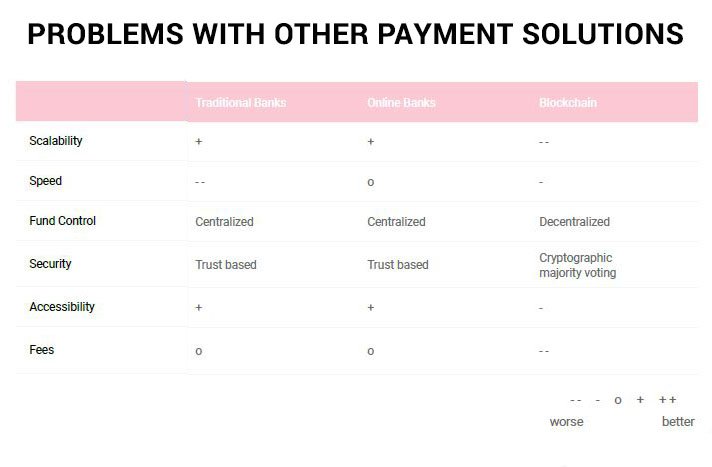
However, time and experience has proven that despite all these advantages that decentralized blockchain technology provides, there are still some short comings currently existing in blockchain platforms. The proof-of-work protocol upon which popular blockchain platforms like Bitcoin and Ethereum are built has proven to be inefficient at effectively processing large number of transactions, thereby making the system slow and congested. Centralized systems on the other hand have the advantage of speedily processing large amount of transactions, primarily because of their centralized computational power.
We can therefore conclude that it’s not wise to out-rightly abandon centralized systems just because decentralized systems have some advantages over them. The most appropriate financial system will be one that will be able to marry both systems, harnessing the advantages that they both provide, thereby being empowered to render financial services such as efficient payments solutions and exchange services. Through this solution, we will not be throwing away the baby (advantages of centralization) with the bathwater (disadvantages of centralization).

2.- PROBLEM DEFINITION
As discussed earlier, the blockchain technology is a phenomenal technology that has brought development and positive changes to the financial sector. When compared to other traditional financial systems (e.g. banks), blockchain has provided tremendous benefits in ways that traditional financial systems could never have. However, time and experience has shown that systems built solely on decentralization have some shortcomings that have hindered them from effectively providing impeccable financial services.
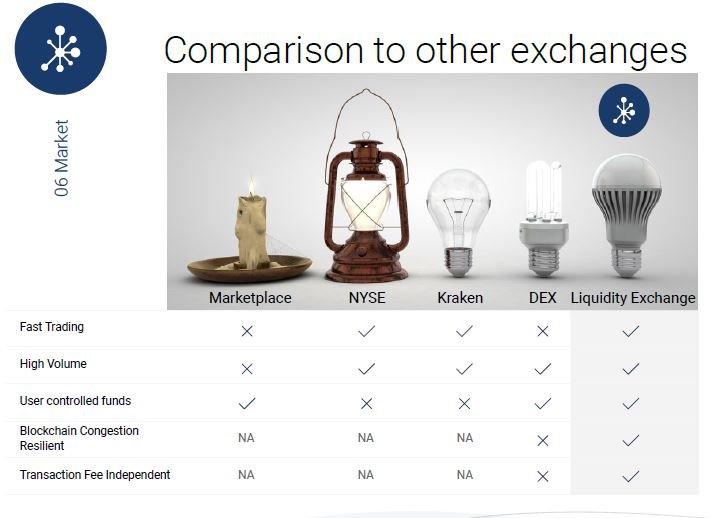
Also, some popular exchanges like NYSE, Kraken, and DEX which are either centralized or decentralized in their design, are experiencing some shortcomings which have hindered the delivery of efficient exchange services to traders.
From these, we can therefore categorize these problems under two categories:
- Challenges with Payment solutions
- Challenges with Exchanges
2.1 – Challenges with Payment solutions
My first experience with the blockchain technology was in 2016 when I purchased my first bitcoin. At that time, it took me less than 3 minutes for me to receive my bitcoin in my wallet. This marveled me and motivated me to read more about the blockchain technology. I found out about the numerous ways that blockchain technology was distorting the traditional financial systems by putting control of money back in the hands of the people through decentralization.
However, I tried carrying out a similar bitcoin transaction in 2018 and it took me close to 30 minutes to complete it. This was shocking to me. I got to realize that increase in the amount of blockchain users had made the system slower by queuing up transactions. Blockchain platforms like Bitcoin and Ethereum operate on the principle of proof-of-work, which is inefficient at handling large amount of transactions, hence leading to low scalability and queueing up of transactions.
2.2 – Challenges with Exchanges
My favorite aunt was to travel to the United States on a business trip, and hence needed to exchange her local currency for U.S dollars, since our local currency will be invalid in the U.S. It took her close to 6 hours to have her currency changed in the bank, in addition to the paper works that needed to be done. This is how slow the marketplace exchanges can be as illustrated in the image above.
For much higher fiat currency, exchanges such as the NYSE might be involved, in which case transactions can be much faster but funds are usually not controlled by the owners, but rather by a centralized body usually a government body.
Also, for digital currencies, exchanges like Kraken give traders the opportunity to exchange digital currencies, but these currencies are under the control of the Kraken exchange, which means that the moment the exchange shuts down or is hacked, users lose all their funds, as was seen in the Mt.Gox case. This type of exchanges put funds of users at risk.
Finally, for digital exchanges like DEX where funds of users are stored in personal wallets and hence under the full control of users, the funds are protected from hackers since they are stored offline. However, when the process of cryptocurrency trading is to take place, they are usually conducted “on-chain”, meaning that the transaction is prone to blockchain congestion since other traders are also making use of blockchain processing capacity. This makes transactions experience lag and delays.
From these listed problems, we can see that despite the fact that decentralized and centralized systems both have numerous advantages individually, they still have limitations when they stand alone as independent systems. There is need for a new platform that will combine the advantages of both decentralized and centralized systems, so as to increase the efficiency with which financial transaction are being carried out.

3.0 – Liquidity Ecosystem
Statistics has shown that close to 200,000 bitocoin transactions have remained unconfirmed because of the blockchain congestion experienced by the bitcoin blockchain.
The proof-of-work protocol upon which these blockchain platforms are founded is an effective protocol, but only when the number of transactions involved is not too large. Unfortunately, because of the astonishing rise in the amount of bitcoin users and hence number of transactions, this protocol has not been able to scale effectively, hence leading to congestion of the blockhain. From this, we can conclude that proof-of-work protocol might be founded upon sound reasoning, but when it comes to dealing with large number of transactions, it depreciates in efficiency. There is therefore need to replace this proof-of-work protocol with a more efficient protocol that will be able to handle large amounts of transaction, and avoid congestion of the blockchain.
Some intellectually sound solutions have been proposed to solve this blockchain congestion problem, which include:
- Totally changing the proof-of-work consensus
- Sharding (Partitioning of the blockchain)
- Off-chain processing of transactions
It is upon the off-chain solution that the Liquidity ecosystem is built.
Liquidity Ecosystem is an Ethereum based community, comprising primarily of the Liquidity Network and the Liquidity exchange (which is built on the Liquidity Network). This ecosystem is founded upon two main pillars:
- The Liquidity hub NO-CUST (which is a short form for non-custodian concept)
- Revive (concept based on the off-chain processing solution listed above)
3.1 – Liquidity Network
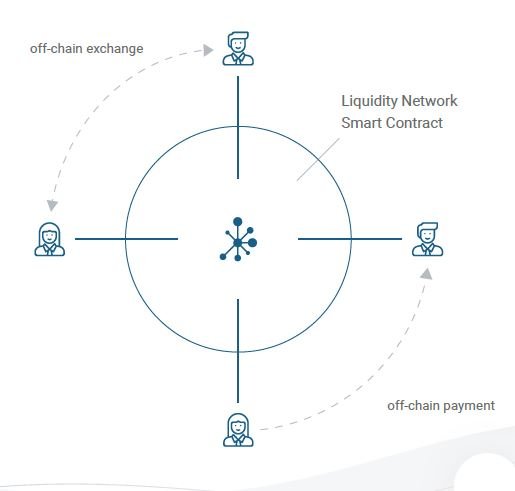
By definition, the Liquidity Network is a non-custodial, off-chain payment source that can efficiently enable millions of users make instant payments and currency exchanges, within a highly secure universal payment hub. In other to provide a solution to the congestion problem experienced in other blockchains, the Liquidity network operates with a simple routing design that functions on the principle of off-line hub creation and operation, enabling members of a hub to transfer funds to other members of that hub, at blazingly fast speed and at cheap transaction fees.
To better understand the importance and role of hubs in the Liquidity network, let us take a look at the architecture.
ARCHITECTURE
If you’ve ever made a transfer of bitcoin from yourself to a receiver, you will realize that it’s only the both of you that have access to that transaction and the funds in that transaction. The sender and receiver are isolated from every other person on the blockchain. This should naturally not cause any delay, however, the delay comes into play when the transaction is to be processed. The transaction is not processed in that isolated connection between the sender and receiver, but rather in the blockchain which is also where every other transaction from various other connections are processed. This is where the congestion and delay comes into play.
Since the delay is with the processing of transactions in the congested blockchain, why don’t we transact off the blockchain (off-chain), but yet store funds on the blockchain for security. Also, rather than having just two people occupy one connection, why don’t we have a hub where two or more people can securely have access to each other’s funds? This is the reason for creating and participating in universal hubs where transactions are conducted off-chain, but yet funds stored securely on the blockchain.
We can hence conclude that this process makes transactions faster (because they are conducted off-chain away from the congested blockchain), of lower transaction fees than on-chain transactions (since funds are instantly accessible to thousands of hub members as opposed to funds locked between just two people), and highly secure (funds are stored on the blockchain)
FOUNDATIONAL PROPERTIES OF LIQUIDITY NETWORK
Every member of a hub has sole control over their funds, hence decentralization based. Each member has his/her funds locked in their private wallets, and each of them alone possess the private keys to those wallets. This is made possible through the security that blockchain technology makes available. Neither the hub operator or any other person can have access to funds, hence eradicating the possibility of fund theft.
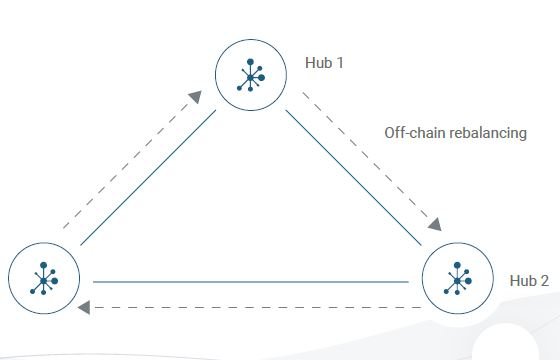
Multiple hubs within the Liquidity network can be connected to each other, so as to facilitate off-chain payment between people of different hubs. This brings about redundancy in the system, providing alternatives to the system’s operation.
A hub operator is the administrator of a hub. He/she can decide which payments go through in the hub. He/she can allow or stop a payment from going through, but cannot have access to funds of members. In the case of a payment being cancelled by hub operators, members can withdraw their funds from the hub’s smart contract and join another hub.
REVIVE
In the foundational properties of Liquidity network, we talked about the interconnection of hubs. With hubs connected, there has to be a mechanism to ensure rebalancing of the balance of the various channels involved in interconnected hubs. This is priority so as to ensure a balance of the entire system.
This is where Revive comes into play. According to the Liquidity whitepaper, Revive is the first solution that allows an arbitrary set of users in a payment channel network to securely rebalance their channels, according to the preferences of the channel owners. For more information, you can check more information on Revive, it has been published in a Tier 1 Academic IT-Security conference (CCS’17). Here
All operations of Revive are conducted off-chain, so as to increase the scalability of the blockchains. It is only in the case of disputes that on-chain blockchain resources are consulted.
Finally, off-chain transactions are separated into two categories:
2-party payment channels (Consisting of Unidirectional, Bi-directional, Linked payment, and 2-party payment hubs)
N-party payment hubs
3.2 – Liquidity Exchange
Built upon the Liquidity Network, the Liquidity Exchange is a non-custodial off-chain exchange designed never to hold funds while performing atomic off-chain exchange.
Taking advantages of the strengths of both decentralized and centralized systems, Liquidity Network is able to create an exchange that is fast and yet highly secure. Centralized exchanges have high speed of operation primarily because of their centralized computational power, while decentralized exchanges have very high security because of their blockchain foundation.
3.3 – LQD Token
The Liquidity token (LQD Token) is the customized currency for the Liquidity Network. Unlike other platforms that limit users to using only platform customized tokens, the Liquidity token is not a restrictive token. It is a means for platform users to pay for auxiliary services. It is a currency that gives platform users access to premium services on the Liquidity network. These services include channel monitoring, service level agreement (users will pay hub provider some LQD tokens so they can guarantee a particular high number of transactions per second) and so on.
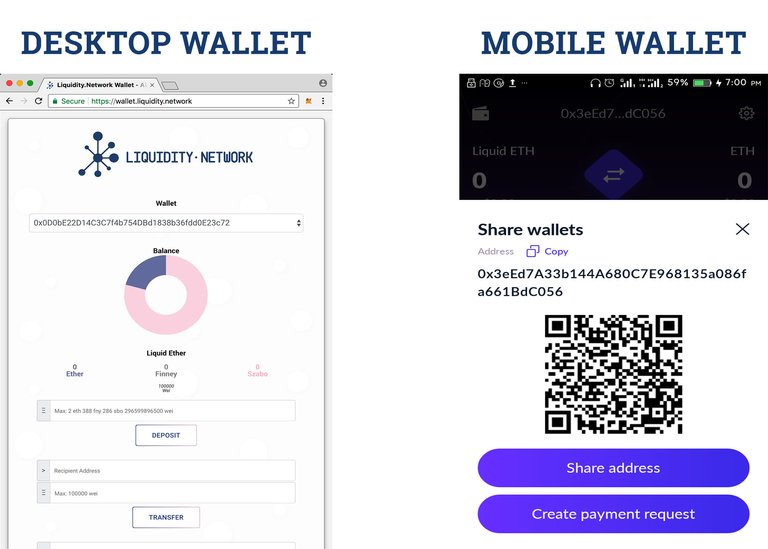
3.4– Liquidity Web and Mobile wallet
Apart from the Liquidity Exchange, there are other applications of the Liquidity Network. These applications are built both for mobile and for desktop. The image shown are mobile wallets and desktop wallets built on the Liquidity network.
3.5 – Comparison between Liquidity Network and other payment solutions, and between Liquidity Exchange and other exchanges
The following images give a graphic illustration of how Liquidity Network compares with other networks, and how Liquidity exchange compares with other exchanges.


4.0 – APPLICATIONS AND USE CASES
4.1 –Application and Use case in instant ecommerce trading
Application
Ecommerce is the sale and purchase of goods and services through the vehicle of the internet. For ecommerce to be effective, there has to be a viable and efficient system of payment for goods and services. The delay in confirmation of transaction in the major cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin and ethereum has tremendously reduced the possible usage of these cryptocurrencies as a means of payment.
Through Liquidity network’s off-chain processing of transactions, the possibility of using cryptocurrencies as a medium of payment for ecommerce transactions has been tremendously increased. The speed with which transactions are processed on the Liquidity network makes payment processes fast and reliable.
Use case
Shopaz is an ecommerce website owned by Anna. She has enjoyed monopoly of the ecommerce business in her country. To stay ahead of the curve, she decides to incorporate cryptocurrency payment system into her website. The problem is that most of the popular cryptocurrencies experience congestion of transactions, hence leading to delays and discouraging her from the idea.
On finding out about Liquidity Network and its ability to speedily process transactions through its implementation of off-chain processing of transactions, she implements the Liquidity Network on her websites and begins to accept payments using this blockchain. This bold move attracts more customers to her website because of the fast and secure means of payment that Liquidity Network makes available.
Anna is happy she is able to move her business to the next level, staying ahead of the curve.
4.2 – Application and Use case on cryptocurrency blog websites.
Application
An exchange is a platform where currencies can be exchanged one for another. Majority of the cryptocurrency blogs have links on their websites to exchange platforms where traders can exchange their currencies. However, exchanges that currently exist keep custody of funds of users, and this comes with the risk of theft due to hackers. This is the situation that was experienced in the Mt.Gox hack, where millions of dollars’ worth of cryptocurrencies were lost. This has hence given those blogs containing the links to these exchanges negative publicity because of the failure of these exchange.
Through the Liquidity exchange founded upon the Liquidity network, bloggers don't have to be worried about failure of exchanges linked to their blogs, since the Liquidity exchange is not in custody of funds of traders, thereby providing secure exchange services, even as these services are conducted off-chain to handle congestion experienced in other exchanges.
Use case
Phil is a cryptocurrency blogger who wants to include a link to an effective exchange service on his website. He is not sure of the exchange to use on his website. He does some research and finds out that one of the primary challenges majority of the exchanges have is their being prone to hack, primarily because funds of traders are in the custody of exchanges. He does not want his website visitors to experience what exchanges like Mt.Gox experienced, and hence is discouraged from carrying on with his plan.
On finding out about Liquidity Exchange, Phil is delighted. He immediately links the Liquidity Exchange to his website, thereby providing non-custodial, off-chain exchange services to his website visitors.
This added property on his website encourages more people to visit his website, providing access to seamless, fast, and safe exchange services.

5.0– MY VIDEO ON LIQUIDITY NETWORK
6.0 – CONCLUSION
The blockchain technology is a revolutionary technology. Upon it, various platforms have been built that have provided solutions to various life challenges, especially in the financial sector where cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and ethereum have made the transfer of money cheaper and faster.
But unfortunately, decentralized blockchain technology alone is insufficient at proffering fast and safe payment and exchange services to traders, hence the need for a fusion between centralized and decentralized operations.
Liquidity Network and Exchange, being non-custodial off-chain services aim at proffering solutions to this insufficiency, by marrying the advantages possessed by centralized and decentralized systems, thereby providing non-custodial, off-chain payment and exchange services to traders.




The Liquidity Network team is made up of professionals who are highly experienced in the field of security, performance, and privacy of proof of work technology of blockchains. With a team of such pedigree, you can’t expect anything lesser than the best.

Liquidity Network has acquired a number of venture capitalist funding as shown in the image above.
If you need further clarification on any issue with regards to Liquidity Network, just do well to drop your questions in the comment section, and I will promptly attend to it.
For more information on Liquidity Network, you can visit any of the following channels:
. Liquidity Network Website
• Liquidity Network Wallet
• Liquidity Network WhitePaper
• Liquidity Network NOCUST Paper
• Liquidity Network REVIVE Paper
• Liquidity Network Apple App Store (IOS)
• Liquidity Network Google Play Store (Android)
• Liquidity Network Twitter
• Liquidity Network Github
• Liquidity Network Blog
To participate in the contest, visit this link
Here is my Twitter link
lqd2019
lqdtwitter2019






Sponsored Writing Contest!
This post has been submitted for the @OriginalWorks You can also follow @contestbot to be notified of future contests!