Information technology and data transfer industry has greatly evolved over the years as a result of the births of the computer and the internet. However, in a bid to create a seamless stream of data creation, processing, delivery and then the subsequent use of the accumulated big data, the Internet of Things was made mainstream in 1999.
The Internet of Things is a network of physical objects – vehicles, machines, home appliances, etc, which uses sensors and APIs(Application Programming Interface) which enables the connection and exchange of data over the Internet and further processing of such data in the cloud to deliver business insights and enable better operation of such device without physical human intervention.
Increasing number of organizations in various industries are using IoT to improve their decision-making and increase the value of the business, operate more efficiently and better understand customers' needs as to deliver enhanced customer service.
Interestingly, any physical object can be transformed into an IoT device if it can be connected to and controlled by the internet(IoT).
The ‘thing' in the internet of things can be a person with a heart monitor implant, a jet engine filled with thousands of sensors collecting and transmitting data back to make sure it is operating efficiently, a farm animal with a biochip transponder, a lightbulb that can be switched on using a mobile app, an automobile that has built-in sensors to alert the driver when tire pressure is low. It can as well be any other natural or artificial object that can be assigned a IP address and is able to transfer data or communicate over a network.
Many companies are organizing themselves to focus on IoT and the connectivity of their future products and services and according to recent data from Juniper Research, the total number of connected Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and devices is expected be up to 50 billion by 2022.
Problems associated with IoT
Connectivity Issues
It’s just a matter of time before users start to experience significant bottlenecks in IoT connectivity, efficiency and overall performance.
Currently, the IoT utilizes a centralized, server-client model to provide connectivity to the various servers, workstations and systems and it seems okay for the number of devices being connected but what happens when billions of devices are all using the network simultaneously? It will result in a major crackdown if the scalability issue is not addressed.
Moreover, the centralization of IoT data creates barriers for data sharing and circulation between the big players in industries.
Security
Default security on most connected devices across the world remains weak; it is certain that cyber criminals will increasingly use AI and machine learning to establish automated attack systems that learn how to defeat security barriers on the go. IoT devices and autonomous vehicles will be the subject of DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks.
Moreover, IoT devices are vulnerable to cyber attacks due to their constrained computational resources. This is due to the fact that these devices are different from PCs, so presently, we cannot install any antivirus software on them and the sophisticated methods can would have been trusted are neither not efficient.
Privacy
Hacking is not only a security breach but a violation of users' privacy. A recent study at the University of Glasgow indicates that consumers are largely not satisfied with the lack of privacy the IoT allows them. Users have grown more aware of the extent of cyber-surveillance, thus, they have begun taking their privacy more seriously, therefore, they are demanding autonomous control over their data.
Cloud Infrastructure
The computing cloud is structured in a way that fast response and real time interactions between increasing number of devices is not feasible. Thus, the cloud is laden with the problem of scalability and speed.
No business model
There has not been any large scale clarified model of an IoT business application that has utilized the huge data resources provided by the IoT established since the inception of the IoT.

The Blockchain and IoT
Due to the increase in number of sensors in vehicles, factory machinery, buildings and city infrastructure, the Internet of Things is evidently in search of a secure and automated way of enabling a mesh network for transactional processes and exchanging data in real time to speed transactions.
The blockchain appears to best fit that bill.
Why?
As the Internet of Things applications are by definition distributed it’s only normal that the DLT(Distributed Ledger Technology), which blockchain is, will definitely play a role in how devices will communicate directly with each other. This will be by keeping a trail(that is, a ledger) of not just devices but also the way they interact, their states during such interactions and in the cases of tagged goods, it can also keep a record how they are being handled.
The electronic, distributed ledger technology (DLT) -The blockchain, offers an automation software that eliminates escrows called smart contracts. This could offer a better supply chain by providing a standardized method for accelerating data exchange and enabling processes between IoT devices by removing the middleman, which in this case, is the server. The server acts as the central validator or processor for requests and other traffic among IoT devices on a network.
With the blockchain, smart contract software, self-executing code that could be embedded on each IoT chip, to determine what action takes place when a condition is met. Those actions would only be executed when an incoming transaction authenticated. So with this, no central agency or server is needed to tell each node when to do something. That is, with a distributed blockchain IoT network, the IoT devices on a peer-to-peer, mesh network could authenticate and execute transactions based on pre-determined rules – without a central server.
Blockchain technology could also improve security and enhance privacy through decentralized interaction and data exchange. This is possible as the blockchain could bring scalability, distributed security, privacy and trust to IoT devices, applications and platforms. This could be achieved as the blockchain technology uses hashing algorithms to create an untouchable record of transactions, and that information can be encrypted and only accessed through public and private keys.
Moreover, blockchain ledgers also reduce the time needed to complete IoT device information exchange and processing time.

Edge Computing and IoT

Edge computing is the practice of processing data near the edge of your network, where the data is being generated(that is, the device or local computer) instead of in a centralized data-processing warehouse. It is a distributed, open information technology architecture that enhances, decentralized processing power, enables mobile computing and support Internet of Things (IoT) technologies.
Edge computing enables data-stream acceleration which includes real-time data processing without latency. It also allows ‘almost-instantaneous’ response of smart applications and devices to data as its being created; eliminating lag time. It’s been proven at this point that traditional cloud computing architecture cannot provide the real-time response requested in many application scenarios thus the edge computing concept is critical for technologies such as driverless trucks and has equally important benefits for business too.
Edge computing eliminates costs and ensures that applications can be used effectively in remote locations by allowing for efficient data processing, such that large amounts of data can be processed near the source, reducing Internet bandwidth usage. It also enhances primacy and security for sensitive data by enabling the ability to process data without ever putting it into a public cloud.
Juniper claims that a substantial part of the estimated 46 billion industrial and enterprise devices connected in 2023 will rely massively on edge computing. This is because the massive growth in IoT connected devices over the next four years, is driven mainly by edge computing services.
Impact of Edge Computing and Blockchain
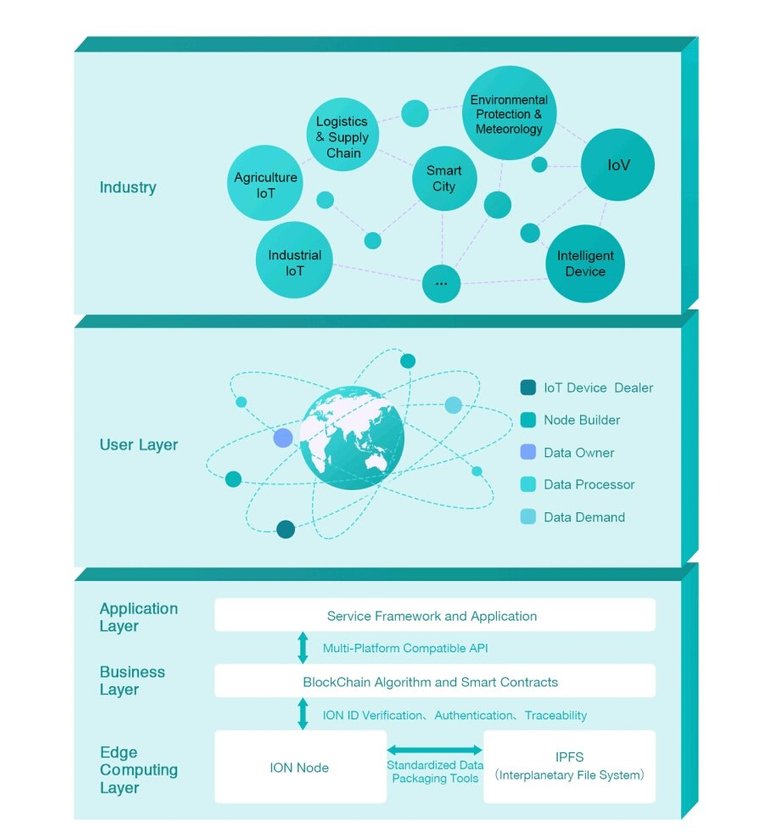
Using the edge computing on the blockchain for Agriculture IoT , Industrial Internet of Things, Internet of Vehicles(IoV), Smart Home technologies, Smart city, Logistics and Supply chain and several other IoT areas is going to decrease the network feedback latency, reduce cost, improve the user experience and significantly increasing the amount of use case scenarios.
Although, combining the blockchain and edge computing always causes limited computing ability and energy supply due to the blockchain mining process. Well, that’s where IONChain comes in.

IONChain; A lethal combination of the blockchain and edge computing.

IONChain is a platform that builds an economic ecosystem that enables the deployment, interaction and automation of IoT devices in a secure, fast and reliable way through the combination a stable blockchain architecture with edge computing technology embedded in various smart devices.
IONChain focuses on ensuring data security and help facilitate data circulation, trading and sharing. IONChain also hopes that with the decentralized blockchain technology and Edge computing, it will disrupt the barriers between IoT devices and platforms and establish a connection with IOT network nodes of any type or scale. With IONChain, all IoT device manufacturers, IoT constructors, data owners and requestors will be able to take something within the IONChain network to form a complete cycle of IoT business.
Utilizing the features of edge computing concept, IONChain introduces the idea that ‘every device is a mining machine”. machine'.
This implies that every IoT device connected to IONChain will be able to mine and receive the precise calculated rewards through the Ionization algorithim.
The rewards will be meted out according to the functions performed by each device, the data volume time length of terminal controlled, time length of data collection, areas covered by terminal, etc.
Although, IoT devices can sense, interact and exchange information with each other to achieve a certain goal of the systems like in healthcare, smart transportation and manufacturing etc. However, presently, IoT devices are low-powered and geographically distributed. This causes limited computing resource and energy supply to IoT devices and has become major barriers when blockchain is applied to IoT systems specifically because of the mining process. Now that’s where IONChain comes in, it incentivizes all the IoT devices and integrates them to create enough power for the whole system.
IONChain ‘One Device, One Code, One Coin' Vision
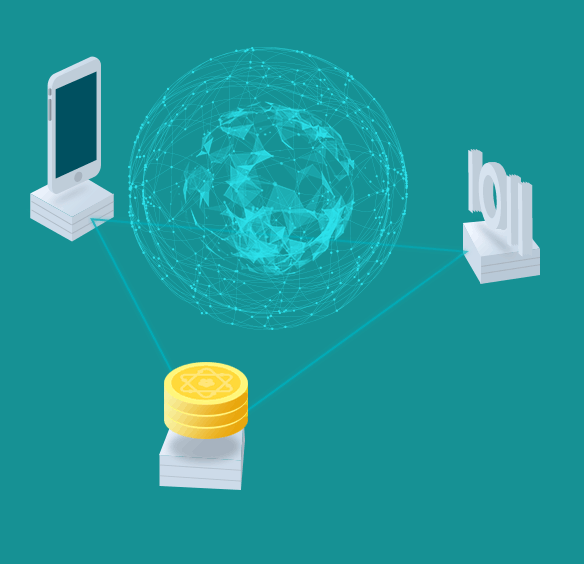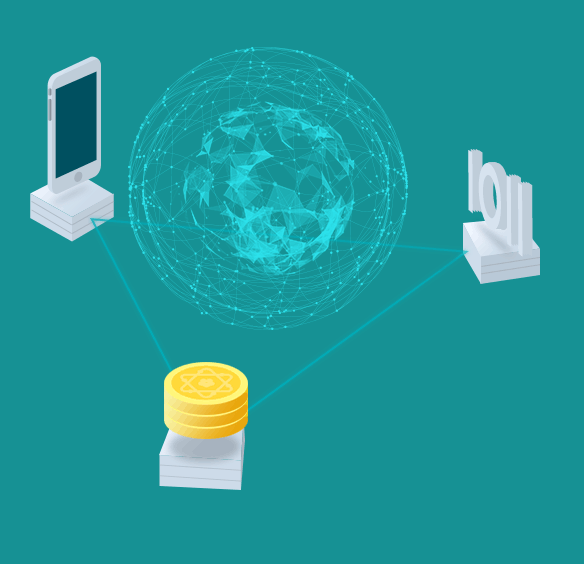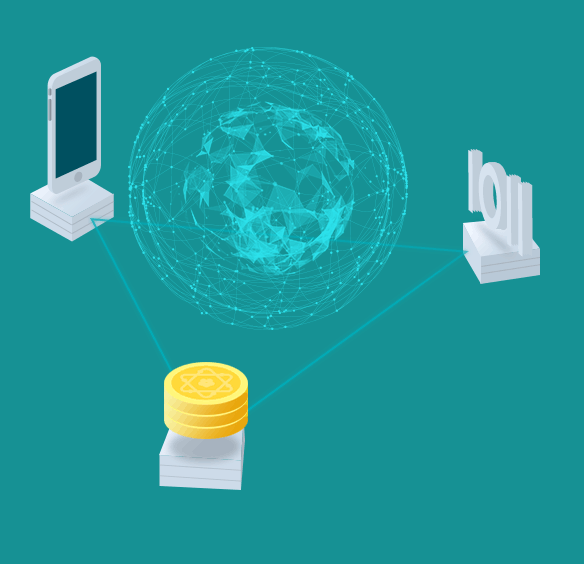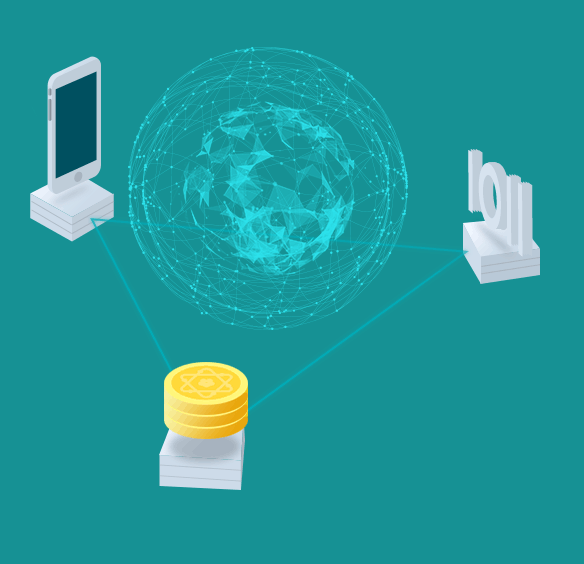
Due to the current IoT structure, IONChain was built around the premise of integrating the current IoT hardware and infrastructure thus, the IONChain team invented a concept called IONChain invented a concept called “One Device, One Coin, One Code”
“Device” stands for all intelligent IoT devices connected the IONChain network, “Coin” stands for the IONC token and “Code” is the unique identification code for the IoT devices inside the IONChain network. This identification code is embedded into the hardware of the IoT devices to stamp the data, all through a cryptocurrency(IONC) that allows the operations in IONChain. This is to build a relationship with device manufacturers and thus integrate identification codes in all smart devices, which will then act as an identifier in the IONChain network, therefore making all devices secure and standardized.
Interestingly, this feature coupled with the immutability of records on the IONChain distributed ledger enabled by the blockchain makes all the data unique, unchangeable, reliable and therefore effectively traceable.
IONChain IPFS (Inter Planetary File System)
IONChain introduces the IPF system to allow for the distributed and encrypted storage of IoT data in order to resolve the problem of friction between data block volume and transaction speed. This feature will give the system the ability to handle massive volume of IoT data in the future; this is an additional layer of protection for the data security.
Private keys are also employed to allow access to only authorized users. Changing or stealing data is made really difficult as the security of IONChain is ensured by the trusted combined computing power of all the mining devices in the system.

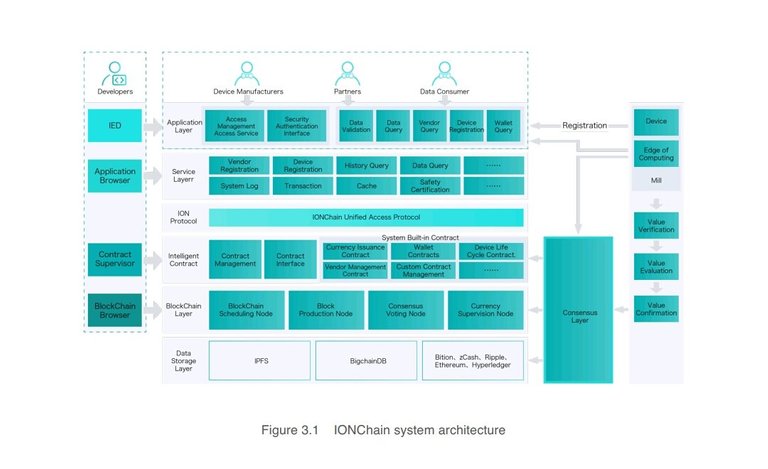
IONChain Architecture
The visions of IONChain ecosystem cannot be achieved if the current combination of the value creation and value transfer is allowed to stay. Thus, the IONIZATION algorithm was developed for IONChain, and it was built to disrupt the value creation and value transfer union.
The IONIZATION algorithm was built from the concept of ions formation. Similar to the formation of ions concept, the IONIZATION algorithm separates two core functions of the blockchain - value creation and value transfer. IONChain algorithms are designed to enable every IoT device interoperated on the network to become a mining machine; allowing them to constantly create value. However as the IoT devices come in all types and forms, the value created is varied depending on the device type and function.
Nevertheless, after the separation has been successfully made, the value creation layer is laden with the responsibility of creating the value. Each type of IoT device will have a specifically tailored algorithm designed, so that, like the ions after ionization, the value created by different IoT devices in the IONChain network can be mixed into new types of consensus algorithms that will ‘translate’ the value generated in different scenarios into the unified standard expressed in IONC coins -the standard across the IONChain platform.
So with this, the value transfer layer gives way for all users on the IONChain ecosystem to freely transfer value within the IONChain system.
IONChain Value Generation Process
The Value generation layer is a combination of IoT devices and Edge Computing Center.
With IONChain, all devices are embedded with unique identification code which contains the manufacturers information, device identification and other useful information. These information are then kept within the device and encrypted with zero proof algorithm. These devices transact through a customized smart contract called the IMQTT protocol, which is, the contract initiator can seamlessly choose the manner in which these information are shared.
IONChain uses the edge computing technology to support the weak computing capability of IoT devices through the Edge computing centers which boost their computing capabilities as intermediary devices. Due to the limited computing abilities of the IoT devices, it is hard to accurately calculate the value created by each device, however, the IONChain protocol uses the Data Quality proof and Time Lapse proof through the mining machine to do so after being updated by the independent IoT devices.
However, the value generation layer can be divided into four (4) layers of system architecture viz; value creation, value verification, value evaluation and the value confirmation.
Value Verification
This is very similar to consensus algorithm used in other public and private blockchains. This layer requires participating nodes to agree to the value generated, as any contradicting response from any node means that the value will be returned as invalid, but if successful, the value is moved on for evaluation.
Value Evaluation
This layer serves as a complement to the preceding process and it completed by the succeeding processes. It adds an extra level of protection tothe IONChain system, ensuring that malicious attacks like double spending are kept at bay.
Value Confirmation
This layer converts the processed value into a form of digital currency and passes it on to the transfer aspect of the system.
Value Transfer in IONChain

This is divided into six layers in the system architecture which are Application layer, service layer, IONChain protocol layer, smart contract layer, blockchain layer and the Data Storage layer.
Application layer:
This a regular interface where devices request access to the IONChain ecosystem. It also interoperates essential Application Programmable Interfaces(APIs) and Plug-in features which allows the whole platform and users to safely and easily interoperate new devices and elements.
Service layer:
This is simply a technical element that ensures the smooth management of internal modules or components within the IONChain network.
Protocol layer Source:
This feature enables the IONChain platform to achieve its goal of interoperating various devices. This is a standard protocol that allows integration of different external protocols to create a unified protocol for third party applications.
Smart contract layer:
This layer of smart contracts are connects the blockchains with the various applications on IONChain and handles all smart contracts operations. Amazingly, this will see that data trading will not only revolve around humans and machines alone but around machines and machines too.
More information on how this works can be seen in page 22 of the whitepaper, the link is provided at the end of the article.
Blockchain layer:
This is the nucleus of the IONChain ecosystem. This uses the IPOS algorithm, which is an upgrade from the traditional PoW or PoS consensus. This new IPOS mechanism chooses the block producers in a more secure way, also this consensus algorithm also allows the blockchain to keep operating even when most of the block producers are temporally unavailable.
This consensus makes IONChain gain more reliability and security.
More information on how this consensus works can be seen in page 23 of the whitepaper, the link can be see at the end of this article.
Data storage layer:
This is a storage layer for IONChain. It has two methods which are IPFS(which was earlier explained) and the “BigChainDB”. The BigChainDB is aa database for blockchains, which will help IONChain with research capabilities for data related to business that are using the IONChain network.

The IONC coin
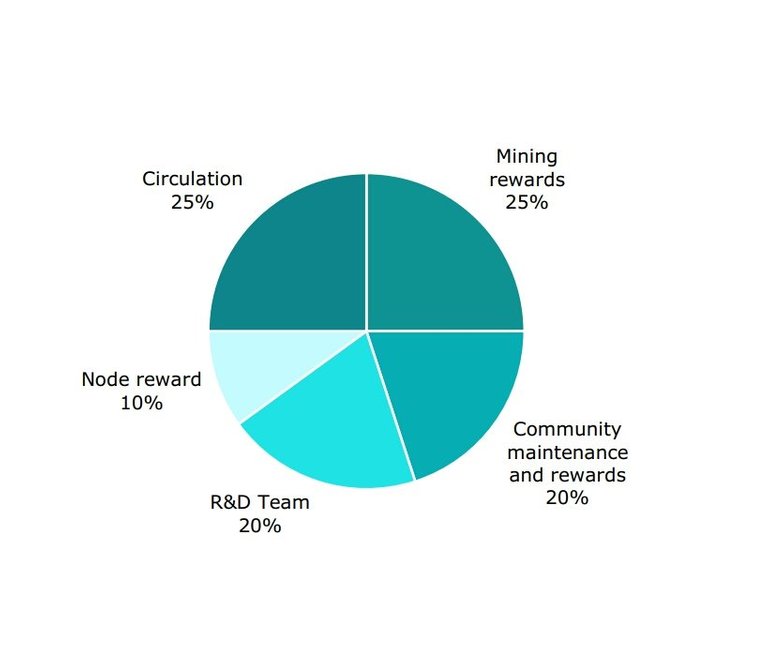
IONC is the official token of IONChain that will be used within the ecosystem. Presently, the maximum supply of IONC is 800 million which will be released gradually for 20 years. Only after two decades will administrative committee elected by IONChain users using the consensus mechanism will decide whether to re-issue IONC tokens based on the growth and net activities on the platform.
On the IONChain ecosystem, the IONC coin, formerly an Erc 20 token will serve as an utility token. It will serve several purposes, namely;
a) Rewards for the IoT devices used as miners;
b) The longer you hold the tokens, the bigger your chance to be elected as the IONChain council member, subject to the Constitution and requirements therein;
c) Compensation for the cost of running data search, statistics and smart contract analysis. Nodes running smart contracts will get awards accordingly;
d) As the fuel for running DAPP on the ion chain, the node running the API called by DAPP will receive the reward corresponding to the running consumption of API;
e) As a transaction fee for transferring the IONC currency between accounts, the billing node award is paid accordingly;
f) Each IONC coin can track its origins, and can save and trace part of the data through the IONC currency;
g) nodes responsible for the communication between IONs (access to IoT devices) on IONChain, and accounting will get corresponding awards;
.h) R&D expense for the developers is a compensation paid by IONC users.
IONC Token Economics

Synopsis
On IONChain, the problems of the IoT are precisely and individually solved. The use of edge computing technology and blockchain eliminate the IoT industry issues of privacy protection, security, latency and the shackles of the cloud computing architecture, lack of interoperating amongst devices and platforms and most importantly, IONChain provides infrastructure to utilize a myriad of IoT which now brings to limelight, numerous feasible business models of the IoT. To shed more lights on the IONChain birth of a new era for the IoT, IONChain provides cross-device compatibility, peer-to-peer communication, IPFS (Inter Planetary File System) and BigChainDB file system to help data research requirements, customizable smart contracts, devices to participate in the mining process, amongst others.
The token, IONC will incentivize self interested small or medium enterprises or even individuals to join IoT projects and push forward the development of IoT facilities to enable the project reach mass adoption.
IONChain provides a global standard for which dApps can be developed, thus easing development and deployment and providing a basis for every type of device to be developed, which enables interoperation with all devices on the network. This is create a seamless world of interaction for all aspects of the IoT for the first time and cause a mass adoption.

Use Cases
- Pharmaceutical Companies
By law, pharmaceuticals are required to be shipped and kept in temperature-controlled conditions, and data about that process is required for regulatory compliance. Since the process for tracking drug shipments is highly fragmented, instead of pharmaceutical companies paying huge sum of money to supply chain aggregators to collect the data along the journey, their owners can use IONChain. Devices which the drugs are stored can be implanted with IONChain code and data throughout the journey is collected to meet the regulatory standards.
IONChain smart contracts can be used to track and manage pharmaceutical supply chains. Nobody will be able to tamper with the records as they are recorded on the blockchain and the private keys are the only access way to it.
- Automobile Manufacturing Plant
In automobile manufacturing plants, as soon as a certain part arrives, that part(node) will alert other parts of it’s arrival, when the other parts confirm it’s arrival through smart contracts, then the new node would be permitted to begin doing its work. Thus, all the needed parts will on their own accord, move for assembly without human intervention. The beauty of this is; there will be no latency and the data accumulated along these processes can be used for further research or improvement purposes.

IONChain Sites and Resources
IONChain Website
IONChain Bitcointalk Explanation
IONChain Whitepaper
IONChain Youtube
IONChain Twitter
IONChain Medium
IONChain LinkedIn
IONChain Github
IONChain Steemit
IONChain Telegram

Watch my video about IONChain below

Team
.png)
Partners

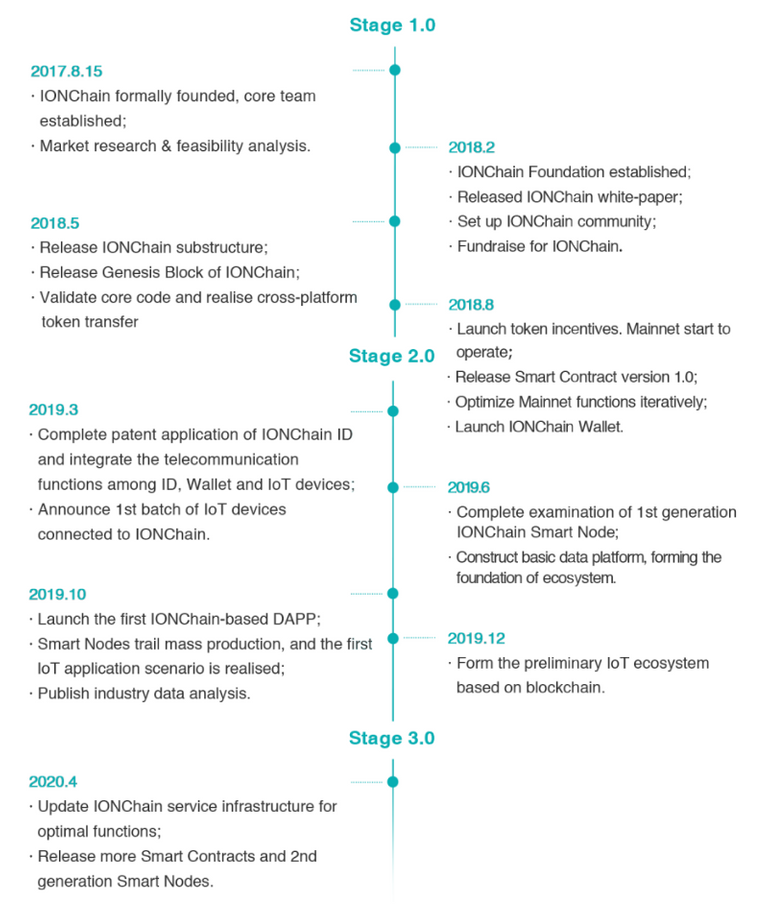
Roadmap

here to check it out.This is an @originalworks contest. Click
Note: All pictures or media without sources used herein are all sourced from the sites of IONChain and are licensed for use in this contest.
Twitter link:
ionchaintwitter
ionchain2018


Sponsored Writing Contest!
This post has been submitted for the @OriginalWorks You can also follow @contestbot to be notified of future contests!
Hi @rexdickson, thank you so much for your response, and our team truly enjoyed reading your interpretation. May you give us the consent to repost your article on our blog? Thank you very much! IONChain team.