Consensus Protocols Overview
Consensus protocol refers to the method by which a blockchain verifies and adds blocks. In an ordinary centralized organization, decisions are made by a single leader or even a board, but because blockchain is decentralized, consensus mechanisms are necessary to determine and confirm the one and only version of the truth in regards to the transactions. In short, consensus allows the network to agree on a single state of the blockchain.
There are a variety of methods through which the truth is determined. First we’ll cover Proof of Work (PoW) as the first and most common consensus protocol introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto in Bitcoin. Through this method, miners use supercomputers to solve cryptographic puzzles in order to add transaction blocks. However, this method requires an immense energy consumption.
Proof of Stake algorithms were designed to overcome this particular disadvantage of PoW, also used for a public blockchain. Instead of miners and puzzles, a validator invests cryptocurrency as a stake to buy proportionate block creation chances. The more you invest the better your chances, paid in processing fees with no new coins mined in the process.
Delegated Proof of Stake allows coin holders to use their balances to elect witnesses that stake blocks and add them to the blockchain, with voting power determined by cyber wealth.
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance is a permissioned consensus protocol, with no anonymity. In this protocol, a decision is determined based on the total decisions submitted and requires less expenditure of energy compared to proof of work.
Now the association between consensus protocols and transaction speeds is that depending on the form consensus, transactions can be processed either faster or slower thus determining TPS. With PoS, the system provides faster processing of transactions and also consumes less energy and less hardware. Some systems use a combination of consensus models.
What is TPS and why is it relevant?
TPS stands for Transactions per second. When talking about how it is used, you can think of the amount of time it takes to get from one wallet to the other, the confirmation time. The amount of transactions per second is a key figure in determining the scalability of a particular cryptocurrency. Transaction speeds may vary due to network congestion and the fee provided when making the transaction.
Top Company/ Cryptocurrency Tested Transactions Per Second
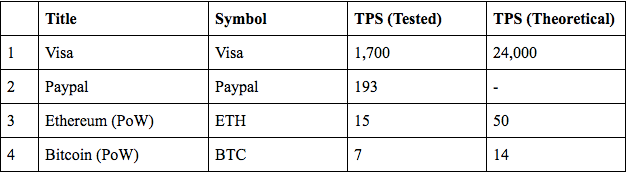
TPS refers to the number of actions performed by certain entity per second.The development of transaction rates capable of scaling to real-world volumes is an important area of research for cryptocurrency technology.