
Monetary organizations have financed the disturbance of incalculable enterprises in the course of the most recent 30 years; they have a thought of what a progressive innovation can do to static officeholders.
In this way, to remain in front of progress, banks have been proactive in setting up R&D labs, building test focuses and building up associations with blockchain designers to completely comprehend the progressive capability of the innovation.
Money related foundations were the first to plunge their feet in, however the scholarly world, governments and counseling firms have likewise contemplated the innovation.
The greater part of this work is, obviously, notwithstanding what the business visionaries and designers are doing, either by finding better approaches to utilize the bitcoin or ethereum blockchains, or else making completely new blockchains.
This has been continuing for more than three years now, and the outcomes are beginning to come in.
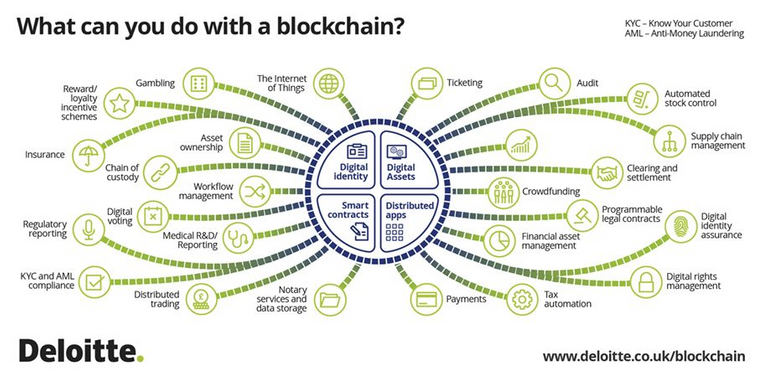
While a portion of the waters are as yet dim, this is the thing that we know a blockchain can do:
Set up computerized character
As examined in our guide "How Does Blockchain Technology Work?", the character segment of blockchain innovation is satisfied using cryptographic keys. Joining an open and private key makes a solid advanced personality reference in light of ownership.
An open key is the way you are recognized in the group (like an email address), a private key is the manner by which you express agree to advanced cooperations. Cryptography is an imperative power behind the blockchain transformation.
Fill in as an arrangement of record
As expressed in our guide "What is a Distributed Ledger?", blockchains are an advancement in data enrollment and dissemination. They are useful for recording both static information (a registry) or dynamic information (exchanges), making it an advancement in frameworks of record.
On account of a registry, information can be put away on blockchains in any blend of three ways:
Decoded information - can be perused by each blockchain member in the blockchain and is completely straightforward.
Scrambled information - can be perused by members with an unscrambling key. The key gives access to the information on the blockchain and can demonstrate who included the information and when it was included.
Hashed information - can be introduced close by the capacity that made it to demonstrate the information wasn't altered.
Blockchain hashes are for the most part done in blend with the first information put away off-chain. Computerized 'fingerprints', for instance, are regularly hashed into the blockchain, while the principle assemblage of data can be put away disconnected.
Such a common arrangement of record can change the way unique associations cooperate.
As of now, with information siloed in private servers, there is a tremendous cost for between organization exchanges including procedures, strategies and cross-checking of records.
Read more on this in our guide "What are the Applications and Use Cases of Blockchains?".
Demonstrate changelessness
A component of a blockchain database is that is has a background marked by itself. Along these lines, they are frequently called permanent. As such, it would be a tremendous push to change a section in the database, since it would require changing the majority of the information that comes thereafter, on each and every hub. Along these lines, it is more an arrangement of record than a database.
Read more on this in our guide "What is the Difference Between a Blockchain and a Database?".
Fill in as a stage
Cryptocurrencies were the principal stage created utilizing blockchain innovation. Presently, individuals have moved from the possibility of a stage to trade cryptocurrencies to a stage for savvy contracts.
The term 'shrewd contracts' has moved toward becoming to some degree a catch-all expression, yet the thought can really be isolated into a few classes:
There are the 'candy machine' brilliant contracts begat in the 1990s by Nick Szabo. This is the place machines connect with subsequent to accepting an outside info (a cryptocurrency), or else send a flag that triggers a blockchain action.
There are likewise shrewd legitimate contracts, or Ricardian contracts. Quite a bit of this application depends on the possibility that an agreement is a gathering of the brains, and that it is the consequence of whatever the consenting gatherings to the agreement consent to. Along these lines, an agreement can be a blend of a verbal assention, a composed understanding, and now likewise a portion of the helpful parts of blockchains like timestamps, tokens, reviewing, record coordination or business rationale.
At long last, there are the ethereum brilliant contracts. These are programs which control blockchain resources, executed over associations on the ethereum blockchain. Ethereum itself is a stage for shrewd contract code.
Blockchains are not worked from another innovation. They are worked from a one of a kind coordination of three existing innovations.