
If you are new to the crypto world, all those loose crypto terms can be very intimidating. To help you get started, you can find the most common crypto terms here. Very useful if you want to follow a discussion, or just to learn. If there are important terms that are missing, or you do not agree with the concise description, do not hesitate to add information in the comment section below. I can then edit the post if necessary.
- 51% attack
A 51% attack is a potential attack on the network whereby an organization is somehow able to control the majority of the network mining power. In other words, a 51% attack represents the situation where more than half of the computer power, within a certain blockchain, comes from one person or one concentrated group. However, hitting 51% network control is not a guarantee of success, just the point where success is likely. An attack has a chance to work, but requires extremely high relative hashrate. A majority attack has never been successfully executed on the bitcoin network, but it has been demonstrated to work on some small altcoins.
- Address
A crypto cash address is the location where you store your crypto coins and from where you send and receive these coins. You could compare it with your home address. This address usually consists of a whole series of numbers and letters, for example: 1KXghhUZRVFmfk9Jreo3vvuV3HDoCJyYJZ. This address is in fact the public part of the two encrypted keys (see private and public key) that are necessary for the holder to verify a transaction.
- Altcoin
This name is used for all crypto coins that are not bitcoin (alternative coins).
- ASIC miner
ASIC stands for Application Specific Integrated Circuit. This is in fact a chip that has been specially created for performing one specific task. For this reason, thanks to ASIC mining you can mine coins much faster than a normal computer or laptop. For blockchain, for example, special ASIC miners have been created that are only concerned with solving the SHA-256 algorithm (the algorithm with which bitcoins are mined). However, crypto coins are now being created that are impossible to mine with an ASIC.
- Blockchain
A blockchain is a kind of digital ledger of transactions that works from a decentralized network. Thanks to cryptography, a ledger can be maintained by a large amount of computers that together create the network. Every time a new transaction is made, this is added to the blockchain as a new block with date, size, etc.
- Block
The blocks are the 'pages' in the digital ledger, the blockchain. These are files with immutable data that are permanently stored on the blockchain.

- Block reward
The block reward is the reward that miners receive for finding a mathematical solution that is related to that block.
- Mining
Mining is the crypto term that is used to look for new block rewards. To find and solve blocks, a reward is distributed to the miner.
- Cryptography
Cryptography is a technique for hiding or encrypting information to be sent, so that someone who has access to the channel on which it is transmitted cannot possibly find out what information has been sent.
- Cryptocurrency (crypto money)
A kind of digital currency that is based on cryptography. This concerns bitcoin and the other altcoins.
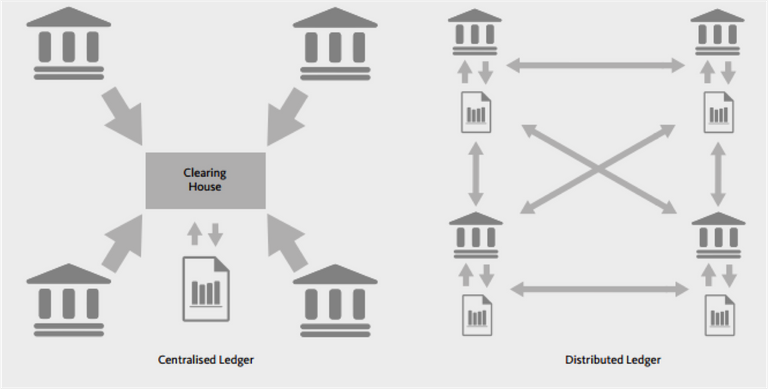
- Distributed and central ledger
A distributed ledger is an agreement of shareable, shared and synchronized data, which in this case is divided over different networks. These networks are then divided over many computers.
With a central ledger, the synchronized and shareable data is controlled by one network or individual.
- Double spending
This means that a particular cryptocoin can be issued more than once. This stops the operation of the blockchain. This is possible when a digital token consists of a digital file that can be duplicated or falsified. As with counterfeit money, such double-spending leads to inflation by creating a new amount of fraudulent currency that did not previously exist.
- Dust transaction
A transaction of extremely few coins that represents almost no value, but costs space on the blockchain.
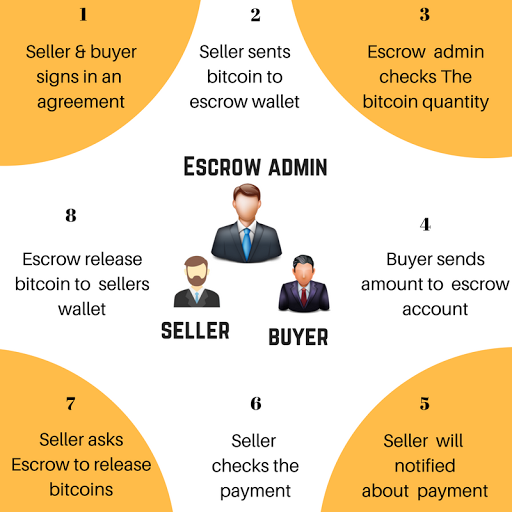
- Escrow
A concept in which a financial instrument or an asset is held by a third party to protect the two other parties during an asynchronous transaction.
- Fiat
A currency that is created out of nothing and only has value because people value it.
- FOMO
"Fear Of Missing Out" (fear of missing something). This often occurs when a crypto coin so quickly increases in value that people are scared of losing out on making money, so the price per coin becomes even higher.
- FUD
"Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt". This cryptoterm is often used to describe the volatility of the crypto market.
- Faucet
A technique that is used when a crypto coin is launched for the first time. A certain amount of coins is pre-mined and given away free of charge. In this way, people are getting interested in the currency and they start to mine the currency themselves.
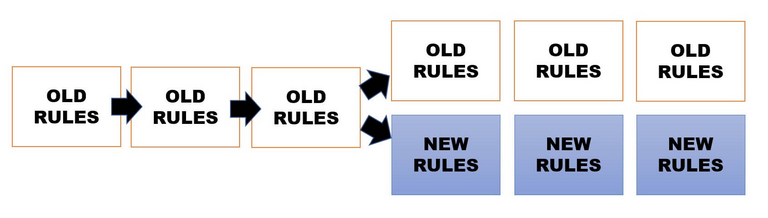
- Fork
A fork happens when an alternative operational version of the current blockchain permanently separates. This can happen in three different ways:
-By a 51% attack
-Because there is a bug in the program
-Because new substantial changes have to be made to the current blockchain.
- Genesis block
The first mined block in a blockchain.
- Halving
This means that the reward for a mined block (see block reward) is halved. This happens every time with a certain amount of mined blocks. At bitcoin this is for example every 210,000 blocks.
- Hash
A hash function is a function in computer science that converts input from a wide domain of values into a (usually) smaller range. It’s a function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size to data of fixed size. A cryptographic hash function has certain properties which make it suitable for use in cryptography.
- Hashrate
This is the speed with which the mathematical problems for certain blocks can be solved. In other words: the speed at which a new block can be discovered. For example, ASIC mining ensures that the hash rate goes down. It is the main reason why the bitcoin network consumes a lot of energy because it has to solve mathematical intensive computations regularly to find the blocks.
- ICO
Stands for Initial Coin Offering. This is a form of crowdfunding, where the public can invest in a blockchain startup in advance. As a thank you for the financial support they are rewarded with a certain amount of coins.
- Multisig
Multi signature is a form of technology that ensures that extra security is added to the transactions. Multi signature addresses require that another user signs the transaction before it can be added to the blockchain.
- P2P
This stands for peer-to-peer. A (crypto-) term that refers to computers that directly build a network without a central server in between.
- Private key
In cryptography, a private key (secret key) is a variable that is used with an algorithm to encrypt and decrypt code. Quality encryption always follows a fundamental rule: the algorithm doesn't need to be kept secret, but the key does.
Public key cryptography, or asymmetrical cryptography, is any cryptographic system that uses pairs of keys: public keys which may be disseminated widely, and private keys which are known only to the owner. This accomplishes two functions: authentication, where the public key verifies a holder of the paired private key sent the message, and encryption, where only the paired private key holder can decrypt the message encrypted with the public key.
- Public key
A string of letters and numbers that is public and can therefore be viewed by everyone. This can be used in combination with a private key to sign a digital transaction.
- Pump and dump
This is a crypto term that is used for the unethical method of pumping and dumping a relatively inexpensive coin. The currency is first obtained in a very cheap way by a certain group of people who then 'pump' the coin (make the value increase strongly) by making a lot of advertising. When the currency has risen enough in value, they dump their coins with a lot of profit.
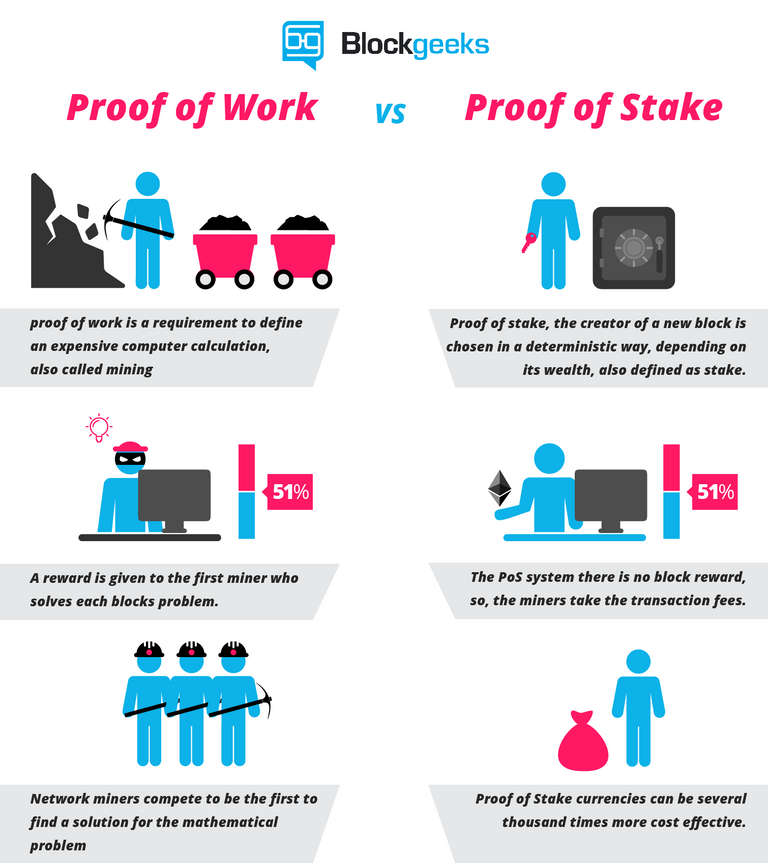
- PoW
Many cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, Ethereum and Dash use the type of Proof of Work, the PoW algorithm. To earn coins it is necessary to solve difficult puzzles with expensive computer equipment (mining). Miners receive coins when they solve a puzzle. In addition, miners also check and verify the transactions that are being done. The fees that people pay to execute these transactions go to the miners as compensation for their activities. Because the miners do intensive work to solve puzzles, check transactions and verify these, the Proof-of-Work method is used.
- PoS
It became clear that mining became slower and more expensive and the solution was presented in the form of the Proof-of-Stake method. It is an alternative to reach an agreement (or decentralized consensus) . Examples of cryptocurrencies that use PoS are Lisk, Peercoin and BitShares.
In this type of consensus model, the number of coins you have stored in the system matters. The larger your “stake” is, the higher the chances are that you won’t breach the system (because you have a huge stake in its optimal performance).
In POS, unlike POW, blocks are not mined, but are rather forged or minted. The participants who have a significant stake in the system get selected pseudo-randomly for forging and then adding blocks onto the blockchain.
This pseudo-random selection happens after analyzing several different factors to ensure that not only people having a huge stake are selected, but others are also selected. Some of these selection factors are randomized block selection, coin age-based selection, masternodes, etc.
POS is generally applied to those cryptocurrencies that are pre-mined so that users have access to the coins for staking. This means that the supply of POS cryptos are fixed from the start and there is no block mining or forging reward like POW.
So the only incentive that POS forgers get is the transaction fee attached to that block.
(Information from coinsutra.com)
- Scam coin
A coin created for the sole purpose of making the creator rich (usually by means of pump and dump).
- SHA-256
The cryptographic algorithm used for the Bitcoin PoW system.
- Signature
A signature is a mathematical process that allows someone to prove that he / she is the owner of his / her wallet. For example, a 'private key' is used here.
- Smart contract
A smart contract is an immutable agreement that is recorded on the blockchain, which contains specific logical actions that are comparable to a 'normal' contract. Once this contract has been signed, it can never be changed again.
A smart contract can be used to identify certain benchmarks that must be met in exchange for money. Smart contracts allow the performance of credible transactions without third parties.
The aim of smart contracts is to provide security that is superior to traditional contract law and to reduce other transaction costs associated with contracting.
- Wallet
See 'address'
- Whale
A whale is someone who owns a large percentage of a certain crypto coin. A whale can often manipulate the price of this crypto coin.
- Whitepaper
A document that describes in detail the protocol of the crypto coin.
This is really good for somone getting into cryptocurrencies