Indian economy is positioned as sixth in terms of the nominal GDP and is considered as the third largest economy in terms of purchasing power parity BPP the year's 2015 in 2016 has played a vital role in Indian economic development. During this period Indian World Bank's expansion growth was observed. This was the major reason why economy develops to seven point six percent. However this growth diminished in 2017 to seven point one percent. But it is assumed that the growth rate rise up to seven point two percent in 2018 following seven point seven percent in 2019. Indian economy is mainly known for its service sectors as it has been one of the leading countries to export business process outscoring BPO services and software services. India is also rich in agricultural sector employing thousands of people in agricultural fields. In seeking a second position in the world in terms of farm output history of Indian economy. Out of the confusion of British rule India's economy grew at the rate of development was slow when India adopted liberalisation. It became one of the fastest growing countries in the world generally. There were three eras in Indian histories that are ancient and medieval period. MCCOLLEY era and British era. Let's discuss these Pieris in detail ancient and medieval era. The ancient period is linked with 1400 B.C. and 28 hundred B.C. when the people used to exercise agricultural activities use uniform measures to weight developed urban sanitation system and brought in various changes. South India and West Asia were the two regions involved in maritime trading and the two spots named Coromandel Coast and Malabar were set as the trading centres.

However the trading could not sustain for a long time as the Crandell coast and Malabar was snatched and controlled by the Jewish Passi Syria Muslim and Christian. In this era the reputed kings and rulers used to take revenues from the small agricultural frames lending from the land to harvest crops. The farmers were given some harvested crops for their hardwork and surfaces. This clearly states that though the Kings had the authority to issue coins and currency the barter system still exist and to the peasants. Noakhali to Immokalee Iraq began in 15 26 and lasted till 1793 in the Indian economy remains stable until the 18th century. The gold silver copper and other important coins were used by the Mukul Ampara before the arrival of Britishers. India was united. There were about 64 percent of the people engaged in agricultural activities and 36 percent of people opted for industrial and service sectors for their daily livelihood. In comparison to the Europe where more than 80 percent of the people were dependent on agriculture Indian economy proved to be better. Indian industrial sector boosted the Mukul period. The cash crops goods equipment tools and other commodities were exported all over the world. The major leading industries of India during the muko rule include textiles steel and shipbuilding. The food that was supplied to sugar oil and butter. In the 17th and 18th century Europe was highly led by the muchos production and hence several commodities like spices Indigo peppers and silks were imported from Europe.
.jpg)
The Mukul Emperor concluded in the 18th century when North India and South India were snatched by the Merav us. This led to the decrease in agricultural productivity and hence the industrial sectors were affected by the slow growth. British sheerer 1793 to 1947 in the 19th century India was controlled by the Britishers who used to take the Indian raw materials and supply the same to Britain for the conversion of raw materials into farm products. These final products were then sold to Indians at an expensive rate. The period of British rule resulted in a decline productivity of food crops mass impoverishment unemployment and various famines. The per capita income which was estimated to be twenty four point four percent during the Makkal period was brought down to four point two percent in 1950s. A large number of Indian markets were conquered by the Britishers and the tariffs and quotas were introduced in India for exporting the commodities to other countries except for Britain. The British government ruined the Indian economy. There were some positive aspects of this colonial rule as well the railways communication airways and roadways were well developed by the British shows for the transfer of Indian commodities to Britain and vice versa. After the conclusion of the British period India adopted the worst economy that comprised of the electorate farmers and labour force in insufficient agricultural production in respect to the Indian population.
Inadequate infrastructure and a massive unemployment three sectors of the economy. Indian adopted three sectors economy including. Agriculture sector crops horticulture milk and animal husbandry fishing aquaculture forestry agriculture and much more. Industry and Manufacturing sector manufacture and processing of steel iron copper and other industrial related goods. Services sector. Construction infrastructure education communication healthcare banking and financing hospitals transport insurance and other such economic activities. Agricultural sector. According to the surveys of 2014 India was placed at second position in agricultural productivity with around 49 percent of the people employed in the same sector. Although Indian agriculture declined till 2011 the green revolution played a major part in improving the irrigation technology adoption of modern agricultural tools and equipment in the towns of Ferus agriculture subsidies the international reports clarify the Indian agricultural contribute 30 percent to 50 percent of the total agricultural production in the world. Uttar Pradesh Madhya Pradesh Telangana Andhra Pradesh Bihar West Bengal Maharashtra and Gujarat are the major contributors of agriculture productivity. Around six million of Indian workforce is engaged in fisheries work. The country has also occupy the sixth position in the largest fishing industries of the world cotton milk and used largely produce in India and exported to diverse parts of the world. The 2011 estimation states that there are a total of 170 million animals present in this land i.e. the second largest country in animal population. India has ranked second in the production of wheat rice sugar cane cotton groundnuts fruit and vegetables and consumer silk.
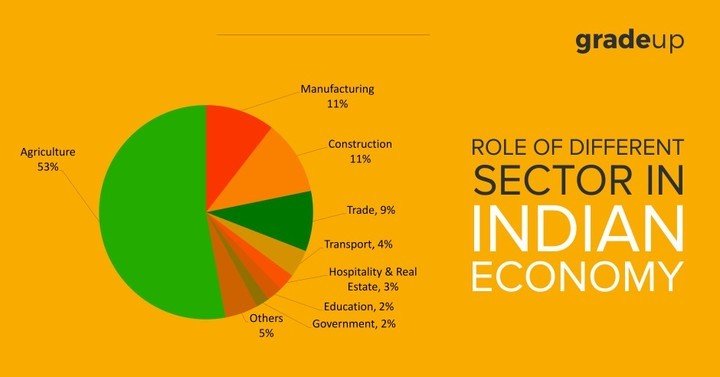
Industrial sector there has recently 22 percent of Indian workforce engaged in the industrial sector. The Indian industries experienced several amendments after the end of colonial rule in 1991. India was liberalized the export and import of foreign countries and hence welcomed the falling investment. The government owned companies that experience losses were privatized and the infrastructure was improved to a great extend leading to the easy flow of goods and services from one place to another. India also adopted the latest in modern technologies reducing labour intensive industries. But this expansion also resulted in increased unemployment. Petroleum products and chemicals. The overall contribution of petroleum and chemicals industries to Indias GDP is 34 percent Jamnagar in India owns the worlds largest refinery. India is also listed in the top five producers of agrochemicals polymers plastic dyes and other such chemicals. At the same time the country also imports a large amount of chemicals to accomplish the domestic requirements engineering the engineering sector includes machine tools Transformers capital goods automobiles switchgear furnaces and much more. India is the third largest exporter of engineering products and this sector also have a major contribution to the GDP gems and jewellery. India has been the major producer and supplier of precious metals like diamonds gold and silver for many years. Surat and Mumbai are mainly known for polishing jewellery cutting finishing and supply the jewellery industries contribute to 7 percent of Indian GDP service sector. In 1950 the service sector has the lowest contribution to GDP that is 15 percent.
But in today's yeara this sector is the major contributor with 57 percent to world's GDP. Around 27 percent of the Indian workforce is employed by the service sector. Banking and Finance are one of the essential service factors that are classified into two types i.e. an organized sector that consists of private banks public banks and falling operated bank. The unorganized sector consists of the moneylenders and other financial institutions. According to the surveys taken in 2006 and 2007 the public ban had around 75 percent of assets and on the other hand the private and foreign owned had eighteen point two percent assets electricity sector indeed is titled as the third largest energy consuming country with China and the United States of America being the first and the second places. India consumes 85 percent of coal and crude oil and the old stock of India accomplishes 25 percent of people's requirement. Awesome. While Gerard Rogers Stan and Mumbai are the major cities where the oil and natural gas fields are sited in 2013. India ranked third in the production of electricity infrastructure. India's infrastructure adds 5 percent to the GDP. The roadways are well built and the Indian roads are second largest roadways in the world. India has government owned railway tracks that are considered as the fourth largest railways in the world. There are about 125 airports in India among which there are 65 airports that have the permit to carry both travellers as well as the cargo.
To the question in your title, my Magic 8-Ball says:
Hi! I'm a bot, and this answer was posted automatically. Check this post out for more information.