Función Racional/Rational function
Se caracteriza por ser el cociente de dos polinomios/It is characterized by being the quotient of two polynomials
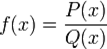
El dominio de esta funcion esta conformado por el conjunto de los números reales a excepción de aquellos que anulan al denominador
Es decir Dom(f)={x ∈R/ x tales que Q(x) ≠0}
The domain of this function is made up of the set of real numbers except for those that cancel the denominator
That is, Dom (f) = {x ∈R / x such that Q (x) ≠ 0}
Ejemplo
Hallar el dominio de la siguiente función racional:
f(x)=(2x - 5)/(x2-5x + 6)
Para resolver este ejercicio se hace el denominador igual a cero para obtener sus raíces y excluirlas del dominio de la función.
Existen diferentes formas para obtener las raíces de esta ecuación de 2do. grado (factorización, resolvente cuadrática, Ruffini, entre otras).
Example
Find the domain of the following rational function:
f (x) = (2x - 5) / (x 2 -5x + 6)
To solve this exercise, the denominator is equal to zero to obtain its roots and exclude them from the domain of the function.
This is: x 2 -5x + 6 = 0
There are different ways to obtain the roots of this 2nd equation. degree (factorization, quadratic resolvent, Ruffini, among others).
Optemos por la factorización:
En este caso buscamos dos números que multiplicados den como resultado +6 y sumados resulten -5.
x2-5x + 6=(x-2)(x-3)=0
Let's opt for factoring:
In this case we are looking for two numbers that multiplied give +6 as a result and added together result -5.
x 2 -5x + 6 = (x-2) (x-3) = 0
Para ello usamos la identidad siguiente: A.B=0 sí y sólo sí A=0 ó B=0
Considerando A= x-2 y B=x-3 se tiene que: x-2=0 ó x-3=0
Despejando se tiene que x=3 ó x=2, estos valores no pertenecen al domino de la función f debido a que anulan al denominador.
En conominio de f es Dom(f)= R -{2,3}
Este es un resultado muy importante al momento de gráficar esta función, ya que la función no existe cuando x=2 y cuando x=3.
For this we use the following identity: A.B = 0 if and only if A = 0 or B = 0
Considering A = x-2 and B = x-3 we have that: x-2 = 0 or x-3 = 0
Solving for x = 3 or x = 2, these values do not belong to the domain of the function f because they cancel the denominator.
The condominium of f is Dom (f) = R - {2,3}
This is a very important result when graphing this function, since the function does not exist when x = 2 and when x = 3.
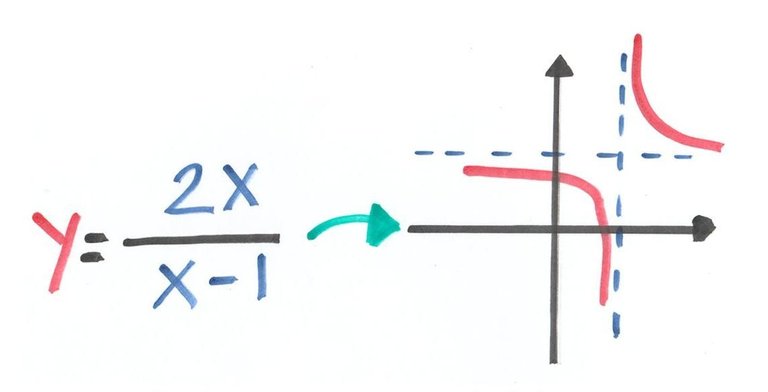
Veamos./Let's see.
Para analizar esta gráfica necesitamos un concepto muy importante en el análisis matemático, dicho concepto categoriza la noción de "Límite de una función en un punto", este concepto lo cubriremos más adelante.
To analyze this graph we need a very important concept in mathematical analysis, this concept categorizes the notion of "Limit of a function at a point", this concept will be covered later.
Actividad:
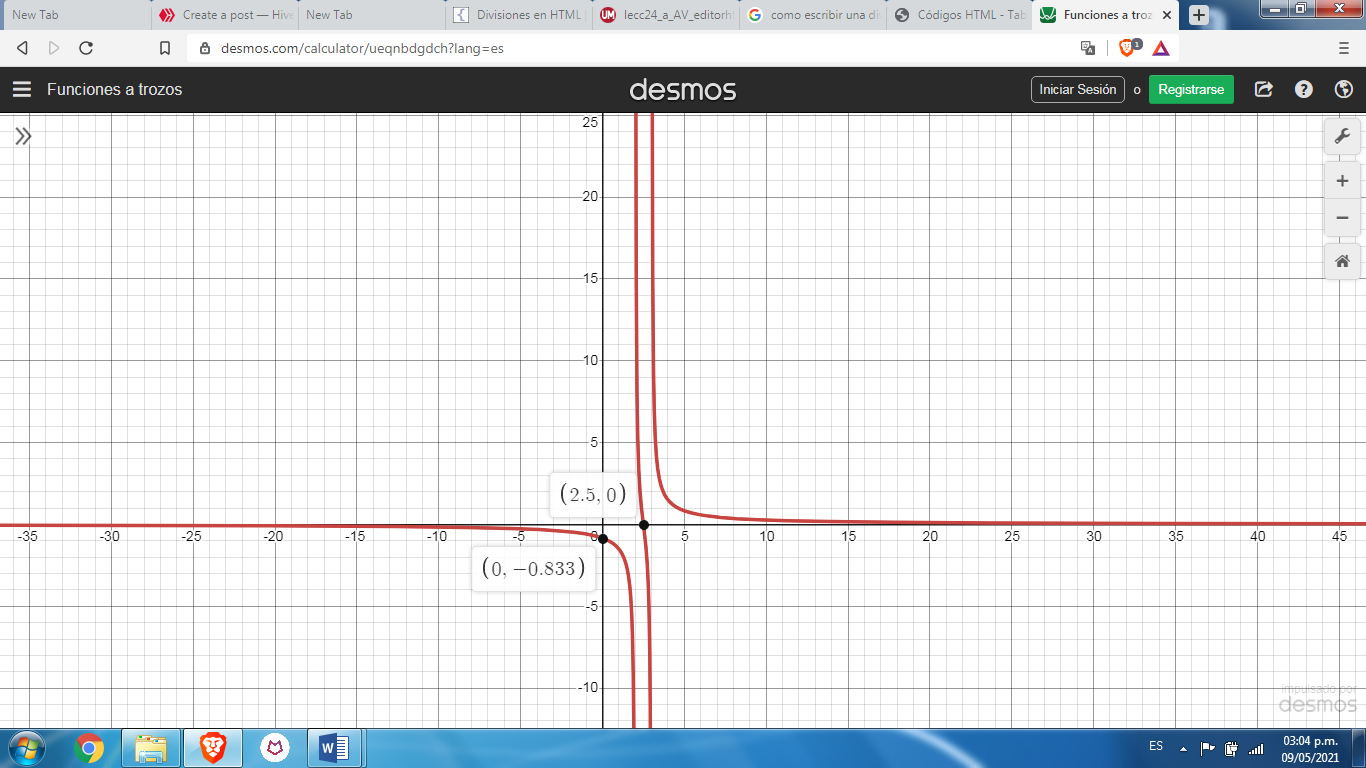
Hallar el Dominio de cada una de las siguientes funciones y con la ayuda de https://www.desmos.com/calculator/ueqnbdgdch?lang=es trazar su gráfica.
Activity
Find the Domain of each of the following functions and with the help of https://www.desmos.com/calculator/ueqnbdgdch?lang=es plot your graph
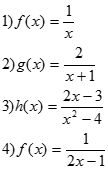
Referencia/Reference
TAN, SOO (2005). MATEMÁTICA PARA ADMINISTRACIÓN Y ECONOMÍA. 3º EDICIÓN. CENGAGE LEARNINGEDITORES./TAN, SOO (2005). MATH FOR ADMINISTRATION AND ECONOMICS. 3rd EDITION. CENGAGE LEARNINGEDITORES.
Créditos
Para la elaboración de la gráfica:
https://www.desmos.com/calculator/ueqnbdgdch?lang=es