Batteries are one of the most common types of voltage sources in our day-to-day lives. There are many different types of batteries, but they all have one thing in common: A battery uses chemical reactions to generate voltage. Every battery consists of two electrodes made of different metals and an electrolyte solution that aids the chemical reactions. On the positive end of the battery is one electrode, called the cathode, and on the negative end is the other electrode, called the anode.
Chemical reactions between the electrodes and the electrolyte cause electrons to move from the cathode to the anode inside the battery. The buildup of electrons in the anode is what generates voltage. However, to keep the chemical reaction going, the electrons need to get back to the cathode somehow, and they can't go back the way they came. To get the electrons from the anode back to the cathode, we have to provide a path external to the battery in the form of an electric circuit. Since these electrons are so energetic and motivated to get from one end of the battery to the other, we can place something like a light bulb or a motor in the circuit to make the electrons do some useful work along the way.
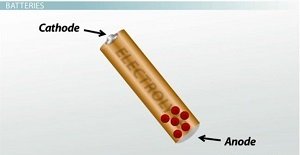
Chemical reactions cause the electrons to move from the cathode to the anode.
As we all know from experience, batteries lose their voltage at some point. This happens when all the chemical reactants in the battery have been used up and can no longer sustain reactions. However, some types of batteries are capable of being recharged, such as the ones in our cell phones, laptops or car. Rechargeable batteries are made of special materials that use reversible chemical reactions. By applying a stronger voltage source across the terminals of the battery, the electrons can be made to flow backwards, from the cathode back to the anode. This is what happens when you put rechargeable batteries on a charger.
Revisiting our water analogy from earlier, we can think of a battery as being like one of those giant water tanks you see in some small towns. Have you ever wondered why those tanks are so tall? Well, you see, as you put the water higher and higher, the pressure available at the ground goes up, which means the water can do more work when it comes out.
This is just like increasing the voltage of our battery so the electrons will do more work when they flow in an electric circuit. The similarities don't end there. Just like our battery can only supply voltage for just so long, the water tank will eventually run out of water, and the pressure will drop as the last bit runs out.
Source: https://study.com/academy/lesson/voltage-sources-energy-conversion-and-examples.html
Not indicating that the content you copy/paste is not your original work could be seen as plagiarism.
Some tips to share content and add value:
Repeated plagiarized posts are considered spam. Spam is discouraged by the community, and may result in action from the cheetah bot.
Creative Commons: If you are posting content under a Creative Commons license, please attribute and link according to the specific license. If you are posting content under CC0 or Public Domain please consider noting that at the end of your post.
If you are actually the original author, please do reply to let us know!
Thank You!
Congratulations @sanctuary! You received a personal award!
Click here to view your Board
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Congratulations @sanctuary! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!