Introduction

Image Source
Electronics is defined as the branch of physics and technology concerned with the design of circuits using transistors and microchips, and with the behavior and movement of electrons in a semiconductor, conductor, vacuum, or gas.
Having known its definition, electronics as dealing with semiconductors, transistors, chips and any other electronic devices include its scope the parameters and the values already determined in a certain component. In a particular circuitry, you can't just directly tell the definite value of a component until you measure it- unless if the values are pre-determined and labeled in the components' chassis.
Electronics has been widely known and spread already throughout the world. As it is the backbone and the skeleton of every innovating technology then and now, it is a necessity for us that at least we could know about the basics of its innovation- to know the measuring devices so essential as needed to determine the values of each components present in a particular circuitry.
"But how can we measure and check predetermined component values?"
This blog introduces you to an informative approach regarding the world of electronics and its basics- what instrument to be used in determining pre-specified values as kept on mentioned above, their different kinds and of course their comparison.
Multimeter/Multitester
- Multimeters are tools used to measure current, voltage and resistance.
- They are very useful instruments that can be utilized in a number of fields, the primary users being electricians.
- There are two primary types of multimeters, the analog and the other is the digital.
ANALOG MULTIMETER
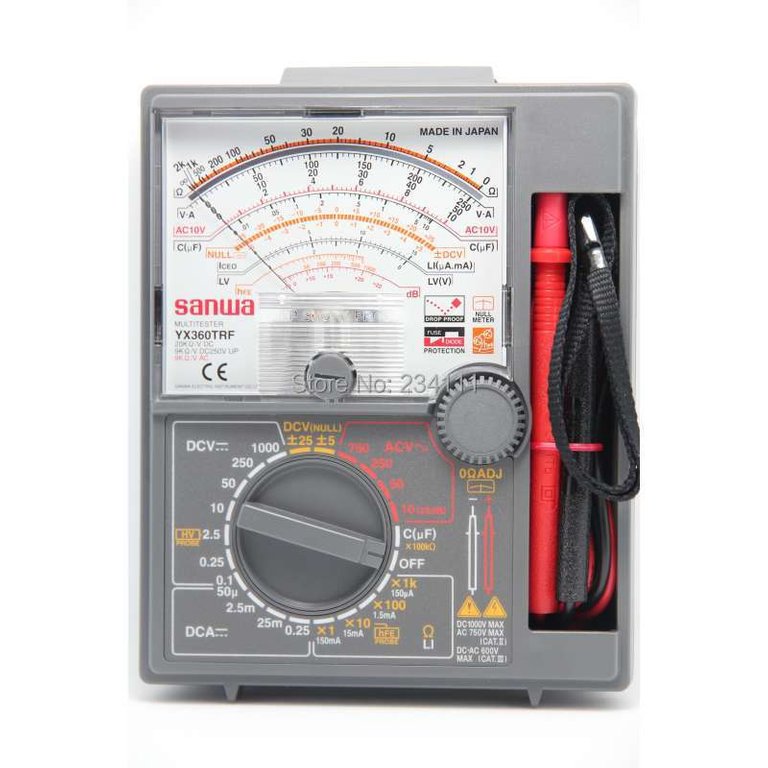

Image Source
- It is used to measure AC and DC current as well as voltage. It is also used to measure resistance.
- consists of a continuous scale over which a deflecting needle indicates the value to be measured
- To make measurements on a scale calibration a analog multimeter moves a needle along the scale.
- excellent for reading voltage, current, resistance, frequency and signal power
- The analog multimeter also exhibits low resistance and high sensitivity with scales down, which can make it difficult to use.
- Inside analog multimeter there is a current measuring moving coil meter with appropriate internal resistors which will be brought into circuit based on range switch selection.
- To take a reading, firstly, the type of measurement (voltage, current, or resistance and whether the current is alternating or direct) and the expected range needs to be selected from the large dial below. Then, the leads (shown docked on the right) are placed at the relevant points on the circuit.
Inside an Analog Multimeter
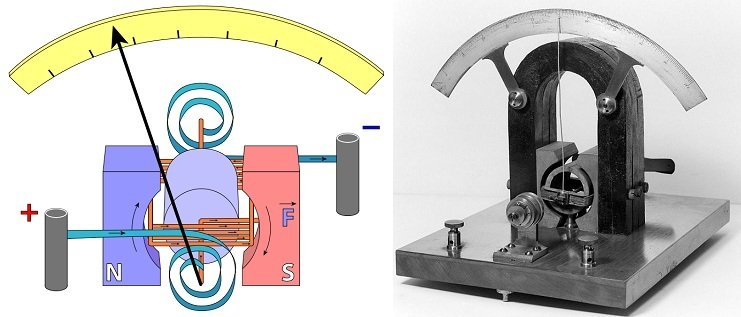
Image Source
Central to the functioning of the analog multimeter is the D’Arsonval galvanometer. This consists of a coil carrying a current attached to a rotatable drum. Two permanent magnets are placed on either side of the coil. As current flows through the coil, a magnetic field forms around it. This magnetic field interacts with the magnetic field of the permanent magnet, so whenever the current flowing through the coil changes, the drum rotates. A needle is attached to the drum, which moves along the reading scale. An analog multimeter primarily measures current. Measurements of voltage and resistance are first converted to a corresponding current, which is then indicated by the needle.
DIGITAL MULTIMETER

Image Source
- A digital multimeter is essentially a voltmeter
- In order to measure current and resistance, some internal circuitry is used to “convert” current and resistance values to corresponding voltage values.
- using an analog to digital converter, the voltage is converted to a digital signal and a value is displayed using a display, which is typically a 7 segment display
Features of New and Old Digital Multimeter
In older digital multimeters, the type of measurement as well as the range needs to be selected manually. Most new digital multimeters have an auto ranging feature. However, users still have the ability to manually select the range (this is especially useful when measuring values that change by large amounts periodically).
Important Differences Between Analog and Digital Multimeter types
• Input resistance of digital multimeter is constant for all the ranges to be measured unlike analog multimeter.
• It measures with accuracy better than analog multimeter as analog multimeter is prone to errors due to wrong pointer based reading.
• The highest frequency of analog multimeter using rectifiers on AC range is about 2KHz. For digital electronic multimeter this range is higher than analog type.
• The comparison between analog and digital meters comes down to one word: precision. Most situations call for as precise a reading as possible, making a digital meter the better choice. However, instead of a single precise reading, some instances call for finding out a range of readings, making an analog meter the better choice.
Summary of Comparison: ANALOG VS. DIGITAL MULTIMETER

Image Source
References
- https://www.circuitspecialists.com/blog/analog-or-digital-multimeter/
- http://www.rfwireless-world.com/Terminology/analog-multimeter-vs-digital-multimeter.html
- http://www.muchbuy.com/blog/985/how-to-choose-multimeters-digital-multimeter-vs-analog-multimeter.html
- https://sciencing.com/advantages-meters-vs-analog-meters-6325756.html
- http://pediaa.com/difference-between-analog-and-digital-multimeter/

Upvoted
thankyou for your wisdom @ivancuyag..keep it up for us steemains..please upvote me