the microprocessor: it is the main electronic component of our computers, computers or data processing cards. The microprocessor has several synonyms: CPU, processor, micro, microchip. The material used to make it is silicon, very abundant in nature.

Parts of the Microprocessor: The microprocessor, also known as a processor, is the brain of the computer, a complex integrated circuit that is responsible for giving programmed instructions through arithmetic and logical operations through the operating system. It has several central processing units, which are constituted by registers, control unit, logical unit and unit that functions as a mathematical coprocessor.
Measuring the performance of the processors is not at all easy, since for example in microprocessors of the same range the loads can have different performance in terms of effectiveness. The clock frequency of the processors indicates the frequency with which the electric current enters and exits the transistors. This physical quantity is measured by Hz (Hertz) and determines the electric cycles per second within a transistor.
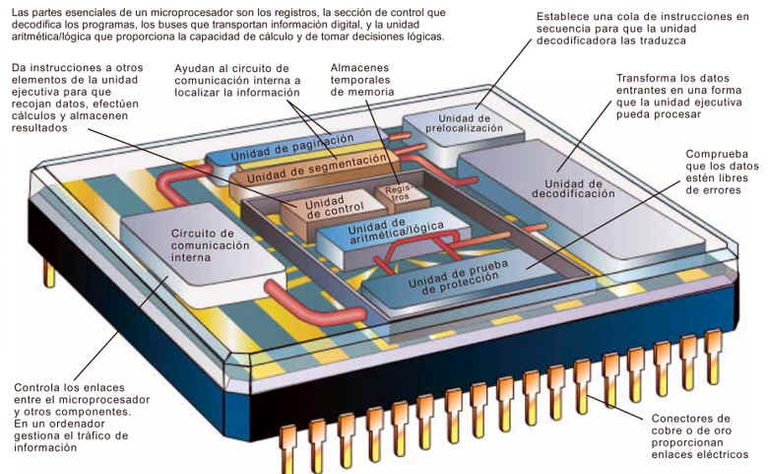
Parts of the microprocessor
The microprocessors have a fairly complex architecture in which the following parts can be differentiated:
Encapsulated
It is what covers the sensitive part of silicon, giving it consistency and fulfilling the function of preventing deterioration, as well as allowing external connectors to fit into the motherboard socket.
Cache
It is the fast access memory that the processor uses to directly access some data, without the need for RAM memory to intervene, thus gaining time in terms of data processing.
Mathematical co-processor
This part is considered as one of the logical parts, since it is specialized in mathematical calculations.
Records
They are small internal memories available for the processor to use when necessary only in special cases.
Memory
This is where the processor accesses to obtain information and data of the programs that it will execute. The memory gives temporary accommodation to the data while it is working in the programs. If the information is not saved, it will be lost, since nothing is stored in this memory.
Ports
The processor must transfer data and results to many parts of the computer, this is done through the ports, whose function is to communicate the circuits with the microprocessor.
Heatsink
The connection of the micro is made directly to the socket of the motherboard that is already soldered to it. Because the microprocessor is one of the main parts of the computer it consumes a lot of energy and needs constant cooling. For this, a heat sink made with copper or aluminum material is placed to allow a high thermal conductivity. In addition, a cooler or fan that removes the heat attracted by the heatsink is placed on top of the heatsink.
Generally, in most computers, grease or thermal paste is added between the heatsink and the lid of the mic to cool even more. But today there are more efficient cooling methods such as the use of peltier cells or liquid cooling for extreme cases, such as overclocking practices (reaching a higher clock speed of the micro to improve its performance from the BIOS).

Operation of the microprocessor
The operation of the microprocessor requires several steps, since these are instructions that are translated into binary numbers which are ordered sequentially in the main memory of the arithmetic logic unit. Next we detail the phases of the operation of the processors.
Everything starts with a prefetch or pre-reading of the instruction just entered. Then the instruction is sent to the decoder, where it is determined what to do with the given instruction. Then proceed to the execution, before reading operands if there is one; that is to say that the processing is carried out by means of a launching of the state machines. And finally we proceed to the writing of results in the system registers.
All these processing steps are done in CPU cycles, one or several cycles according to the structure of the micro and its segmentation capacity. The clock frequency determines the duration of these cycles that can not be shorter than the time needed to perform the individual operation. The processor is connected to a PLL circuit made of quartz crystal, which is capable of generating pulses constantly, maintaining a continuous rhythm in one second. It currently generates thousands of Mhz per second.