*This post is about Proof of Stake of Ethereum 2.0, writing by BISCARAS Axelle (@abiscaras) and BOURDREL Hugo (@akiyon) for cryptocurrency course in 'Master 2 Mathématiques Finance Computationnelle et Actuariat' at the University of Lille supervised by @pboulet *

I - What is Ethereum 2.0?
Ethereum 2.0 is made up of two layers:
- The application layer allows transactions to be carried out and which operates decentralized applications while keeping the balances of each of the addresses.
- The consensus layer to ensure the security of the entire network. The latter is currently undergoing a change: from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS).
Ethereum 2.0 is the update To PoS , the main motivation for this change is to allow the network to process more transactions per second. However, this is not the only motivation, following the rise in gas prices, a solution had to be found to reduce the ecological impact of the Ethereum blockchain. The Merge meets these expectations, which is a big plus.
II - PoS consensus algorithm
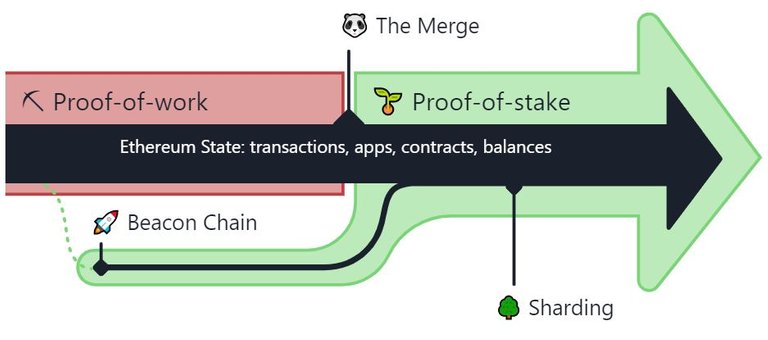
On December 1, 2020, the new PoS called “Beacon Chain” which runs alongside the ETH Mainnet Consensus. At the beginning, Beacon Chain was not implemented to manage Mainnet's transactions but faced with the soaring number of validators, it is decided to merge the consensuses in September 2022 so that the Beacon becomes the main consensus of ETH .
However, the change to PoS is very controversial due to the fact that it marks the end of mining rewards (we are moving to a stacking and reward system over time). So, Forks are created in order to continue working with PoW.
How to become a validator?
A validator is a person who has made a specific deposit of 32 ETH in stacking. So it comes naturally that a user can be multiple validators if they deposit 32 ETH multiple times.
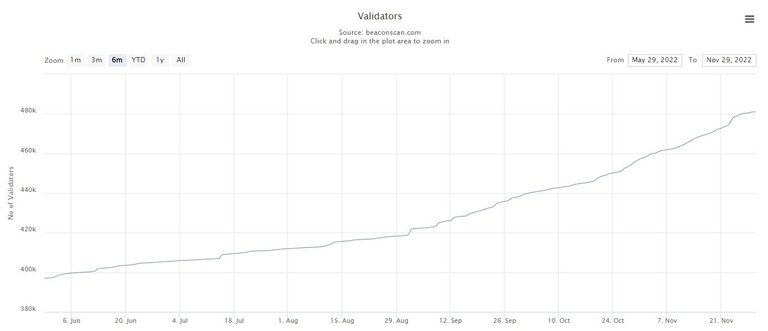
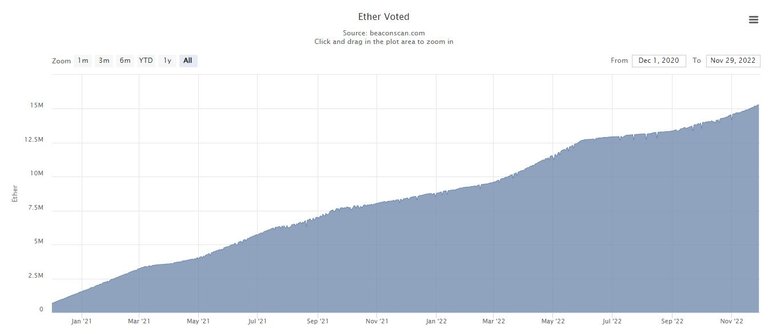
Today, with over 470k validators there are over 15 million ETH stacked.
How does PoS work?
A 'slot' is generated every 12 seconds, and a single validator is randomly chosen to submit a block in the 'slot'. An epoch is made up of 32 slots, which represents 6.4 minutes. If a validator is offline and does not offer a block in his slot then this slot is left empty. The first block of each epoch is treated as the control block.
How is the validator chosen?
The random choice of the 'slot' validator is generated by “RANDAO”. This means that there are very few choices for the generated seed; validators can either contribute a verifiable unique value or have their block ignored altogether. The hash signature is mixed with the RANDAO of the chain by XOR, which provides an additional improvement in security due to its commutativity.
III - Ethereum Virtual Machines (EVM)
Ethereum Virtual Machines are, in a way, the brains of the Ethereum blockchain. It allows it to be updated continuously, according to the transactions and interactions included in the blocks and prevents nodes from having a different version of the blockchain.
The concept of the "World State"
There is an entity on Ethereum, called World State. This represents the state of the blockchain at a given time.
In particular, we find all the accounts linked to their public address and their balances of ETH and tokens, but also all the applications, accompanied by modifiable storage and immutable source code.
This World State is in the form of a gigantic tree, called Merkle Patricia Tree, which, when encrypted, takes the form of a Merkle root.
Since all these transactions are performed and validated in blocks, it is necessary to update the World State each time a new block is processed, on all nodes of the Ethereum network (so that everyone will be on the same page). This is where the Ethereum Virtual Machine, or EVM, comes into play.
L’EVM is a « Full Turning » system, this means she can do a lot of operations (recursive, simple calculations, comparisons, modification of variables, etc.).
The EVM allows Ethereum to process smart contracts and therefore to host complex decentralized applications, this is what differentiates this blockchain from others such as Bitcoin. This is called an infrastructure blockchain.
IV - Layer 2 and Blockchain Trilemma
Layer 2 is a separate blockchain that extends Ethereum and inherits Ethereum's security guarantees. For the sake of optimization, a blockchain must have three properties:
- Decentralization
- Security
- Scalability
This is called the 'Blockchain Trilemma' and it has been shown that for the Blockchain to be simple it can only ensure two of the above three points.
Scalability has been an issue for the Ethereum blockchain since its inception, as the latter is only designed to process around 30 transactions per second. Which was good enough at first, but the explosive growth of cryptocurrencies and blockchains over the past few years has changed the game. This is when layer 2 comes into play.
Layer 2 gathers scalability solutions of Ethereum that allow transactions to be processed outside of layer 1, while taking advantage of the decentralization and security of layer 1. Layer 2 relieves Layer 1 of many transactions and writes finalized proofs to Layer 1.
Ethereum's layer 2 is not implemented yet. Ethereum 2.0 will contain Sharding (its launch is scheduled for 2023), a scalability function that will divide the blockchain into several chains. Each chain will operate independently and validate its own transactions. This will result in increasing the throughput of the blockchain up to 100,000 transactions per second.
However, initially sharding will only serve as data storage (a storage blockchain is easy to run). This implies that Smart Contracts will not be available when Sharding will be launched. Currently there is a discussion for the implementation of Smart Contracts in the shards in order to know if all the shards will be able to support them or only a part of them.
Despite Sharding to fix the scalability issue, the Ethereum blockchain has become increasingly centralized over time, with a few mining pools wielding significant power over the network and its consensus.
V - Applications
The number of applications due to Ethereum could be described as infinite :
- Enables the functionality of smart contracts and decentralized applications (financial applications, games or even tools for other applications)
- Allows any application / process / transaction / mechanism to operate WITHOUT downtime that implies eradication third party fraud, control or interference.
- Allows the deployment of codes of any algorithmic complexity, in particular thanks to the EVM.
Sources :
French :
- Ethereum c'est quoi ? Ethereum avis, prédictions et définition (cryptonaute.fr)
- Qu'est-ce que la machine virtuelle Ethereum (EVM) ? (cryptoast.fr)
English :
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
Congratulations @akiyon! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 300 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCheck out the last post from @hivebuzz:
Support the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!