Este post lo vamos a dedicar a las operaciones con funciones, es decir: adición, sustracción, multiplicación y división de funciones.
This post is going to be dedicated to operations with functions, that is: addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of functions.
Veamos:
Sean f y g dos funciones cualesquiera con sus respectivos: Dom(f), Dom(g)
Sean f y g dos funciones cualesquiera con sus respectivos: Dom(f), Dom(g)
Let's see:
Let f and g be any two functions with their respective functions: Dom(f), Dom (g)
Let f and g be any two functions with their respective functions: Dom(f), Dom (g)
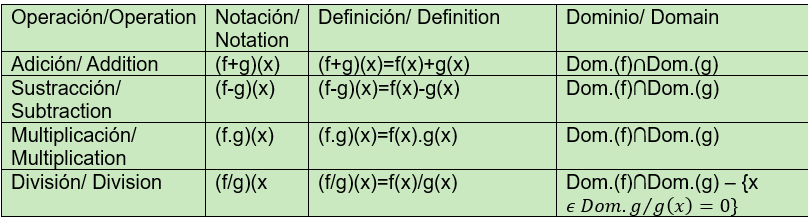
Definimos:
We define:
 |
|---|
Veamos algunos ejemplos: // Let's look at some examples:
Si: // If:
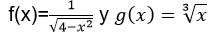
Hallar:
f+g, f-g, f.g y f/g con sus dominios. // Find: f+g, f-g, f.g and f/g with their domains.
Solución:
Primero hallemos los dominios de f y g respectivamente:
La función f está definida mediante un cociente, esto significa que debemos excluir los valores de x que hacen que el denominador √(4-x2 ) sea igual a 0, es decir: 2 y -2. Por otro lado, 4-x2 deberá ser positiva para que pueda existir su raiz cuadrada en R, es decir, para que sea un número real; de tal forma que la cantidad subradical de √(4-x2 ), es decir : 4-x2, deberá ser mayor que 0; todo lo referido anteriormentte se resuelve afirmando que 4-x2>0.
Por lo tanto, corresponde resolver esa desigualdad cuadrática
Solution:
First let's find the domains of f and g respectively:
The function f is defined by a quotient, this means that we must exclude the values of x that make the denominator √(4-x2 ) equal to 0, that is: 2 and -2. On the other hand, 4-x2 must be positive for its square root to exist in R, that is, for it to be a real number; in such a way that the subradical quantity of √(4-x2), that is: 4-x2, must be greater than 0; Everything mentioned above is resolved by stating that 4-x2>0.
Therefore, it is necessary to solve this quadratic inequality
4-x2>0.
Esto es:// This is:
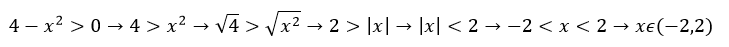
En consecuencia, el Dom(f)= (-2,2)//Consequently, the Dom(f)= (-2,2)
En el caso de la función g estamos tratando con una función definida por una raíz cúbica , este tipo de raíz admite valores positivos y negativos para la x, en consecuencia, el Dom(g)=R.
In the case of the function g we are dealing with a function defined by a cube root, this type of root admits positive and negative values for the x, consequently, the Dom(g)=R.
Representemos en una recta al dominio de estas dos funciones y escojamos la intersección de ambos dominios, es decir: todos aquellos valores de x que se encuentren en ambos dominios, excluiremos los que están en uno y no en el otro dominio.
Let's represent the domain of these two functions on a straight line and choose the intersection of both domains, that is: all those values of x that are in both domains, we will exclude those that are in one and not in the other domain.
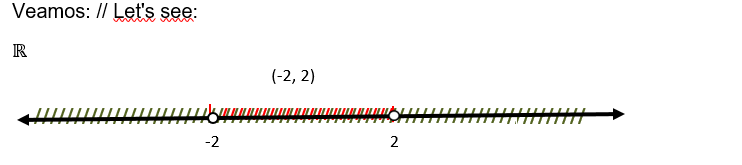
Las líneas verdes representan el dominio de la función g y las líneas rojas representan el dominio de la función f; la intersección de ambos dominios está representado por el cruce de las líneas rojas y verdes, es decir: (-2, 2). Los puntos abiertos indican que -2 y 2 no están en el dominio de f, consecuentemente no están en la intersección.
The green lines represent the domain of the g function and the red lines represent the f function domain; The intersection of both domains is represented by the crossing of the red and green lines, i.e.: (-2, 2). The open points indicate that -2 and 2 are not in the domain of f, therefore they are not in the intersection.
Conclusión:// Conclusion:
Dom(f)∩Dom(g)= (-2, 2)
Vamos ahora con las operaciones:// Now let's go with the operations:

¿Por qué excluimos el 0 en el dominio de la función cociente? /Why do we exclude 0 in the domain of the quotient function?
Ejercicio para el lector:// Exercise for the reader:
Dadas las siguientes funciones: // Given the following functions:

Hallar:// Find
f+g, f-g, f.g y f/g con sus respectivos dominios.// with their respective domains

Créditos
El texto es original de la autora, una de las imágenes es elaborada con inteligencia artificial y la otra es de Pixabay.
Credits
The text is original from the author, one of the images is created with artificial intelligence and the other is from Pixabay.
Su publicación ha sido votada por @Edu-venezuela, se trasladará a otros proyectos de curación para obtener más apoyo. ¡Sigan con el buen trabajo!
Thank you very much.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
Thank you very much.