etc is the chain before the fork, the old chain, the classic chain, is the price of more than 8 yuan chain. In this chain, many core members of the currency was stolen hackers. So many developers have abandoned this chain.
eth is the fork after the chain is the price of 80 yuan in the chain, the data is rolled back. A lot of the stolen currency is back, so it is called a pseudo-chain. Originally 80 yuan price should belong to the old chain, but embracing, transformed, 80 yuan price grafted to the pseudo-chain. Many developers to the development of pseudo-chain came.
If you think you should not use a rollback to recover the stolen currency, then you should support etc, which is strictly decentralized.
If you think you should roll back and migrate to these core developers, you should support eth, which violates the irrevocable vows but may be more flexible, easier to scale, evolve, and have more applications in the future.First talk about Ethereum, Ethereum is currently the most widely used to support the development of complete application of the public blockchain system. Compared with bitcoin, Ethereum belongs to the category of blockchain 2.0, which is a blockchain system redesigned to solve some problems in bitcoin networks. Why Ethereum? Because Bitcoin is designed to encrypt digital currency scenarios only, does not have Turing completeness, and lacks the concept of an account that holds real-time status, there is the issue of efficiency and waste of resources caused by the PoW mechanism. The key issue is that in a business environment, there is a need for an efficient consensus mechanism with Turing completeness and support for multi-application scenarios such as smart contracts. So, Ethereum came into being in this situation, its founder is called Vitalik Buterin, known as V God. What is the characteristics of Ethereum? First, it is a universal, global blockchain, meaning that it belongs to the public chain, which is the same as bitcoin and can be used to manage both financial and non-financial types of applications. At the same time, Ethereum is also a platform and programming language, including Ether, the digital currency, and Ethernet scripting to build and distribute distributed applications, known as smart contract programming languages.
As shown, this is one of the biggest differences between Ethereum and Bitcoin - providing a much more powerful contract programming environment. If the function of bitcoin is just the digital currency itself, then on Ethereum, users can also write smart contract applications that directly bring the development of blockchain technology into the 2.0 era. Through the design and development of smart contracts, Ethereum can implement complex logic in a variety of commercial and non-commercial environments, such as crowdfunding systems, digital currency, financial leasing asset management, multiple sign-on secure accounts, supply chain tracking and monitoring. Through the application of smart contracts, the traditional software system can be chained to exert more powerful management capabilities, which is equivalent to hiding the complexity of the underlying technology and allowing application developers to concentrate more on application logic and business logic. The module structure of Ethereum is not essentially different from that of bitcoin, or are the objects such as blockchain ledger, consensus mechanism, core node, P2P network, programmable logic, etc. The essence of Ethereum is the full realization of intelligent contract, Support for a new contract programming language, and an additional Ethereum virtual machine to run the contract. Therefore, when we understand Ethereum, we can basically refer to the structure of Bitcoin. If Bitcoin is a specialized calculator developed using blockchain technology, then Ethereum is a general-purpose computer developed using blockchain technology. In short, Ethereum = Blockchain + Smart Contracts. From a platform perspective, Ethereum is similar to Apple's App Store; Technically, Ethereum resembles a blockchain operating system. Let's take a look at Ethereum's composition:
The smart contract in Ethereum runs on a virtual machine, which is commonly known as the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This is a smart contract sandbox, the contract is stored in Ethereum's blockchain and compiled into Ethereum virtual machine bytecode to run the smart contract through the virtual machine. Because of this middle tier, Ethereum also implements multilingual contract code compilation, and every Ethereum node in the network runs an EVM implementation and executes the same instructions. If Bitcoin is a two-dimensional world, then Ethereum is a three-dimensional world that can countless different two-dimensional worlds. (Ethereum's source is maintained on GitHub: https://github.com/ethereum)
So what is Ether? In fact, like bitcoin, ethernet is a digital currency built into Ethereum. In Ethereum, the concept of a transaction is more general because Ethereum does not only support contractual functions such as transfer transactions, but is defined as follows: In Ethereum, a signed packet stores the message sent from an external account . The so-called transaction is a message, and the message is signed by the sender. In the Ethereum transaction, new concepts of Price and GasLimit are added, in other words, to prevent accidental or intentional infinite loops in the code or other computational waste, each of which requires a limit to limit it The total calculation steps, to put it plainly is to bring the cost of the implementation of the transaction, each transaction must pay a fee. Gas is determined by the amount of contract execution in Ethereum, which can be simply considered as a consumptive resource, such as a SHA3 hash that consumes 20 Gas and an ordinary transfer transaction 21,000 Gas, and so on, all have a price tag in Ethereum's steps that consume computing resources. And the minimum unit of this fee is wei, then every 1000 units by a unit, as follows:
Through the above conversion, we can find that 1ether = 1000000000000000000wei, enough 18 0s. Ethereum itself has built-in support for ether and can also be sent from one account to another. In other words, if Ethereum is a well-established banking system, then Ether is one of the banknotes. Of course, on many exchanges,
Many people refer to the unit they trade as "Ethereum," which is not entirely accurate, but it is already a convention. Let us talk about the difference between etc and eth, the two want to make it clear, we must first popularize a concept and an event. A concept that is hard forked.
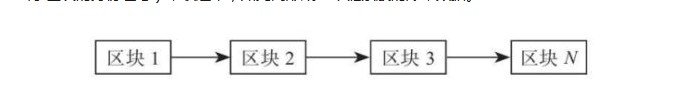
We know that the so-called blockchain, is a block of data, through the hash of the block (equivalent to the block ID number) in series, so as to form a chain-like book data.
So, assuming the block grows to No. 2, then the software upgrade, adding some of the data structure can not be identified in the previous version, what will happen? In the traditional centralized software system, there seems to be no problem, because these centralized systems, data storage is centralized, version management is also focused, if it is a major upgrade, can be set to not update To the latest version can not log in to ensure that users always use the correct version.
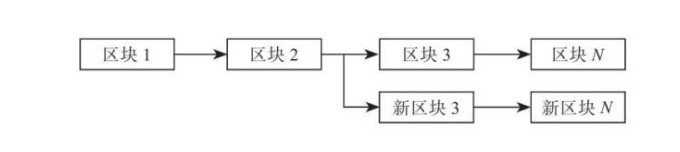
However, the blockchain is inherently a center-to-center approach. Once a new software release is available, is not everyone going to upgrade to a new version that is hard to control? This could lead to problems such as the following: Number of blocks generated when the release of a new version, and the new version adds a data structure can not be recognized before the version, when some users upgrade the new version, some users have not upgraded, these old and new versions of the software are still in their The mining, verification, packing block, after a period of time will become like this:
This is called forked. What is hard forking? When the version does not change to a certain extent, the old version of the node can also know the new version of the node, which is called soft forked. On the contrary, when the old version of the node has no way to recognize the new node after the fork, It's a hard fork The result of a hard fork is to step out of the two chains and separate their own ways. Of course, the "sub-candy" that everyone is keen to follow recently came as a result.
What is an incident? This incident was the attack on TheDAS in June 2016. TheDAO, the largest crowdfunding program in the blockchain industry, was hacked and led to the separation of more than 3 million ether assets from the TheDAO asset pool, which, if based on today's data, is roughly equivalent to 2 billion U.S. dollars. You know, digital money is anonymous. The bank lost $ 2 billion in cash, almost 100% looking for it, and finding a needle in a haystack in the blockchain world.
So this time, the founder of Ethereum V God came out to speak: this matter, I know, or we do not forget, directly to a soft fork, recalculate. Starting from the block height of 1760000 to any transaction related to The DAO and child DAO as invalid transaction, not solved? However, some people have raised objections. They think that smart contracts are contractual. Even if TheDAO team's money is stolen, but as long as the data is written on the block, it is irrevocable and the transfer transaction should be acknowledged. Therefore, they do not cooperate with the divination of V God, still try the old version.
In this way, the soft fork eventually became a hard fork, V God's new ETH is still recognized by most miners and developers, but there are still a few people insist on trying out the old node, when the coins were dug Known as ethereum classic, that is, too classic.
以太坊,以太币, etc和eth的区别,90%的人都被蒙蔽了? 哪个更有前途?
etc是分叉之前的链,旧链,经典链,是价格8元多的链。在这个链上,很多核心成员的币被黑客盗走了。所以很多开发者抛弃了这个链。
eth是分叉之后的链,是价格80元的链,在这个链上,数据被回滚了。很多被盗走的币,又回来了,所以被称作伪链。本来80元的价格应该是属于旧链,但是移花接木,摇身一变,80元的价格嫁接到了伪链上。很多开发者到伪链上做开发来了。
如果你认为不该用回滚的方式找回被盗的币,那么你就应该支持etc,这是严格的去中心化。
如果你认为应该回滚,迁就这些核心开发者,那么就应该支持eth,虽然违背了不可撤销的誓言,但是也许更灵活、更容易扩展、进化,今后承载的应用更多
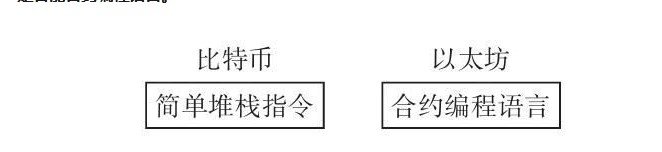
先说说以太坊,以太坊是目前使用最广泛的支持完备应用开发的公有区块链系统。与比特币相比,以太坊属于区块链 2.0 的范畴,是为了解决比特币网络的一些问题而重新设计的一个区块链系统。为什么会有以太坊呢?因为比特币的设计只适合加密数字货币场景,不具备图灵完备性,也缺乏保存实时状态的账户概念,而且存在 PoW 机制带来的效率和资源浪费的问题。最关键的问题是,在商业环境下,需要有高效的共识机制、具有图灵完备性、支持智能合约等多应用场景。所以,以太坊在这种情况下应运而生,它的创始人叫做Vitalik Buterin,人称V神。而以太坊的特点是什么?首先,它是一个通用的全球性区块链,也就是说它属于公有链,这一点与比特币是一样的,并且可以用来管理金融和非金融类型的应用。同时,以太坊也是一个平台和编程语言,包括数字货币以太币(Ether)以及用来构建和发布分布式应用的以太脚本,也就是智能合约编程语言
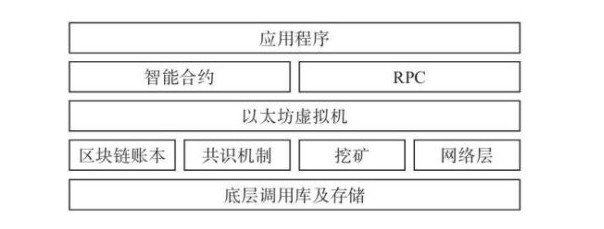
如图所示,这就是以太坊与比特币最大的一个区别——提供了一个功能更强大的合约编程环境。如果说比特币的功能只是数字货币本身,那么在以太坊上,用户还可以编写智能合约应用程序,直接将区块链技术的发展带入到 2.0 时代。而通过智能合约的设计开发,以太坊可以实现各种商业与非商业环境下的复杂逻辑,如众筹系统、数字货币、融资租赁资产管理、多重签名的安全账户、供应链的追踪监控等。通过智能合约的应用,可以将传统的软件系统链化,发挥出更强大的管理能力,相当于隐藏了底层技术的复杂性而让应用开发者更多地专注在应用逻辑及商业逻辑上。以太坊的模块结构与比特币其实并没有本质的差别,还是那些物件,如区块链账本、共识机制、核心节点、P2P 网络、可编程逻辑等,而本质的特点是智能合约的全面实现,支持了全新的合约编程语言,以及为了运行合约增加了一个以太坊虚拟机。因此我们在理解以太坊的时候,基本上可以参照比特币的结构思路。如果说比特币是利用区块链技术开发的专用计算器,那么以太坊就是利用区块链技术开发的通用计算机。简单地说,以太坊 = 区块链 + 智能合约。从平台的角度来讲,以太坊类似于苹果的应用商店;从技术角度来讲,以太坊类似于一个区块链操作系统。我们来看一下以太坊的组成结构
以太坊中的智能合约是运行在虚拟机上的,也就是通常说的 EVM(Ethereum Virtual Machine,以太坊虚拟机)。这是一个智能合约的沙盒,合约存储在以太坊的区块链上,并被编译为以太坊虚拟机字节码,通过虚拟机来运行智能合约。由于这个中间层的存在,以太坊也实现了多种语言的合约代码编译,网络中的每个以太坊节点运行 EVM 实现并执行相同的指令。如果说比特币是二维世界的话,那么以太坊就是三维世界,可以实现无数个不同的二维世界。(以太坊的源码是维护在 GitHub 上的: https://github.com/ethereum) 那么以太币是什么呢?其实和比特币一样,以太币就是以太坊内置的数字货币。在以太坊中,交易的概念是比较广义的,因为以太坊并不仅仅支持转账交易这样的合约功能,它的定义如下:在以太坊中,签名的数据包中存储了从外部账户发送的消息。所谓的交易就是一个消息,而这个消息被发送者签名了。而在以太坊的交易过程中,新增加了Price 与 GasLimit的概念,换句话说就是为了防止在代码中出现意外或有意无限循环或其他计算浪费,每个交易都需要设置一个限制,以限制它的计算总步骤,说白了就是让交易的执行带上成本,每进行一次交易都要支付一定的手续费。Gas 是通过以太坊中合约的执行计算量来决定的,这个计算量可以简单地认为是算力资源的消耗,比如执行一次 SHA3 哈希计算会消耗 20 个 Gas,执行一次普通的转账交易会需要 21000 个 Gas,诸如此类,在以太坊中只要是会消耗计算资源的步骤都有个标价。而这个手续费的最小单位是 wei,然后每 1000 个递进一个单位,如下所示: kwei=1000wei mwei=1000kwei gwei=1000mwei szabo=1000gwei finney=1000szabo ether=1000finney通过以上的换算关系,我们可以发现,1ether=1000000000000000000wei,足有 18 个 0。以太坊本身内置支持了以太币,也可以从一个账户往另一个账户转账发送。换句话说,如果以太坊是一套完善的银行系统,那么以太币就是其中的钞票。当然,在很多交易所上,很多人都将交易的单位也称为“以太坊”,这其实并不完全准确,但是也已经是约定俗成了。我们再来说说etc和eth的区别,这两者想要讲清楚,就要先普及一下一个概念和一个事件。一个概念,就是硬分叉。我们知道,所谓区块链,就是一个个的区块数据,通过区块的哈希值(相当于区块的身份证号)串联起来,如此而形成一个链条般的账本数据。
那么,假设在区块增长到 2 号的时候,此时软件升级了,增加了之前版本中不能识别的一些数据结构,会发生什么?在传统的中心化软件体系中,似乎并没有什么问题,这是因为这些中心化的系统,数据存储都是集中的,版本管理也是集中的,如果是重大的升级,完全可以设置为若不更新到最新版就不能进行登录操作,从而确保用户使用的总是正确的版本。然而区块链先天是去中心的使用方式,一旦有新的软件版本发布后,是不是每个人都会去升级到新版本是很难控制的,这就可能导致如下图所示的问题:在 2 号区块生成的时候发布了新的版本,且新的版本增加了之前版本不能识别的数据结构,此时部分用户升级了新版,部分用户还没有升级,这些新旧版本的软件仍然在各自不停的挖矿、验证、打包区块,一段时间过后就会变成这样
这个就叫分叉。那什么是硬分叉呢?当版本变动没达到某个程度,老版本的节点就还可以认识新版本的节点,这叫软分叉;而反之,当老版本的节点已经没办法认识分叉后新出现的节点,那么这就是一次硬分叉了。硬分叉的结果就是走出两条链,各自分道扬镳,当然,最近大家热衷的“分糖果”也是由此而来的。一个事件,是什么呢?这件事情就是2016年6月的TheDAS被攻击事件。区块链业界最大的众筹项目TheDAO遭到黑客攻击,导致300多万以太币资产被分离出TheDAO 资产池,如果按照今天的数据,那么大概相当于20亿美元。要知道,数字货币是匿名性质的。银行丢了20亿美元现金,想找回来的可能性几乎是100%,可在区块链世界里就是大海捞针。所以这个时候,以太坊的创始人V神出来说话了:这个事情,我知道了,要不我们就都别算了,直接来个软分叉,重新算账。从块高度1760000开始把任何与 The DAO和child DAO相关的交易认做无效交易,不就解决了吗?然而,还是有人提出来反对。他们认为,智能合约是具有契约性的。哪怕TheDAO团队的钱被偷走了,但是只要数据被写在了区块上,就是不可撤销的,这笔转账交易应该被承认。因此,他们并不配合V神的分叉,依然试用老版本。就这样,软分叉最后生生搞成了一次硬分叉,V神的新ETH依然获得了大多数矿工和开发者的认可,但是还是有少数人坚持试用老节点,这时挖出来的币被称为ethereum classic,也就是以太经典。