Under the collective name Serenity or Ethereum 2.0, the second most successful blockchain is working on the market for new solutions for its known vulnerabilities. After a long puzzling, now finally there seems to happen an activation in the matter. Are the first goals of the roadmap still to be achieved in 2019?)
Vitalik Buterin presented the concept of Ethereum 2.0 in detail already at the Devcon 2018. The goal is to make some changes and restructurings that improve the scalability of the blockchain and reduce transaction costs. These measures are all summarized in the Serenity phase.
#ethereum #bitcoin #serenity #blockchain #cryptocurrency #scalability #vitalikbuterin
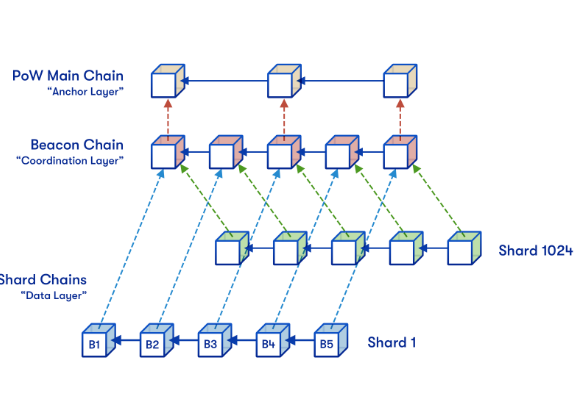
How System Works?
The new model can be explained in three parts;
1-Main Chain: It is the previous original Ethereum Blockchain.
2-Beacon Chain: It is a coordinating and validating layer. Its consensus algorithm is Casper (PoS). The Beacon Chain replaces Miner with validators. If a validator wants to participate in the review of shard blocks, he must first deposit a fixed amount in ether in the Validator Main Contract (VMC). The VMC is a smart contract that is stored on the main chain. The beacon chain regularly checks the smart contracts for new validators and then adds them to a list. From this list, the waiting validators are then assigned to random shards. In addition, existing groups of validators are regularly remixed. This sampling process is critical for the security of Ethereum 2.0. Because of the random distribution, the validators can make no collusion with each other and perform 51% attacks on individual shards.
3-Sharding Chain: This is where the Smart Contracs are executed and their data stored. Ethereum is based on traditional databases and their sharding techniques. Both transaction processing and blockchain data storage are divided into multiple computer groups called shards. Every shard is like its own little blockchain. Ethereum addresses, account balances and smart contract data are split between these shards. When a transaction is sent to the network, it is executed in the shard that has the address that signed the transaction. As a result, only a subset of all the computers involved in the whole network have to deal with this specific transaction, which significantly reduces the burden on participants.
Who deals with the blockchain technology, will quickly stumble over the problem of scalability. Many blockchain projects are trying to get this problem under control. As a guide value for a sufficient transaction rate the performance of Visa with several thousand transactions per second is well taken a model. Currently, however, Ethereum can only handle about 15 transactions. However, this is not enough for the mass acceptance of blockchain and everyday use. In 2017, Ethereum experienced an overload of its blockchain several times due to ICOs and the massive trade in collectibles such as cryptokitties.
But why is the scalability solution such a big problem? There are several approaches to solving the problem, but none has been satisfying so far. Vitalik Buterin called it a blockchain trilemma. Because the approaches presented so far can only guarantee 2 of the 3 pillars of the blockchain. These are: security, decentralization or scalability. As a result, one would have to sacrifice either a piece of decentralization or a piece of security to achieve more scalability. Ethereum 2.0 wants to achieve that this trilemma is solved. With the implementation of Serenity, Ethereum would be able to process up to 15,000 transactions per second without moving away from the decentralized model or risking security.
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://medium.com/@thecryptoconsultant/ethereum-2-0-consensys-publishes-roadmap-to-serenity-e1ce76fa34f2