Hello friends and brothers of steemchurch, farms, for those who are in tune to create a farm to feed the world, I present an important element...
The seed is the structure that is inside the fruit, from which, a new plant is produced.
If we are going to start an orchard, it is normal to buy the seeds to start cultivating, but if we already have a little experience, to the pleasure of growing our own vegetables, we can unite to produce our own seeds.
In this way, apart from obtaining seeds with characteristics that we want to achieve, we will know the whole cycle of our plants, we will see them glean, flourish and bear fruit.
We must make a good selection, we will choose the most vigorous, tasty, productive and resistant plants.
One of the most important things in a garden is seeds. Good seeds will help you to have better germination, growth, harvest and later seeds.
To start a good ecological garden, the first thing is to approach the "world of seeds" and know what is its importance. We must think that the seed is the instruction kit for the development of the plant, and therefore the success of the germination, growth, harvest and future seeds that we obtain will depend to a great extent on the state of the seed or seed.
Many times we will make mistakes and believe that our mistake was due to poor irrigation, sunstroke, pests, lack of nutrients ... and in fact many times it may be due to a bad seed. In summary, the quality of the seed is fundamental, we must check several aspects to avoid a bad seed:
Immaturity in the collection of seeds (there is a physiological and morphological maturity)
Nutrient deficiencies during the growth of the plant
Aged seed
Physical damage in handling or conservation
Pests and diseases of the plant
Genetic issue of the species (size, taste, color, precocity, resistance to pests ...)

WHAT SEEDS DO YOU USE AND WHERE TO FIND THEM?
Normally when we make our first orchard, we usually buy some conventional seed packets to try. To start in horticulture is fine, but in the future, it is advisable to start using local or rural varieties of the area, which adapt better to the climate and soil of the area, and therefore will give us greater guarantee of success in our orchard. In addition we will be contributing to conserve and maintain the biodiversity of agriculture, which is missing from it.
Important, to see where those seeds are from ...:
The seeds obtained from vegetables on the market run the risk of not having sufficiently matured in the fruit or being a seed of a hybrid F1 commercial variety. Hybrid seeds are not transgenic seeds, but they are not recommended if we want to create our own garden seed bank. Although the F1 plants are very vigorous and have a high production and beautiful shapes and colors, they do not produce seeds with the same qualities, lowering their performance in the second year. We would have two options: buy new F1 seeds or carefully work several crops for years to recover the F1 generation again.
Some seeds of commercial envelopes are treated with chemical products, we can be sure because many have a very striking color powder: pink, gray, bright blue.
The purchase of organic seeds and the exchange with other gardeners and farmers guarantee us excellent seeds for our urban garden.
Poorly preserved or old seeds: odors of moisture, absence of embryo, easy to break (indicator that they are too dry)
Below I will give you some tips so that you can start building your own seed bank:
-The first thing is to observe well the plant from which you will get the seeds, I hope that plant is not with any plague or fungus.
-The seeds that are not covered from the outside, the ideal is to take them out and store them immediately, as they are more influenced by environmental conditions.
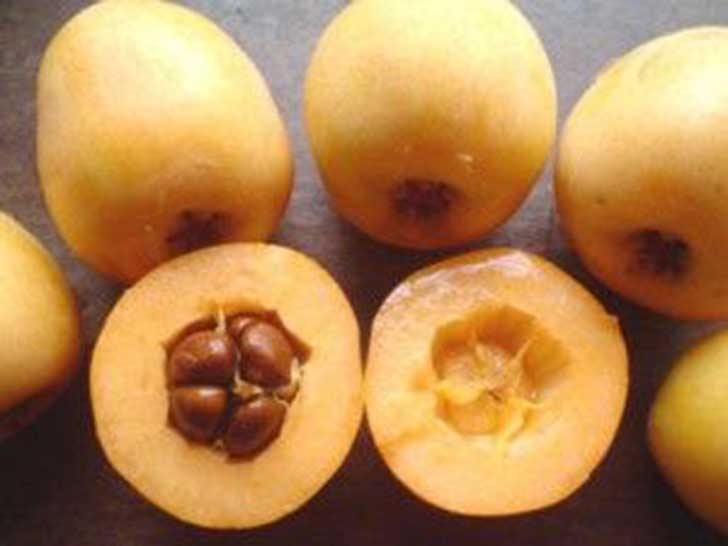
-The seeds that come inside a fruit, it is very important to put a tutor so that the fruit does not have contact with the earth and rot. For the collection of this type of seeds, the fleshy part of the fruit containing the seeds is removed and allowed to dry. Or you can also let the fruit dry on the plant and then collect them.
-In the case of tomato and cucumber, you must extract the pulp and let it ferment in a glass, when you see a white fungus, you have to strain the seeds and let them dry, with this, pathogenic microorganisms are eliminated, and the gelatinous covering of the seeds, therefore, will germinate better.
How to obtain the seed of the vegetables
1-Select one or two bushes of the crop that interests you, of medium size. Observe that the plants are strong and healthy, that they show no symptoms of disease or damage by pests, since if they are sick or attacked by insects they can be weakened and therefore affect the subsequent development of the seeds.
2-Let them mature to the fullest, even beyond the point of consumption.
Collect the fleshy fruits, such as eggplant or cucumber, when they soften; and the pods (peas and beans) when they dry and start to open.
3-Separate the seeds from the rest of the fruit. You can wash them under running water using a strainer, if it is easier to clean them. Spread them on a tray and let them dry for a week or so in a ventilated place, dry and in the shade.
4-To preserve them, store them in an airtight jar and a dry place. The tubes of effervescent tablets are perfect for this, because the stopper usually contains a desiccant agent that absorbs moisture. If not, use a plastic bag for food and put it in the refrigerator's vegetable tray
5-Take them out at planting time, and plant pumpkins!
Some tips for getting seeds at home
-To start, I recommend you pick the seed of vegetables with fruit, because they are easier to pick up than others such as leafy vegetables, such as chard or lettuce, which must be left to glean and whose seeds are very very small. Some of the vegetables from which we can obtain the seeds are: eggplant, cucumber, zucchini, pumpkin, pepper, haricot, pea, melon or watermelon.
-For the seeds to germinate well later, be sure to choose those that have a thicker appearance, because, generally, they will have more reserves than other finer ones.
-Before planting, put them in a container with water for a few hours. You will find that some float, and some do not. Get rid of those that float, they probably are not viable. Also, by soaking them, we soften the seed coat making it much easier for the germ to go outside.
-It is useless to harvest hybrid varieties, since their viability is very limited in most cases and, in the case that the seeds are viable, the offspring will probably be very different from the parentals from which we have obtained the seeds, especially in terms of performance.
-We usually collect more seeds than we actually use. In that case, you can keep them for the next year or, what is better, encourage you to make exchanges with neighbors or through the Internet on barter pages.
Some exceptions of plants that do not reproduce by seeds
Some aromatic plants such as parsley, dill, coriander or thyme will "reseed" spontaneously if you let the flowers dry on the stems. When they have dried, usually in late summer, shake them by hand before cutting them. The seeds that fall will germinate the following spring. Have the seedlings located and then transplant them where it suits you best.
In the case of potatoes, the "seed" is a tuber, that is, a potato, which is buried again in the soil, since in this way it is much easier to multiply.
Seed conservation:
It is very important to preserve the seeds properly. For this we must think about the conditions contrary to germination. That is to say; if for a good germination you have to have; light, humidity, oxygen and heat, for conservation you must have; Low humidity, low temperature that reduces oxygen and no light.
Then you should dry the seeds well and put them in dark envelopes or store them in tightly closed glass jars. And leave them in the refrigerator or in dark and cool places. To avoid humidity you can mix your seeds with rice.
The feasibility of a seed to germinate and give rise to a new plant. These can remain viable for a certain amount of time or years, from one year to 10 or more years. Actually, a batch of seeds in a Seed Bank does not lose its viability in a sudden way.


This is truly useful to us @farms. Indeed we @farms find this post informative and educative, thanks for sharing
Resteem
(to be a part of this community; ensure to always use #farms and #steemchurch for agricultural related post)