.png)
Digital currencies, also known as cryptocurrencies, and Blockchains have become very pervasive in recent years, especially in the act of sending or receiving money or paying remittance; However, there is a problem is comes with the utilization of these digital currencies and platforms which makes it cumbersome to keep pace with their demand on the market. The pioneers in this business are the Bitcoin and Ethereum cryptocurrencies.

These currencies utilize what is referred to as “blocks” in processing their transactions. In the case of Bitcoin, its fullest size of the blocks was restricted to 1 Megabyte; this was meant to make the Bitcoin very secure, and it did not raise any concerns in its early stages since few transactions occurred. This framework has failed to rapidly serve the myriad of transactions which happens every day due to its mass adoption. Bitcoin can handle very few transactions every second. This translates into high fees and slow confirmations on the blockchain due to delays. This makes it unattractive to many businesses and consumers. Unfortunately, Ethereum likewise suffers the same disease with its capacity to process 15 transactions every second.

Hence measures should be taken due to the high probability that future digital transactions may even take much longer time to be processed, and they may also come with higher fees. Sadly, augmenting the capacity of these blockchains is far from easy due to several factors such as cost, the disparity of opinions on the size of the expansion, and many others.
image source: ccnews24.net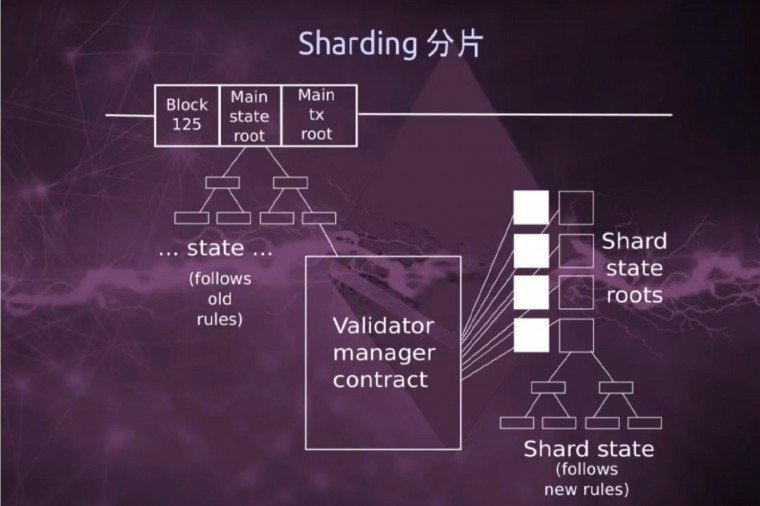
Some of the alternatives to solving the issues regarding scalability include Sharding, Plasma, State Channel, and several others. Some of the alternative solutions come at the expense of security and decentralization. The scalability solution that has the ability to address issues regarding security and decentralization is called Sharding, which simply apportions a chain state into minute segments called shards. Nodes found in a shard ought to process every single transaction that originates from that specific shard. As a result, the total transaction throughout grows linearly as the number of shards also increase. The data stored in a shard can be shared amongst other nodes, this contributes to the ledger’s decentralization and security because all the ledger entries are transparent. The first public blockchain that resorted to Sharding in dealing with the scalability is known as Zilliqa; however, their approach had its shortcomings. For one part, the storage of blockchain data ware not apportioned, and this restricted machines with limited resources from engaging in the network. For the other part, the Sharding process utilized in Zilliqa is prone to attacks since it depends on the Proof of Work as its arbitrary generation mechanism.
When it comes to issues regarding public blockchains, consensus protocols becomes one of the obstinate problems to address. Consensus Protocol is fundamentally about reaching an agreement from users on the issue of the authenticity of the proposed transactions and whether they should be an addition to a distributed ledger; Proof of Work (PoW) mechanism is the popular consensus protocol. In a Proof of Work (PoW) based blockchain, each node which is authenticating stores every data on the chain and becomes a member of the consensus process. PoW’s security is based on the notion that over 50% of the hashing power is controlled by honest nodes.

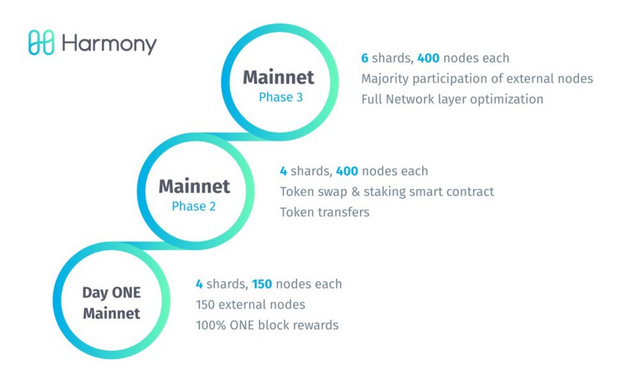
To efficiently combat the issue of scalability, an ultramodern Sharding-based blockchain called Harmony was developed by business and academia experts with the zeal to make the world a better place for everyone.

Harmony stands tall amongst other Sharding variants due to the following features which are lucidly imprinted in the Harmony whitepaper as follows:
"
Fully Scalable: Harmony shards not only the network communication and transaction validation like Zilliqa, but also shards the blockchain state. This makes Harmony a fully scalable blockchain.
Secure Sharding: Harmony’s Sharding process is provably secure thanks to the distributed randomness generation (DRG) process which is unpredictable, unbiased, verifiable and scalable. Harmony also reshards the network in a non-interruptive manner to prevent against slowly adaptive byzantine adversaries.
Efficient and Fast Consensus: Unlike other Sharding-based blockchains which require
PoW to select validators, Harmony is based on PoS and thus energy efficient. The consensus is reached with a linearly scalable BFT algorithm that’s 100 times faster than PBFT.
Adaptive-Thresholded PoS: The threshold of stakes required for a node to join the network is adjusted based on the volume of total staking in a way that malicious stakers cannot concentrate their power in a single shard. Moreover, the threshold is low enough so that small stakers can still participate in the network and earn rewards.
Scalable Networking Infrastructure: With RaptorQ fountain code, Harmony can propagate blocks quickly within shards or across the network by using the Adaptive Information Dispersal Algorithm. Harmony also adopts Kademlia routing to achieve cross-shard transactions that scale logarithmically with the number of shards.
Consistent Cross-Shard Transactions: Harmony supports cross-shard transactions with shards directly communicating with each other. An atomic locking mechanism is used to ensure the consistency of cross-shard transactions. "
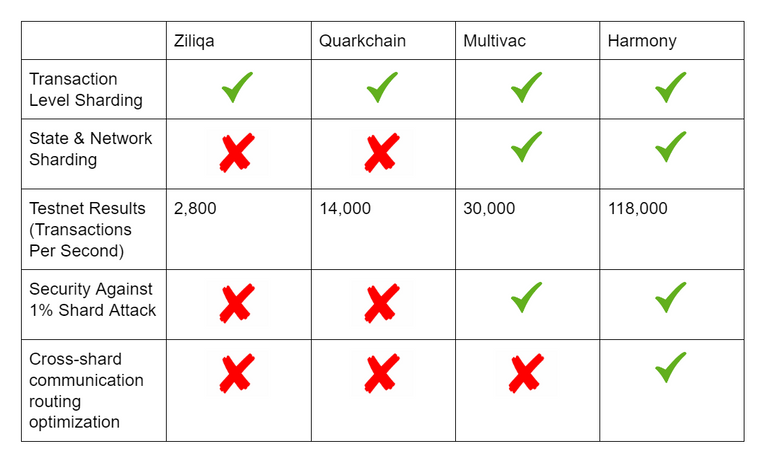
Comparison Table to other leading PoS blockchains:
As mentioned earlier, Harmony utilizes linearly scalable and secure PoS-based full Sharding framework. Harmony comprises chiefly two chains: a multiple shard chain and a beacon chain. The beacon chain functions as the arbitrary beacon and identity register, whereas the shard chains record separate blockchain states and at the same time processes the transactions. Harmony’s efficient algorithm combines Verifiable Random Function (VRF) and Verifiable Delay Function (VDF). Additionally, Harmony uses PoS in its Sharding process which changes the security consideration of a shard from the least number of nodes to the least number of votes shared. In the Harmony ecosystem, the consensus and Sharding process are planned by the ideology of epochs. An epoch is basically the predetermined time lapse during which the Sharding framework is fixed and every single shard continuously performs consensus with the same set of validators. In order for a participant to become a Harmony validator, prospective stakers need to stake a certain number of tokens in order to be eligible. The number of tokens staked will, in turn, decide the number of voting shares to be assigned to the validator.
In the case where an epoch is over, the validators which take out their stakes are thereby removed from the network. The validators who remain obtain new voting shares for the subsequent epoch. The new shares are assigned arbitrarily to other shards that possess more voting shares than the median of the whole network; then some consistent amount of all shares will be disbursed to shards that have less voting shares than the median of all voting shares. This, therefore, means that shards used in Harmony do not need to reset from scratch whenever an epoch comes to an end. Hence, the computational requirements will be minimized.
Harmony has realistic use cases. Below are a few examples I managed to come up with:
- Sarah sells coffee at her shop. Remittances were usually paid in fiat, but due to the notoriety of cryptocurrencies, she decided to accept cryptocurrencies. Initially, she tried the major cryptocurrencies; however, she encountered several problems with her huge number of customers she had because the payment was very slow and came with huge fees. Sarah began to lose hope in cryptocurrency until she came across Harmony. Now, the plethora of payments from her customers are processed successfully in real-time and are secure as well with little fees. Sarah is now happy and can’t stop recommending Harmony to everyone.
- Frank is an avid gamer. He recently embarked on the journey of setting a video platform where his fans could watch him play and have the option to tip him money without any hassle. Frank needs a reliable blockchain to set his platform on. He tries other blockchains recommended to him, but he realizes that most of the platforms are slow, insecure, and also come with significant transaction fees. Furthermore, it takes longer for several tips to be received from his fans. Harmony comes in, and it is everything Frank prayed for.

For more information about Harmony, visit them at https://harmony.one/
#harmonyone