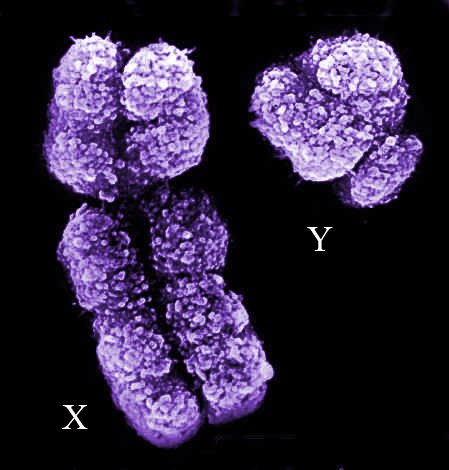
RegardsWithin the human genome there are 23 pairs of chromosomes, that is to say that in total we have 46 chromosomes (normally) among which we have two sex chromosomes known as "X" chromosome and "Y" chromosome.
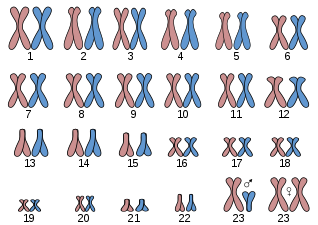
When the chromosome pair number 23 is composed of a double X chromosome, "XX", the sex of the individual is female.If the chromosomal pair on the contrary results in "XY", the sex of the individual is masculine.
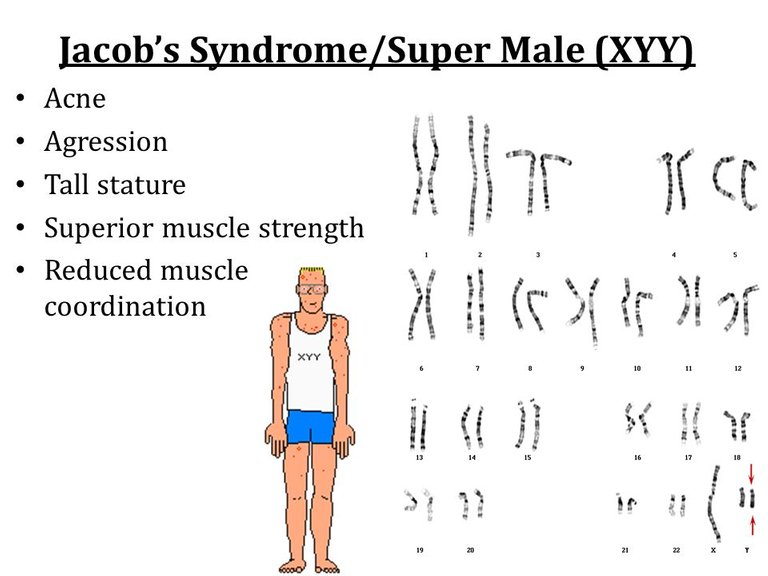
There are other circumstances in which it does not turn out to be a pair but a chromosomal trio "XXY" or "XYY", abnormal syndromes that affect the sexuality or morphology of the individual.
Now which predecessor distributes the genes?As we said that the pair "XX" is feminine, the mother can only provide a chromosome that will have a 100% probability of being an "X" chromosome (only option).The father, therefore, by having the chromosome pair "XY", will provide a chromosome that will have a 50% probability of being the "X" chromosome or being the "Y" chromosome, which will define the sex of the fetus.
Conclusion
The distribution of chromosomes of the father's par 23 will determine the sex of the fetus.