Firstly it is important to understand the possible causes of amputation in the upper limb and we may have to look at it in the following categories:
- Trauma – Resulting from road traffic accident (RTA), domestic accident, industrial/occupational injury etc.
- Disease/Infection – Resulting from arteriosclerosis, embolism, thrombosis etc.
- Congenital malformation - Resulting from excessive exposure to radiation, drug abuse, attempted abortion etc.
- Cancer/Tumor of the bone or skeletal system – Resulting from Osteo Sarcoma, Malignant tumor.
- Frost bite.
- Cultural and religious beliefs.
Types of Amputation
Amputations are mainly classified in three types:
- Traumatic – it does not give room for surgical finish and not usually a planned amputation, no particular method is employed.
- Surgical – Classical or revised.
- Congenital – Polydactyl, Amelia etc.
Levels of Upper-Limb Amputation.
This depends on the region of the upper-limb that is affected, the naming follows the region e.g Transhumeral (through the humerus bone), elbow disarticulation, trans-radial (through the radius bone), wrist disarticulation, partial hands amputation/mutation.
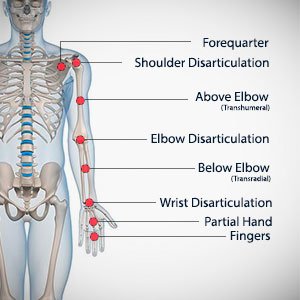
The levels may fall on long medium and short in respect to the region/part of upper-limb involved.
Effects of Upper-limb amputation.
You may see the following as the possible and most common effects of upper limb amputations from the amputee to his environment.
Amputee: Loss of self image, reduced earning capacity for living and limitations of activities for daily living (ADL)
Relations: Abscondment of close relations, diminished/inadequate support in terms of attention, financial and communication.
Society: Stigmatization, pity as opposed to empathy.
Government: Lack of job opportunities, lack of basic infrastructures.
Prosthetic Rehabilitation of The Upper-Limb Amputee.
The considerations in prosthetic rehabilitation of amputees could be classified into the categories and sub-categories. I will briefly take a close look on these considerations.
- Rehabilitation.
- Psychology of amputation.
- Functional limitations
- Functional failures.
- Pain related to prosthetic wear /phantom
- Societal perspectives
- Vocational and economic factors
- Auditory (noise) considerations
Rehabilitation: This is the process of restoring an individual with physical challenge to his pre-state (pre-accident period), or restore to normal or more normal condition. Rehabilitation of an amputee involves teamwork which includes the efforts of Surgeon, Physiotherapist, Prosthetist/Orthotist, Occupational therapist, Psychologist and Social workers etc.
Psychology of amputation: This is the thinking or attitude of the amputee towards his/her loss. I will thus narrow our discussion to the subcategories of psychology of amputation.
Functional limitations involves limitation or problem the amputee is facing as a result of the loss. For example, the loss of the right upper extremity in a right handed person is a functional lost and a limitation. Adapting to the use of alternatives may not be easy, perfect and even take time.
Functional failures: This results as failure even of the willingness of the amputee to adapt to the use of the prosthesis. An amputee may will to make effective use of the device to mimic the natural lost which fails most of the time. For example the inability to use the dexterity of the prosthetic hand.
Pain related to prosthetic wear: The most common pain related to prosthetic wear is phantom pain which is a sensation of pain coming from an amputated part of the body or in which the nerves have been destroyed, the amputated limb will now present false sensation.
Societal perspectives: In the sense or related to stigmatization, seeing the person/victim with pity and being deprived of holding position/office in the society.
Vocational and economic factors: Loss of the upper limb may result in loss of vocational jobs, earnings and even one’s professional job. Loss of job is like loss of economic status of the individual as one may not be able to meet his basic needs.
Auditory/noise considerations: This is mainly the noise or sound coming from friction within the mechanical components of the prosthesis.
Bilateral Bebionic hand prosthesis
Goals of rehabilitation
- Restorations of pre-accident state.
- Adaptation to a new life.
- To discourage stigmatization of any kind.
- Restore personality.
Thank you for reading this far. I hope you found this very educating. In another post we will discuss the upper-limb prosthetic componentry parts and the alignment principles of the upper-limb prosthesis. But that would not be before discussing Amputee Locomotion in the next post.
Image source: CPOUSA