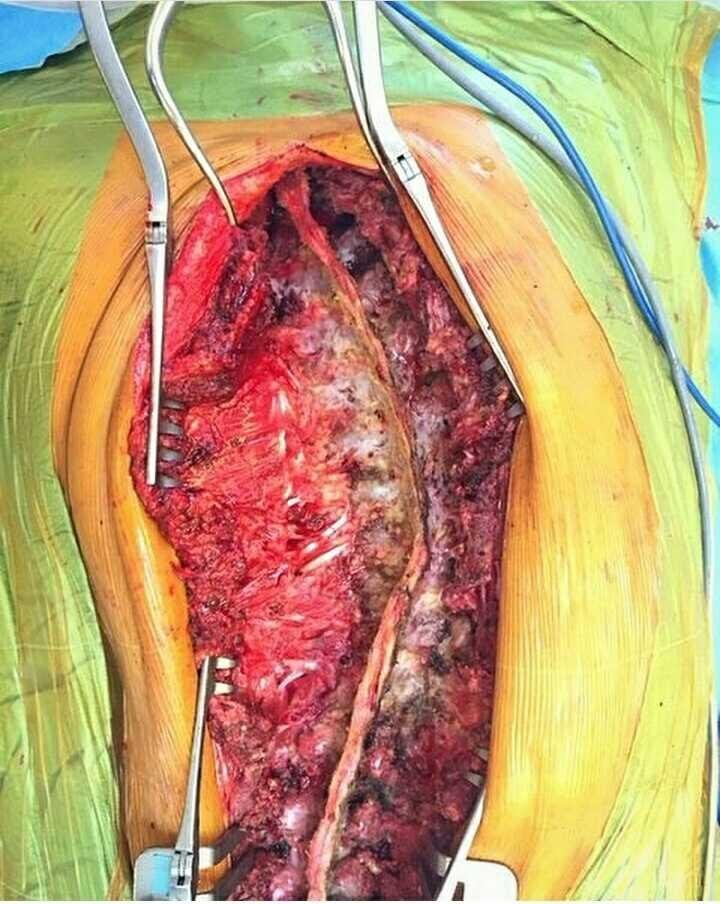
scoliosis is a progresisive diases that leads to an abnormal curvature of the backbone or spine. in all cases, prior corrective surgery,the degree of the spinal deformity is measured by cobb angle, with scoliosis defined as a lateral spinal curvature with a cobb angle of 10 derajat or more.
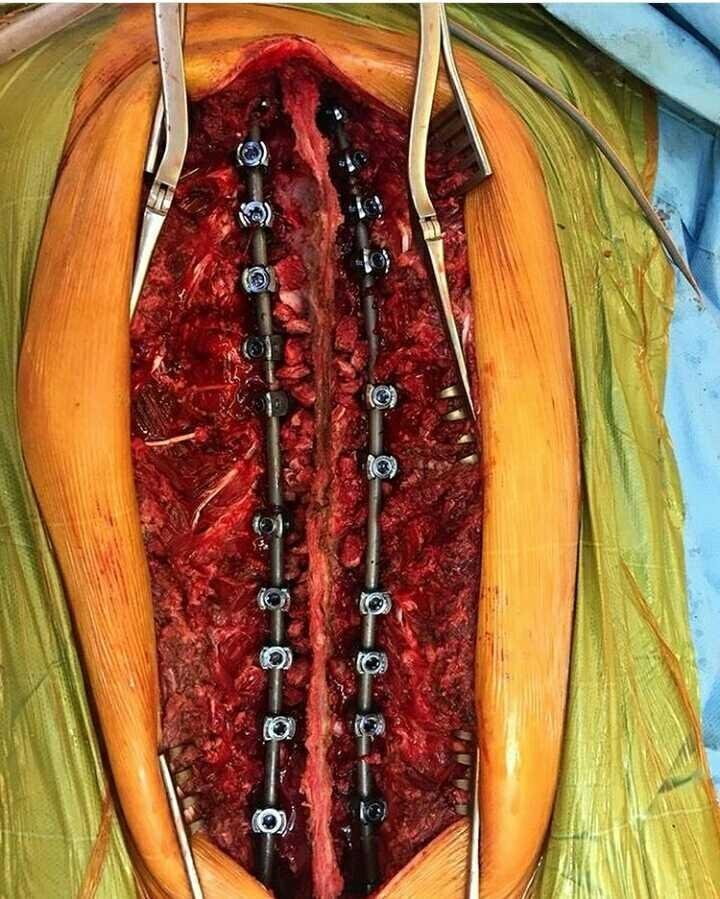
reasons for scoliosis are broad, including congenital (from birth), neuromuscular scoliosis seen in spina bifida and patients with cerebal palsy, degenerative scoliosis due to a trauma, major previous back surgery ,or osteoporosis, and idiopathich scoliosis with no apparent reason. scoliosis surgery typically involves the use of modern instrumentation system in which hooks and screws are applied to the spine to anchor long rods, ensuring the correction of the curvature and its stability over time.
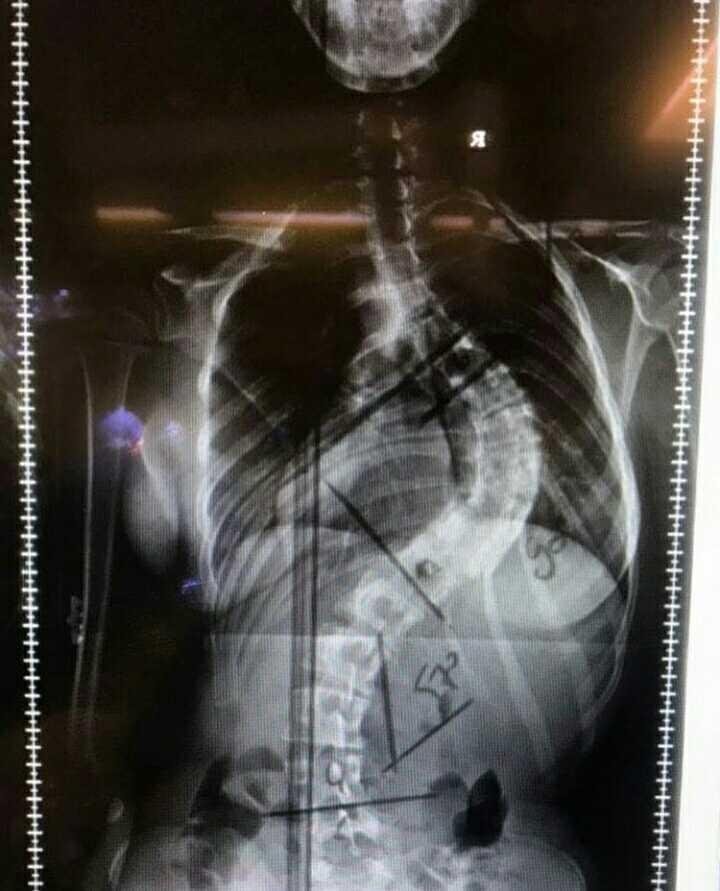
To see if a person is affected by scoliosis then it can be done by physical examination. In addition to the physical examination, some forms of imaging tests will be used to look at bone conditions more clearly. The types of checks in this group include:
🌷X-rays or rongsen: using radiation to create a picture of the spine.
🌷MRI: using radio waves and magnets to get a detailed picture of the bones and surrounding tissues. 🌷CT scan: X-rays are taken at various angles to get a 3D picture of the skeleton