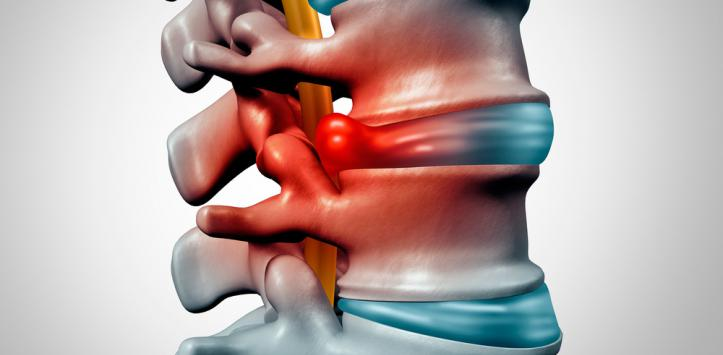
The spine, also called the spine, is a complex consisting of 26 bones called vertebrae. Between the vertebrae there are soft discs filled with a gelatinous substance; in these discs they support the vertebrae, which are thus kept in place. Over the years, discs can go to rupture or degeneration and this causes the loss of their ability to pay off and possibly the onset of back pain. The herniated disc is the name given to this process, which then identifies the damage to the intervertebral disc; the disc is subject to a movement that can cause irritation of the neighboring nerves, with the consequent appearance of back pain and sciatica
The diagnosis usually occurs through a medical examination and possibly imaging tests; the treatment, in many cases unnecessary, can foresee
• Anti-inflammatory drugs
• Physical therapy,
• Sometimes surgery.
Can it heal spontaneously from the herniated disc?
A herniated disc usually improves with a conservative treatment and it is not always necessary to resort to surgery, let's see why.
We start from a fundamental concept, the hernia ejected does not fall and from this point of view there can be no spontaneous healing, but there are two mechanisms that can take over:
The expelled fragment undergoes evolution phenomena of physiological adaptation, in particular it dehydrates, thus losing a great part of the volume and finds a position and a more neutral conformation towards the adjacent structures responsible for the pain. This is a mechanism that occurs in the three months after the expulsion of the hernia in approximately three out of four cases, for this reason the current trend is increasingly oriented towards a conservative approach in the first months after diagnosis.
In case of protrusion of the disc and the presence of a small hernia, the increase in muscle tone of the back that can be achieved through a gymnastic path and improve posture is able to allow at least a partial regression of protrusion
Causes
The vertebral column is formed by 24 bones called vertebrae (26, if we consider sacred and coccyx in the count) stacked one on top of the other.
Between one vertebra and the next there are circular formations of connective tissue (cartilage) called discs, which are characterized by an internal gelatinous substance (nucleus) and a harder outer layer (ring); its function is to help maintain the necessary flexibility to guarantee the wide range of possible movements of the back
The spinal cord is a bundle of nerve fibers through the spinal column; These nerve fibers connect all parts of the body with the brain and allow the transmission of nerve signals in both directions (from the brain to the periphery and vice versa).
The damaged disc can put pressure on the entire spinal cord or on a single nerve fiber, at the point where the nerve moves away from the spinal cord; This means that the herniated disc can cause pain in the affected area (back pain) and also in the area of the body controlled by the nerve that undergoes pressure in the nucleus.
It is not always clear what causes degeneration and disc failure, but age is one of the most common factors; When you grow, the discs begin to lose their water content (dehydrate), becoming less flexible and more prone to breakage.
Risk factor's
Risk factor's
• Several factors make it more susceptible to a herniated disc:
• Age. Disc hernias are more common in middle age, especially between 30 and 50 years, due to disc degeneration related to age.
• Men are twice as affected as women.
• Smoke. Smoking tobacco increases the risk of disc herniation because it decreases oxygen levels in the blood, depriving the body's tissues of vital nutrients and, therefore, reducing the elasticity of the disc.
• Weight. Excess body weight causes additional stress on the discs in the lower back.
• Height. Being high increases the risk of herniated disc. Men over 180 centimeters and women over 170 centimeters seem to have a higher risk of suffering a herniated disc.
Occupations that stretch the spine. People with physically demanding jobs have a higher risk of back problems. Lifting, pulling, pushing, bending sideways and repeatedly turning the back can increase the risk of herniated discs. Jobs that require a prolonged sitting position or standing in the same position may increase the risk of a disc slipping.
• A sitting position for long periods of time, for example, while driving.
• Weight lifting practice.
• Serious back injuries, such as a fall or car accident
This happens when the part of the ring that breaks is small and does not cause pressure on the nerves and the spinal cord.
Most patients with herniated discs suffer instead of pain experienced on one side of the body, which starts slowly and gets worse over time. The pain tends to get worse in situations where pressure is exerted on the nerve, for example, when coughing, sneezing or sitting.
When present, symptoms may also vary depending on the location of the affected disc:
• Herniated cervical disc (neck):
• Neck pain during movement,
• Numbness or tingling in the neck, shoulder, arm or hand,
• Muscle weakness, which can limit the range of possible movements.
• Herniated lumbar disc (lower back):
• Back pain during movement,
• Feeling of numbness or tingling in the back, buttocks, genitals, legs or feet.
Sciatica
Sciatica
The sciatic nerve is the longest nerve in the body and is made up of several smaller nerves; runs from the back of the pelvis, through the buttocks, to reach the legs and feet.
In the case of herniated disc that presses on the sciatic nerve, classic symptoms of sciatica (or sciatica) may appear, even with very intense pain and tingling in the leg, hip and / or buttocks.
Other nerves
If the disc presses on any of the other nerves that descend along the spinal cord, symptoms may include:
• Muscular paralysis,
• Muscle spasms (sudden and painful contractions)
Dangers
Although it can be painful, a herniated disc is usually not a medical emergency.
The exception is horsetail syndrome, a rare but serious condition caused by compression of the nerves at the base of the spinal cord; Symptoms include:
• Lumbar back pain (that is, lower back)
• Numbness felt at the level of the groin,
• Paralysis of one or both legs,
• Rectal pain
• Loss of intestinal control (intestinal incontinence),
• Loss of bladder control (urinary incontinence),
• Internal pain in the thighs.
This is a medical emergency that requires immediate hospital assistance, because in the absence of treatment, the nerves of the bladder and bowel can be irreparably damaged.
Treatments
The treatment for the herniated disc depends largely on the type of symptoms, the affected area and, above all, the functional limitations and normal daily activities that the person is going to fulfill.
For the most serious cases, we have the surgical approach, which is increasingly discouraged for less severe cases whose prognosis varies from a minimum of 4 weeks to a few months.
To accelerate these times, it is possible to use medications and physical therapies, but it is above all a conservative treatment, consisting mainly of physiotherapy to obtain the best results:
• Postural gymnastics
• Mobilization exercises
• Proprioception exercises
• Central stability training
• Targeted muscle strengthening and stretching exercises
• mobilization
• Massages, manual and fascial therapy
• Treatment of compensation contracts and trigger points
This is only part of the treatments that can be applied and that will be different according to the present symptoms and especially the affected area.
There are also additional complementary approaches or alternative remedies such as plantar reflexology, acupuncture or other very useful methods in several cases.
herniated lumbar disc.