HELLO FELLOW STEEMIANS,
I am here with a new series of medical science entitled with ophthalmology cases. In this series i will be posting numbers of ophthalmology cases with their signs, symptoms, pathology, their causes and treatment.
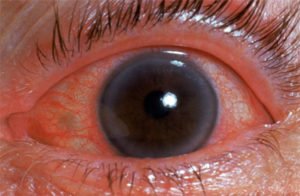
Today i will be posting about simple topic Red Eye, Its causes, symptoms, treatment and complications.
First I will like to tell about normal eye and I will tell about Red Eye throughly.
- Eyeball consists of 3 protective layers.
- sclera ( The whitish portion of the eye)
- cornea ( The transparent layer, through which the light passes into lens and retina)
- Uveal tract ( consists of choroid, ciliary body and iris)
Beyond the cornea there are no. of structures through which light pass and finally forms image in the retina as you can see in the figure.
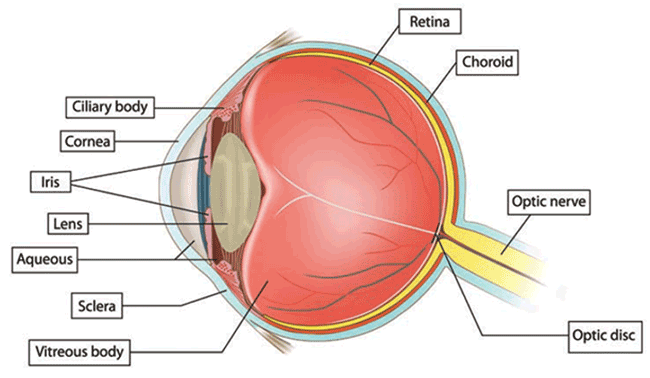
- Anterior chamber ( contains transparent fluid known as aqueous humour)
- pupil ( circular opening in front of the lens)
- iris
- lens
- vitreous chamber
- retina
Now I am going to talk about Red Eye. Red Eye may be painful and painless
Causes of painful Red Eye are as follows:
- Acute Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma
- Injuries/ trauma
- Uveitis
- Scleritis
- Keratitis
- Iridocyclitis
- Herpes Zoster ophthalmicus
Causes of painless Red Eye are
- Conjunctivitis
- Sub conjunctival hemorrhage.
- Blepharitis
- Episcleritis
- Dry Eyes
- Drugs
- Pinguecula and pterygium
Today I will tell about Acute Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma. Glaucoma is associated with the increased Intra Occular Pressure (IOP). The IOP refers to the pressure exerted by intraoccular fluids on the coats of the eyeball. The normal IOP varies 10-21 mm of Hg. The Normal level of IOP is essentially maintained by a dynamic equilibirium between the formation and outflow of the Aqueous humour.
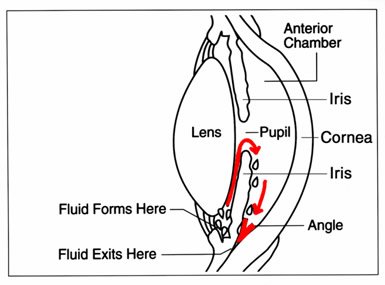
Aqueous humour is a clear watery fluid filling the anterior chamber (0.25 ml) and posterior chamber(0.06ml) of the eyeball. Aqueous humour helps in maintenance of a proper intra ocular pressure. Constituents of the normal aqueous humour are :-
- water (99.9%) and solids (0.1 %)
- proteins
- amino acids
- Glucose, Urea, Ascorbate, Lactic acid, inositol, Na+, K+, Cl-, and HCO3-
The Aqueous Humour is derived from plasma within the capillary network of ciliary processes. The normal aqueous production rate is 2.3microlitre/min.
GLAUCOMA is a group of disorders characterized by a progressive optic neuropathy resulting in a characteristic appearance of the optic disc and a specific pattern of irreversible visual field defects that are associated with raised IOP. An attack of acute rise in IOP in patients with Primary angle closure may occour due to pupillary block causing sudden closure of the angle. It is a sight of threatening emergency.
Clinical Features of Primary angle closure glaucoma.
Symptoms:-
- Pain :- sudden onset of very severe pain
- Nausea, Vomiting and prostrations
- Rapidly progressive impairment of vision, redness, photophobia and lacrimation
Signs :-
- Oedematous lid
- conjunctiva is chemosed and congested
- Cornea becomes oedematous
- Anterior chamber is shallow.
- pupil is semidilated, vertically oval and fixed. It is non reactive to both light and accomodation.
- IOP is markedly elevated, between 40- 70 mm of Hg.
Management:- It is a serious medical emergency. If not treated it can cause blindness within 8-10 hrs.
- Immediate medical therapy to lower IOP.
- Intravenous manintol ( 1 gm/kg body weight ) should be preferred in the presence of nausea and vomiting.
- Oral hyperosmotics, e.g., glycerol 1gm/kg body weight of 50 % solution in lemon juice may be given. ( not with patients with diabetes)
- Systemic Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, e,g., acetazolamide 500mg IV stat followed by 250 mg tab 3 times a day.
- Typical anti glaucoma Drugs to be instilled immediately includes:-
- Beta-blockers, e.g., 0.5 % timolol or 0.5 % betaxlol
- pilocarpine 2 % QID should be started after 1hr of commencement of treatment, i.e., when IOP is lowered.
- Analgesics for pain.
- Topicl steroid e.g., prednisolone acetate 1 % eye drops 3-4 times a day reduces the inflammation.
- Definitive therapy
- Laser peripheral iridotomy (LPI) :- should be done if PAC are seen in 270 degree angle. LPI re- establishes communication between posterior and anterior chamber, so it bypasses the pupilary block and immediately relieves the crowding of the angle.
- Filtration surgery , i.e., trabecluectomy should be performed in cases where IOP is not controlled with the maximum medical therapy following an attack of acute primary angle closure.
- Clear lens extractions by phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation has been recently recommended by some medical personnels.
Thats all for today, I will be writing about other causes of painful red eyes in next episode. Thank you for your time. If you have any questions and queries I would be glad to answer. If you liked my post upvote and resteem and follow @life.goals. Stay tuned for more.
References
- comprehensive ophthalmology, A.K Khurana 6th edition, page 220 to 250.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glaucoma

Good content plus it's very informative to me. Keep it up 👆 @life.goals
thank you @torpedooptimist
You got a 1.69% upvote from @postpromoter courtesy of @life.goals! Want to promote your posts too? Check out the Steem Bot Tracker website for more info. If you would like to support development of @postpromoter and the bot tracker please vote for @yabapmatt for witness!
thankyou @postpromoter
it was an amazing article dr.max @life.goals