Eczema is a condition that makes the skin inflamed, red, itchy, cracked and rough, sometimes, blisters may occur. Mostly people have eczema after the age of 5, but then some children below this age also have it but with few symptoms. Some people tend to outgrow this condition, while others continue to have it all through adulthood.
Some facts about eczema
- Foods such as nut could trigger the symptoms of eczema, especially itching
- Eczema is not contagious
- People who develop eczema in childhood might continue to have the symptoms as an adult
- One important risk factor for eczema is family history
Eczema could be cause by exposure to irritants such as dusts, pollens, soaps, detergents, and so on. Children are also likely to have eczema if their parents do, the symptoms becomes severe if both parents have it.
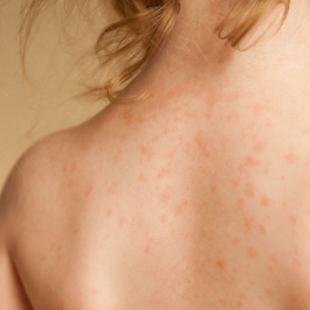
Symptoms
- Dry skin
- Itching which may be severe especially at night
- Rashes that commonly appear in creases of the elbow or knee, nape of the neck
- Raw swollen skin as a result of continuous scratching
- Thickened, cracked, scaly skin.
Treatment
So far, no cure has been found for eczema, however, some self care measures can help relieve itching. The aim of the treatment is to relieve, itching and regain healthy skin.
Home care
- Take warm bath instead of hot bath
- Use mild soap
- When drying the body, avoid rubbing the towel over the skin, instead pat the skin gently
- Apply skin moisturizer within 3 minutes after bathing.
- Avoid rough, scratchy and tight-fitted cloth
- Avoid irritants that could trigger the symptoms.
- Keep the fingernails low at all times to prevent skin break while scratching
Medications
- Applying corticosteroid cream or ointment on the skin
- Use of antibiotics if eczema occurs together with a bacteria infection.
- Use of antihistamine to reduce itching.
Thanks for reading. It's @omooluwa17
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/14417.php
Thanks, the site is referenced