.png)
¡BENDICIONES PARA TODOS!
¡Hola, espero se encuentren bien!
En esta oportunidad les quiero compartir la segunda parte de nuestro estudio de las plantas, donde les hablaré de la propagación, crecimiento, proceso de fotosíntesis y utilidad de las mismas.
Esperando sea de su agrado y utilidad, comencemos...
BLESSINGS TO ALL!
Hello, I hope you are well!
In this opportunity I want to share with you the second part of our study of plants, where I will talk about their propagation, growth, photosynthesis process and usefulness.
I hope you like it and that it will be useful, let's start...
.gif)
PROPAGACIÓN Y CRECIMIENTO DE LAS PLANTAS
Cada especie de planta se reproduce y desarrolla en los lugares donde puede obtener los nutrientes del suelo, agua, aire y la luz que necesita.
La propagación de la planta está relacionada con el proceso de reproducción, los principales medios para esto son: semilla, estaca y bulbo.
PROPAGATION AND GROWTH OF PLANTS
Each plant species reproduces and develops where it can obtain the nutrients from soil, water, air and light it needs.
Plant propagation is related to the process of reproduction, the main means for this are: seed, cutting and bulb.
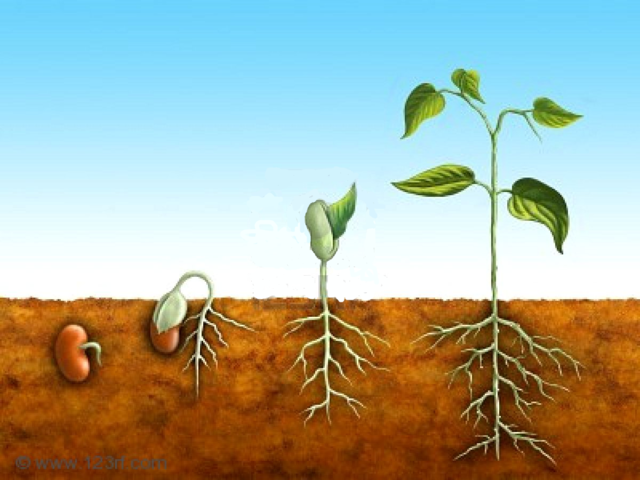
PROPAGACIÓN POR SEMILLA
Para que una semilla pueda germinar tiene que estar madura y con su embrión sano. Necesita del agua para que se ablande la semilla y penetre en sus tejidos para disolver la sustancia de que se va a alimentar el embrión. también necesita del aire para asegurar la respiración de la semilla y del calor del sol para darle fuerza y vida al embrión.
El embrión empieza desarrollarse a los pocos días de ser plantada la semilla, esta se hincha y se rompe saliendo así la primera raíz.
En la raíz crecen pequeños pelos que absorben agua. Luego aparece el primer brote, le salen las hojas y poco a poco la planta se va desarrollando hasta que llega a su completo crecimiento.
Todo este fenómeno que interviene el la reproducción de la planta, se denomina germinación.
PROPAGATION BY SEED
For a seed to germinate, it must be mature and have a healthy embryo. It needs water to soften the seed and penetrate its tissues to dissolve the substance that will feed the embryo. It also needs air to ensure the respiration of the seed and the heat of the sun to give strength and life to the embryo.
The embryo begins to develop a few days after the seed is planted, it swells and breaks and the first root emerges.
The root grows small hairs that absorb water. Then the first sprout appears, leaves appear and little by little the plant develops until it reaches its full growth.
This whole phenomenon involved in the reproduction of the plant is called germination.
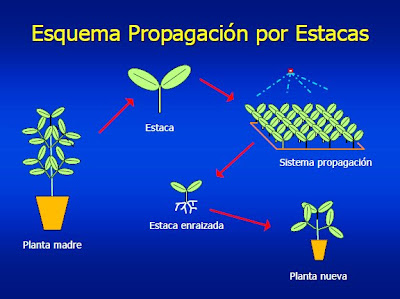
PROPAGACIÓN POR ESTACA
Esta consiste en cortar un trozo de tallo y enterrarlo en forma inclinada, con aproximadamente 7 cm de profundidad, Por ejemplo, así se reproduce la yuca.
PROPAGATION BY STAKE
This consists of cutting a piece of stem and burying it at a slant, approximately 7 cm deep. For example, this is how cassava reproduces.
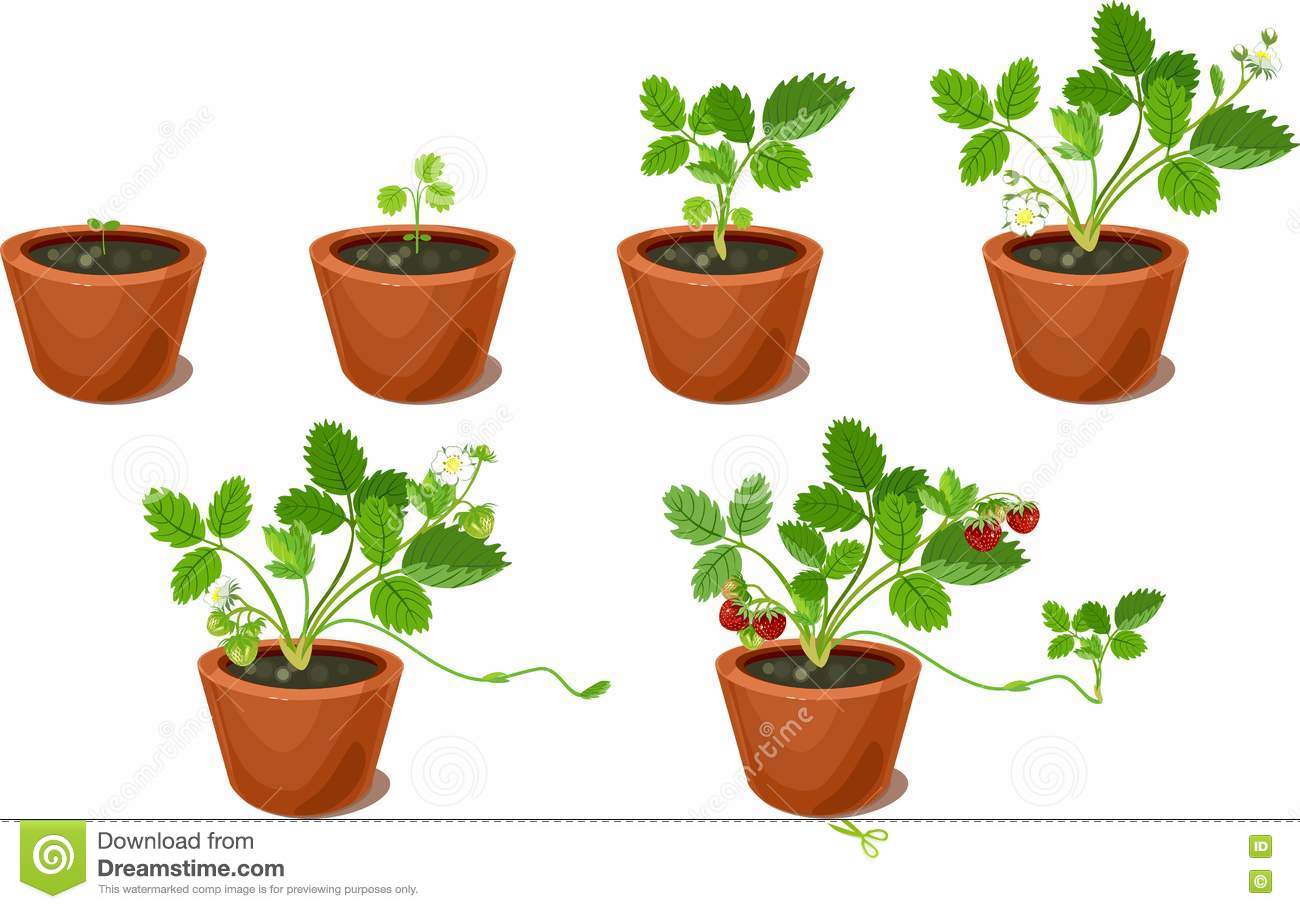
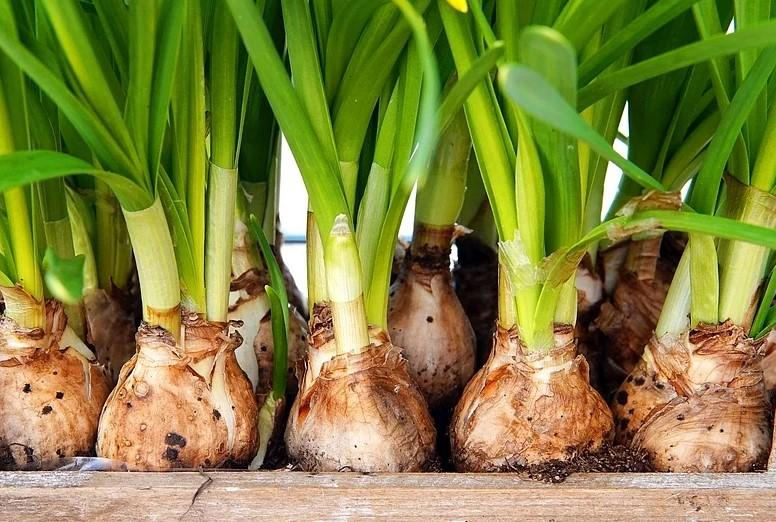
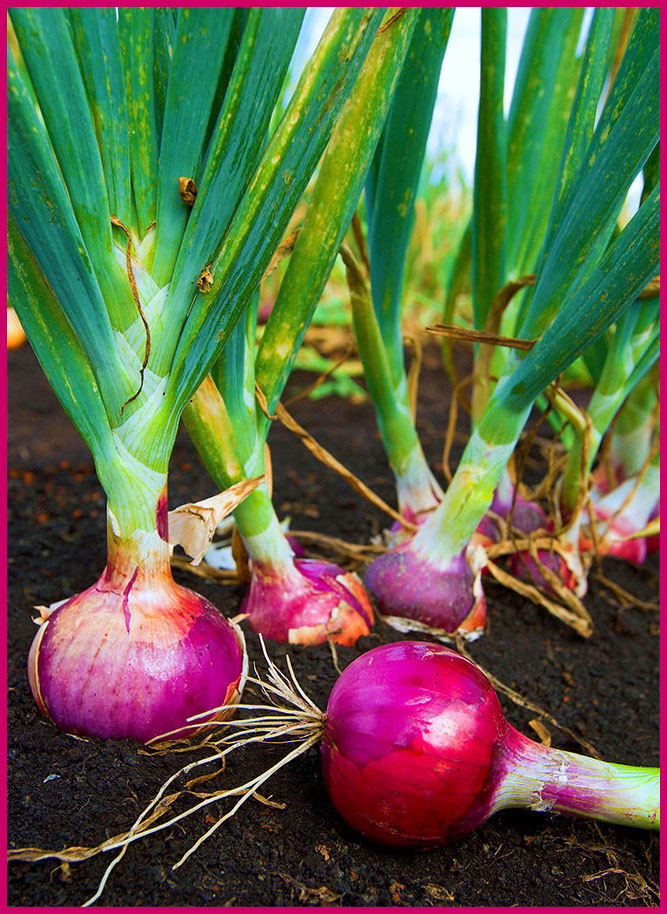
PROPAGACIÓN POR BULBO
Existen dos tipos:
- La primera forma es por raíces que se desarrollan al lado de la planta madre, como por ejemplo el lirio.
- La segunda forma es por medio de brotes, como por ejemplo la fresa.
BULB PROPAGATION
There are two types:
- The first way is by roots that develop next to the mother plant, as for example the lily.
- The second way is by means of shoots, as for example the strawberry.
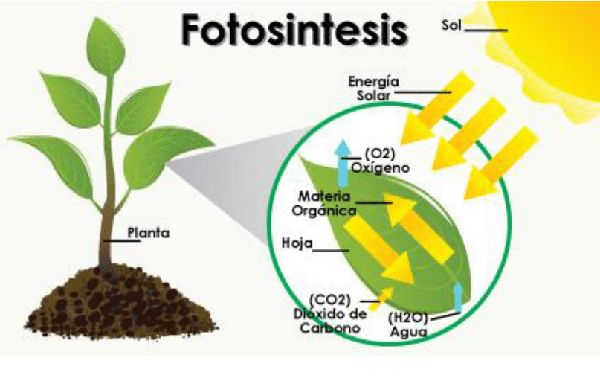
PROCESO DE FOTOSÍNTESIS
Las plantas son los únicos seres vivos capaces de hacer sus propios alimentos, y para elaborarlos solo necesitan agua, minerales y luz solar, también un gas del aire llamado dióxido de carbono.
Las hojas de las plantas contienen una sustancia llamada clorofila , esta atrapa la luz solar y la utiliza para convertir el dióxido de carbono y el agua en diversos tipos de azúcares ricos en energía. Estos azúcares son el alimento de la planta. El proceso de elaborar el alimento mediante la luz solar se denomina fotosíntesis.
La fotosíntesis es el proceso mediante el cual las hojas de las plantas transforman la energía solar en energía química. La energía química es almacenada en forma de almidón en los frutos, tallos, en la madera y en las hojas de las plantas, y sirve para alimentar a otros seres vivos.
PHOTOSYNTHESIS PROCESS
Plants are the only living things capable of making their own food, and to make it they only need water, minerals and sunlight, as well as a gas from the air called carbon dioxide.
The leaves of plants contain a substance called chlorophyll, which traps sunlight and uses it to convert carbon dioxide and water into various types of energy-rich sugars. These sugars are the plant's food. The process of making food from sunlight is called photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plant leaves convert solar energy into chemical energy. The chemical energy is stored in the form of starch in the fruits, stems, wood and leaves of plants, and is used to feed other living things.
UTILIDAD DE LAS PLANTAS
Las plantas son de gran utilidad porque de ellas obtenemos muchos beneficios: alimentos, fibras para fabricar prendas de vestir y otros objetos que son muy útiles, hojas para envolver alimentos, cosméticos, medicamentos, cauchos, madera y pulpa para fabricar cartón y papel. Además, las plantas y sus flores las podemos utilizar con fines ornamentales, como embellecer jardines, casas, parques y calles.
USEFULNESS OF PLANTS
Plants are very useful because we obtain many benefits from them: food, fibers to make clothes and other useful objects, leaves to wrap food, cosmetics, medicines, rubber, wood and pulp to make cardboard and paper. In addition, plants and their flowers can be used for ornamental purposes, such as beautifying gardens, houses, parks and streets.
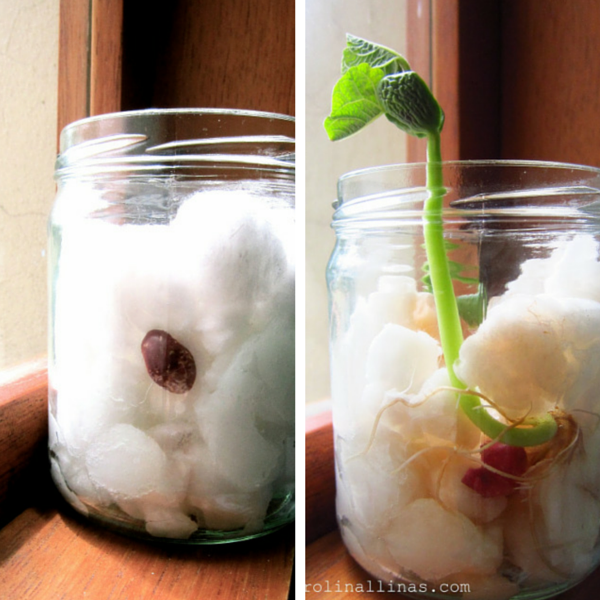
ACTIVIDAD PARA REALIZAR EN CASA
Te invito a realizar el siguiente experimento:
Elabora un germinador. Para esto necesitas un frasco de vidrio, papel secante o higiénico, y unos pocos granos que pueden ser de: maíz, caraotas, alpiste, etc.
- Forra el interior del frasco con el papel secante.
- Mete los granos en diferentes posiciones, cuidando que queden entre el papel y el frasco.
- Puedes rellenar el centro del frasco con un poco de tierra.
- Coloca el frasco en un lugar cálido y mantén húmedo el papel secante, rociando diariamente con un poco de agua.
- Observa la germinación a los pocos días y toma nota en tu cuaderno.
ACTIVITY TO DO AT HOME
I invite you to perform the following experiment:
Make a germinator. For this you need a glass jar, blotting paper or toilet paper, and a few grains that can be of: corn, beans, canary seed, etc.
- Line the inside of the jar with the blotting paper.
- Put the grains in different positions, taking care that they are between the paper and the jar.
- You can fill the center of the jar with a little soil.
- Place the jar in a warm place and keep the blotting paper damp, spraying daily with a little water.
- Observe the germination after a few days and make notes in your notebook.
.gif)
Espero les haya sido útil esta información.
Hasta la próxima publicación! ❤️
I hope this information has been useful.
See you next time! ❤️
.gif)
Las imágenes utilizadas tienen sus respectivas fuentes.
Fuente consultada "Enciclopedia Girasol" Juan Gutiérrez.
Separadores y miniatura, editados en Canva.
The images used have their respective sources.
Source consulted "Sunflower Encyclopedia" Juan Gutierrez.
Dividers and thumbnail, edited in Canva.
.gif)











Excelente y didáctico post, para orientar en las actividades educativas sobre el proceso de propagación de las plantas y la utilidad de estas.
Saludos
Muchas gracias por su apoyo y apreciación! Lo valoro mucho! Saludos ..
The rewards earned on this comment will go directly to the person sharing the post on Twitter as long as they are registered with @poshtoken. Sign up at https://hiveposh.com.