

Hoy les hablaré sobre una patología muy frecuente en la edad pediátrica: el impétigo.

Today I will talk about a very common pathology in children: impetigo.
A cordial greeting to the entire community, a pleasure to greet you, here is your server: @galejandrovv.

¿QUÉ ES EL IMPÉTIGO?
¿WHAT IS IMPETIGO?

¿CÓMO SE TRANSMITE?
¿HOW IS IT TRANSMITTED?
Se puede producir autoinfección durante el rascado, es decir, la persona se rasca las lesiones y luego se lleva las manos a otra parte del cuerpo, donde posteriormente se producen nuevas lesiones. También es posible la infección de persona a persona, sobre todo cuando hay contacto de una persona infectada con la piel lesionada de otra persona.
Autoinfection can occur during scratching, that is, the person scratches the lesions and then moves their hands to another part of the body, where new lesions are subsequently produced. Person-to-person infection is also possible, especially when an infected person comes into contact with the broken skin of another person.

TIPOS DE IMPÉTIGO
TYPES OF IMPETIGO
Ampolloso: es el menos frecuente y con menos transmisible; consiste en ampollas llenas de líquido claro, la cual se rompe con facilidad y dejan costras; afecta, principalmente, tronco y genitales.
No ampolloso: es el más frecuente y con mayor tasa de transmisibilidad; consiste en pápulas que luego se convierten en vesículas, de bordes eritematosos; éstas se rompen con facilidad, forman exudado y posteriormente dejan costras; afecta, principalmente, cara y extremidades.
Bullous: is the least frequent and least communicable; consists of blisters filled with clear fluid, which break easily and leave crusts; It mainly affects the trunk and genitals.
Non-bullous: it is the most frequent and with the highest rate of transmissibility; consists of papules that later become vesicles, with erythematous edges; these break easily, form an exudate and later leave scabs; It mainly affects the face and extremities.
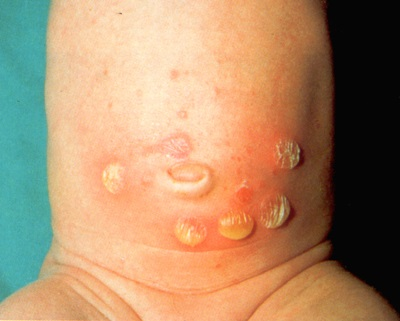
Fuente / Source Impétigo ampolloso
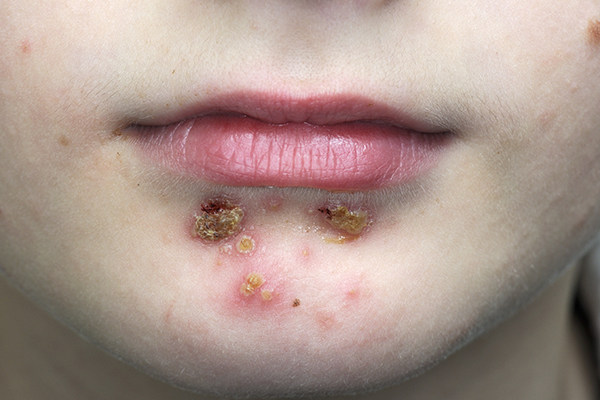
Fuente / Source Impétigo no ampolloso (costroso)

TRATAMIENTO
TREATMENT
El tratamiento sistémico dependerá de la gravedad y extensión de las lesiones, generalmente se indica tratamiento por vía oral a base de oxacilina, amoxicilina con ácido clávulanico, cefadroxilo o algún macrólido. Si las lesiones son graves y extensas, se debe iniciar tratamiento endovenoso a base de los antibióticos mencionados anteriormente.
Systemic treatment will depend on the severity and extent of the lesions. Oral treatment based on oxacillin, amoxicillin with clavulanic acid, cefadroxil or a macrolide is generally indicated. If the lesions are severe and extensive, intravenous treatment should be started based on the antibiotics mentioned above.

Texto traducido en XTranslate
Separadores creados en Gravit Designer
Vectores descargados de Flaticon
Banner's creados en Canva
Translated text with the extension XTranslate
Separators created in Gravit Designer
Vectors downloaded from Flaticon
Banner's created in Canva

PRIMUM NON NOCERE








The rewards earned on this comment will go directly to the person sharing the post on Twitter as long as they are registered with @poshtoken. Sign up at https://hiveposh.com.
Congratulations @galejandrovv! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s):
Your next target is to reach 50 posts.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Support the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!