Parálisis facial

La parálisis facial consiste en la pérdida total o parcial de movimiento muscular voluntario en un lado de la cara. Se produce por un fallo en el nervio facial, que no lleva las órdenes nerviosas a los principales músculos de la cara.
Se manifiesta clínicamente por la imposibilidad para levantar la ceja, cerrar el ojo, incapacidad para sonreír, alteraciones en el habla, etc.
Facial paralysis consists of the total or partial loss of voluntary muscle movement on one side of the face. It is caused by a failure of the facial nerve, which does not carry nerve orders to the main muscles of the face.
It is clinically manifested by the impossibility to raise the eyebrow, close the eye, inability to smile, speech alterations, etc.
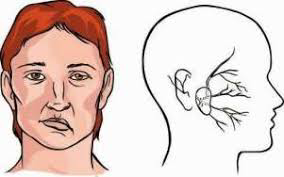
Foto de BOT Plus
El nervio facial está unido directamente con el cerebro y su función es controlar la musculatura de la cara, la producción de lágrimas y saliva, la percepción auditiva, el cierre y apertura de los ojos y el sentido de gusto, alojado en la lengua.
Este nervio facial puede verse afectado por múltiples situaciones que provocan su mal funcionamiento. Entre estas causas de la parálisis facial podemos encontrar:
Parálisis de Bell, es la causa más común de la parálisis facial. Tiene un origen desconocido y se puede presentar de forma aguda y brusca a cualquier edad. En la mayoría de los casos, esta parálisis es temporal y el paciente alcanza la recuperación completa en unos seis meses como máximo. Existe una pequeña cantidad de casos en los que este problema deja secuelas de por vida.
Herpes zóster ótico. Se trata de una manifestación infrecuente del herpes zóster que afecta a los ganglios nerviosos encargados de controlar los nervios de la audición y el equilibrio.
The facial nerve is responsible for the control of the following functions: tears and saliva, auditory perception, the closing and opening of the eyes and the sense of taste, housed in the tongue.
This facial nerve can be affected by multiple situations that cause it to malfunction. Among these causes of facial paralysis we can find:
Bell's palsy. It is the most common cause of facial paralysis. It has an unknown origin and can present itself acutely and abruptly at any age. In most cases, this paralysis is temporary and the patient reaches full recovery in about six months at the most. There are a small number of cases in which this problem leaves lifelong sequelae.
Herpes zoster oticus. This is a rare manifestation of herpes zoster that affects the nerve ganglia responsible for controlling the hearing and balance nerves.
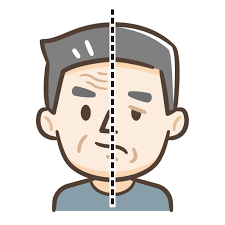
Por lo tanto, tiene consecuencias sobre todo a nivel auditivo.
- Otitis.
- Traumatismos craneales.
- Accidente cerebrovascular.
- Tumores cerebrales o que presionan o son adyacentes al nervio facial (neurinoma del acústico).
Therefore, it has consequences mainly at the auditory level.
- Otitis.
- Cranial traumas.
- Cerebrovascular accident.
- Brain tumors or tumors pressing on or adjacent to the facial nerve (acoustic neurinoma).
Existen dos tipos de parálisis facial que se clasifican en función de si el nervio facial se ha visto afectado directa o indirectamente:
- Parálisis facial periférica, Se produce cuando la lesión afecta directamente al nervio facial y se manifiesta en todos los músculos de la cara en el mismo lado donde se encuentra la lesión. La más habitual es la parálisis periférica idiopática, primaria o de Bell.
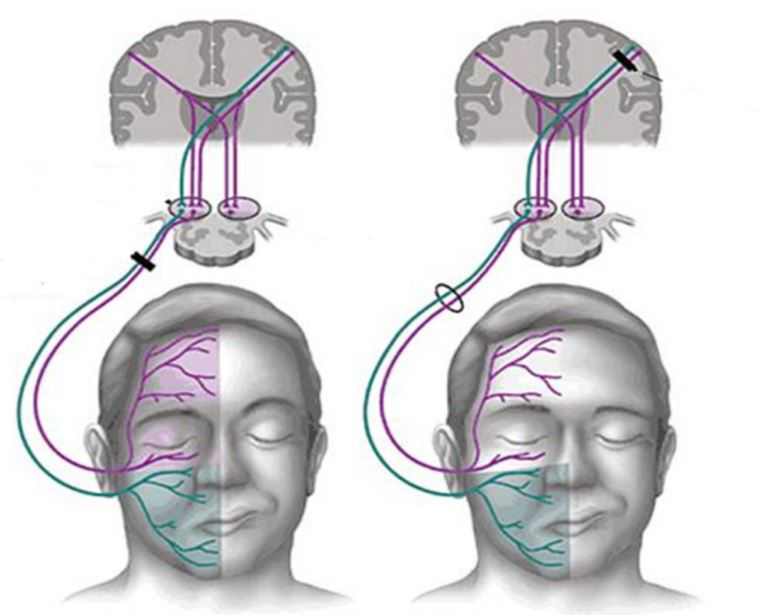
Foto de Fisioterapia Online
- Parálisis facial central, afecta a las fibras que unen la corteza cerebral con el nervio facial. Se manifiesta en síntomas que afectan a los músculos de la parte inferior de la cara (boca y mejilla) en el lado contrario a donde está la lesión y no suele tener consecuencias sobre el sistema visual, ya que el paciente no tiene dificultades para cerrar el ojo o para levantar la ceja.
There are two types of facial paralysis that are classified according to whether the facial nerve has been affected directly or indirectly:
- Peripheral facial paralysis, Occurs when the lesion directly affects the facial nerve and manifests in all the muscles of the face on the same side where the lesion is located. The most common is idiopathic, primary or Bell's peripheral paralysis.
- Central facial palsy affects the fibers that connect the cerebral cortex with the facial nerve. It manifests itself in symptoms affecting the muscles of the lower part of the face (mouth and cheek) on the side opposite to where the lesion is located and does not usually have consequences on the visual system, since the patient has no difficulty in closing the eye or raising the eyebrow.
Los síntomas de la parálisis facial pueden variar mucho dependiendo de las características de la persona y del alcance de la lesión y pueden ir desde una manifestación débil a una total, llegando a producir graves alteraciones de la calidad de vida del paciente (dificultad para comer, beber, hablar o expresar sus emociones).
Los principales síntomas son:
- Pérdida o disminución de movilidad voluntaria de los músculos faciales que puede ocurrir en cuestión de horas o días.
- Ausencia de expresiones faciales: el paciente no puede subir las cejas, arrugar la frente o sonreír.
- Dolor facial.
- Dolor en el oído y presencia de ruidos fuertes.
- Dolor de cabeza.
- Ausencia de sensibilidad auditiva.
- Pérdida o disminución del sentido del gusto.
- Ausencia de saliva o babeo.
The symptoms of facial paralysis can vary greatly depending on the characteristics of the person and the extent of the lesion and can range from a weak to a total manifestation, producing serious alterations in the patient's quality of life (difficulty eating, drinking, speaking or expressing emotions).
The main symptoms are:
- Loss or decrease of voluntary mobility of facial muscles that can occur in a matter of hours or days.
- Absence of facial expressions: the patient cannot raise his eyebrows, wrinkle his forehead or smile.
- Facial pain.
- Ear pain and presence of loud noises.
- Headache.
- Absence of hearing sensitivity.
- Loss or diminished sense of taste.
- Absence of saliva or drooling.

Un fisioterapeuta interviene en disminuir dolor y estimular los músculos afectados, así como relajar la musculatura contraria donde suelen aparecer tensiones y pequeñas contracturas, se encargara de realizar los movimientos faciales con sus dedos en el lado paralizado.
A physiotherapist intervenes to reduce pain and stimulate the affected muscles, as well as to relax the opposite musculature where tensions and small contractures usually appear. He will be in charge of performing facial movements with his fingers on the paralyzed side.
Congratulations @espaciofisio05! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Your next target is to reach 200 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPSource of plagiarism 1
Source of plagiarism 2
Plagiarism is the copying & pasting of others' work without giving credit to the original author or artist. Plagiarized posts are considered fraud and violate the intellectual property rights of the original creator.
Fraud is discouraged by the community and may result in the account being Blacklisted.