Source
Tidal energy is a form of renewable energy obtained from the movement of the tides.
This energy is generated by the gravitational forces exerted by the moon and the sun on the oceans, resulting in a constant flow of tides.
The potential of tidal energy lies in the difference in height between high tide and low tide. Different technologies are used to harness it, the most common being tidal power plants and tidal current harnessing systems.
Source
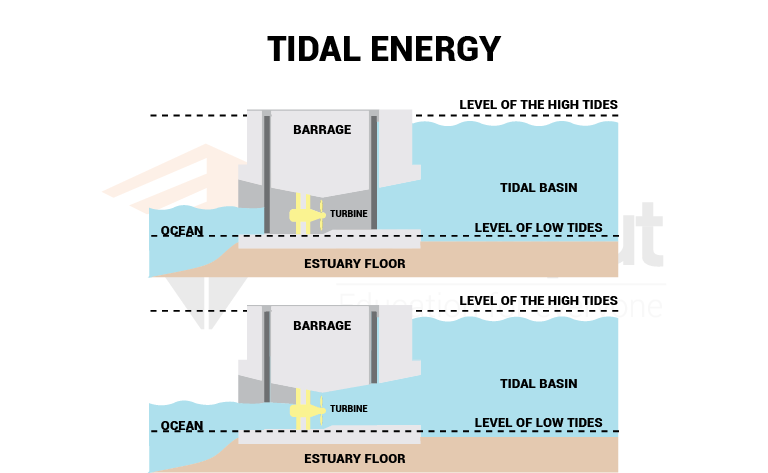
Tidal power plants operate through the use of weirs or estuaries, where water is captured at high tide and released at low tide through turbines.
As the water flows, the turbines move and generate electricity. This system is similar to hydroelectric power plants, but adapted to the marine environment.
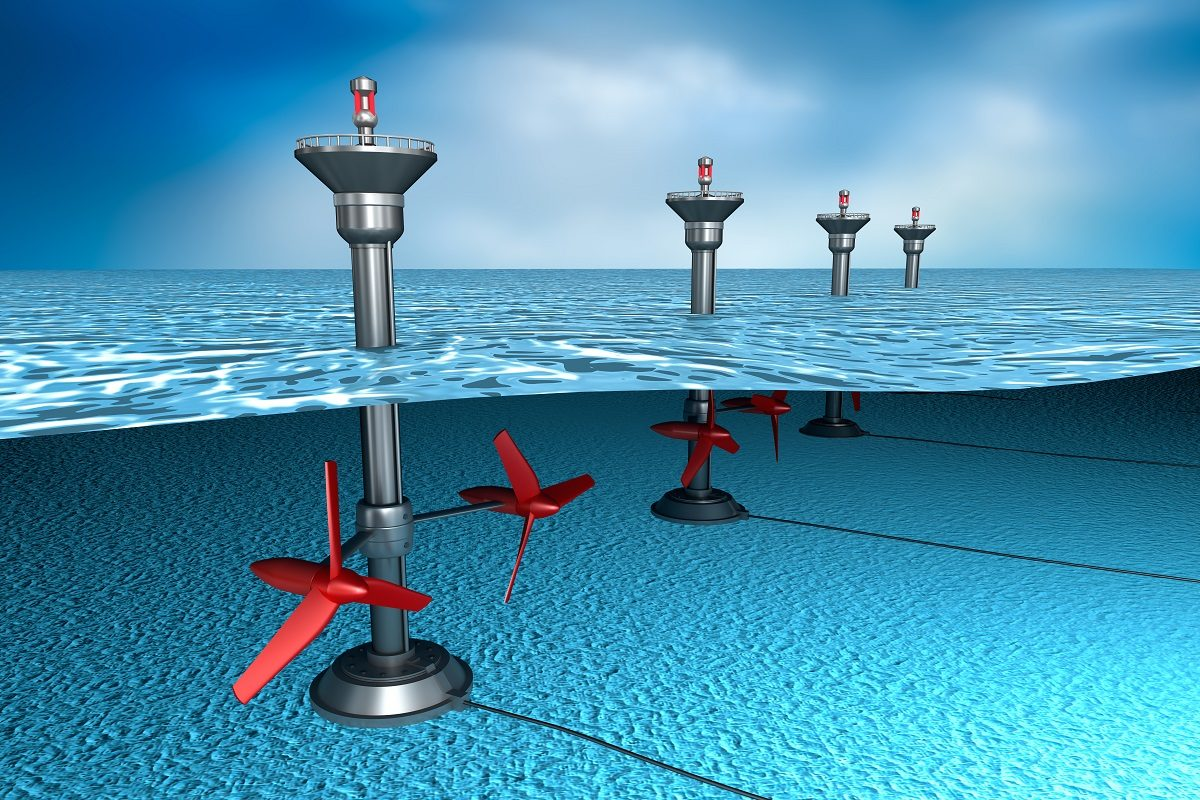
On the other hand, marine current harnessing systems use underwater turbines or floating buoys that capture the kinetic energy of ocean currents.
These devices are installed in strategic locations where ocean currents are strongest and most constant, such as straits or sea channels.

Source
One of the advantages of tidal energy is that it is a clean and renewable energy source, as it does not produce greenhouse gas emissions or pollute the water.
Moreover, the tides are predictable and constant, ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply.
However, tidal power also presents challenges. The construction of tidal power plants can have an environmental impact on coastal and marine ecosystems.
In addition, the technology needed to harness this energy is expensive and requires specific conditions for installation, limiting its use to certain geographical areas.
Source
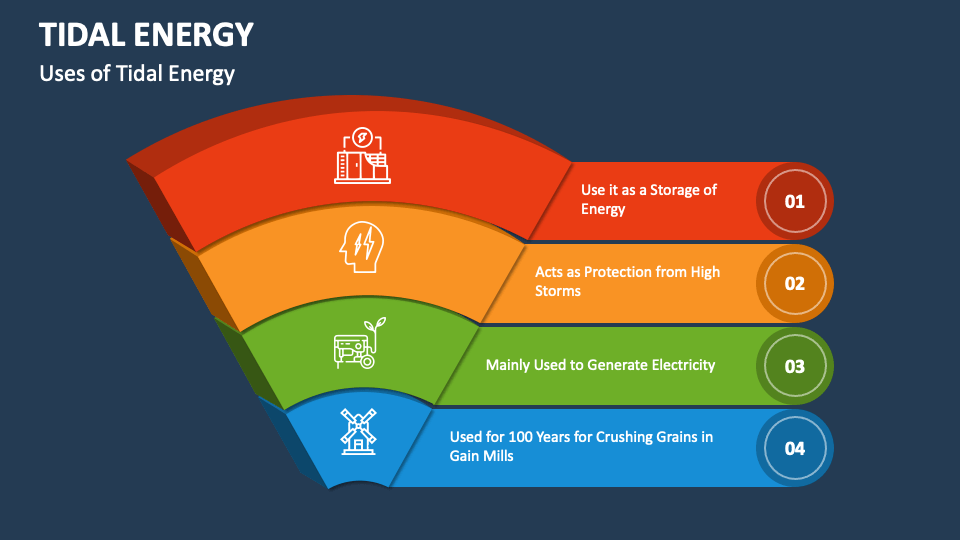
Despite these challenges, tidal energy has great potential and is considered a promising form of sustainable energy generation.
As technology advances and new solutions are developed, we may see greater deployment of this energy source in the future.