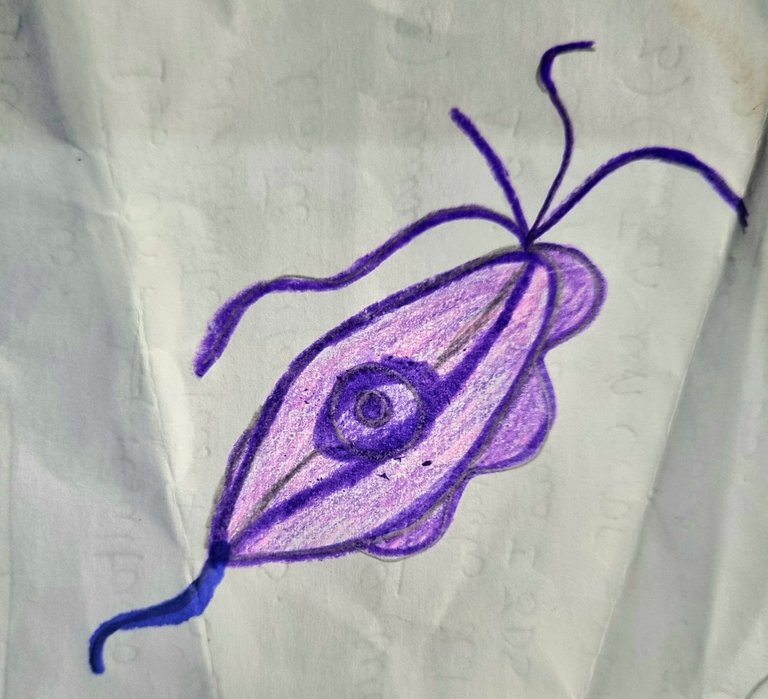
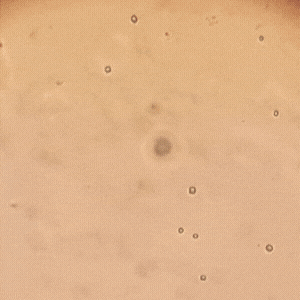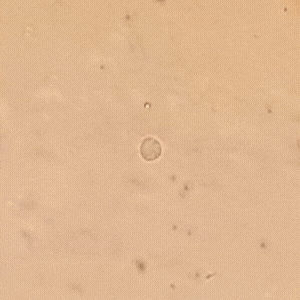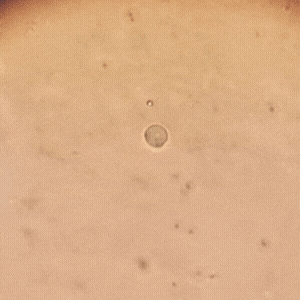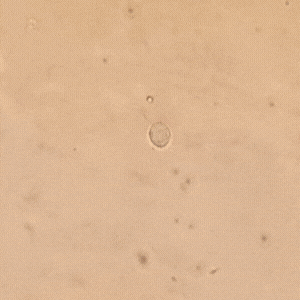
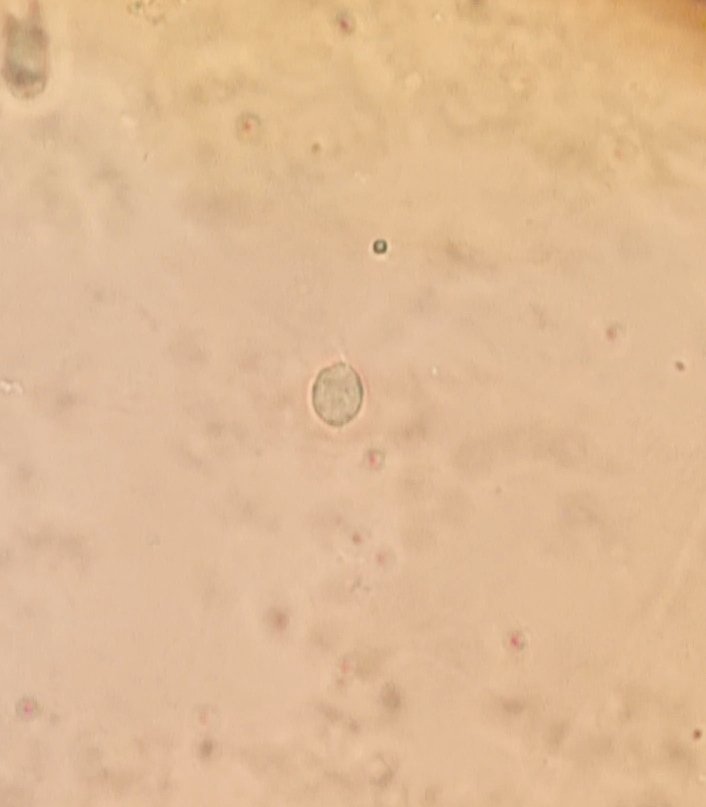
Compartiendo un poco más de mi día en el laboratorio donde cumplo mis pasantías rurales, hoy recibimos la muestra de una paciente de 21 años que presentaba flujo vaginal anormal y molestias al orinar. Al observar su muestra en un examen en fresco bajo el microscopio, encontramos la presencia de Trichomonas vaginalis, un protozoo responsable de la tricomoniasis, una de las infecciones de transmisión sexual más comunes.
Sharing a little more of my day in the lab where I do my rural internships, today we received a sample from a 21 year old patient who presented with abnormal vaginal discharge and discomfort when urinating. Upon observing her sample in a fresh examination under the microscope, we found the presence of Trichomonas vaginalis, a protozoan responsible for trichomoniasis, one of the most common sexually transmitted infections.

¿Cómo se transmite?
Este parásito se transmite principalmente por contacto sexual, ya que vive en el tracto urogenital de hombres y mujeres. Aunque menos frecuente, también puede transmitirse por compartir objetos contaminados como toallas húmedas o ropa interior.
Muchas veces las infecciones de transmisión sexual muchas veces son poco habladas y tratadas como un "taboo" pero es importante conocerlas, para poder prevenir.
**How is it transmitted?
This parasite is mainly transmitted by sexual contact, as it lives in the urogenital tract of both men and women. Although less frequent, it can also be transmitted by sharing contaminated objects such as wet towels or underwear.
Sexually transmitted infections are often little talked about and treated as a "taboo" but it is important to know about them, in order to prevent them.
Ciclo de vida
A diferencia de otros parásitos, T. vaginalis no forma quistes, lo que significa que su transmisión ocurre solo en su forma activa (trofozoíto). Se adhiere a la mucosa vaginal o uretral, multiplicándose por fisión binaria y causando inflamación e irritación.
Life cycle
Unlike other parasites, T. vaginalis does not form cysts, which means that its transmission occurs only in its active form (trophozoite). It adheres to the vaginal or urethral mucosa, multiplying by binary fission and causing inflammation and irritation.

¿Dónde es más frecuente?
La tricomoniasis es más común en mujeres jóvenes y sexualmente activas, especialmente en aquellas con múltiples parejas o con acceso limitado a servicios médicos.
**Where is it most common?
Trichomoniasis is most common in young, sexually active women, especially those with multiple partners or with limited access to medical services.
¿Cómo prevenirlo?
✅ Uso de preservativo en todas las relaciones sexuales.
✅ Higiene íntima adecuada, evitando compartir objetos personales.
✅ Controles médicos regulares, especialmente si hay síntomas como flujo anormal o irritación.
✅ Tratamiento oportuno, ya que muchas veces la infección es asintomática pero sigue siendo contagiosa.
How to prevent it?
✅Use of condoms** in all sexual relations.
✅Adequate intimate hygiene, avoiding sharing personal items.
✅Regular medical check-ups, especially if there are symptoms such as abnormal discharge or irritation.
✅Timely treatment, as many times the infection is asymptomatic but still contagious.
Este caso nos recuerda lo importante que es la educación en salud sexual y la prevención de infecciones silenciosas pero frecuentes. ¡Gracias por leer! 🩷
This case reminds us how important sexual health education and prevention of silent but frequent infections is. Thank you for reading! 🩷

Fuente: https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/trichomoniasis/index.html
Creditos: Fotos de mi propiedad// gif hecho en Gif Market app // traductor DeepL.com// separadores hechos en canva.com// icono de Instagram Creditos a Freepik