
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

14-04-2025 - Physics - Fluids [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_70)
Fluids
image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction
When we are in the physical field and we talk about Fluids in general, we must keep in mind that we are talking about both liquids and gases. So the term fluid can refer to both water and air.
We can give another definition regarding what fluid means in physics. Fluid in physics is a substance that can flow, therefore it has no shape of its own and is easily deformed. The fact that it has no shape of its own means that it takes the shape of the container, while the fact that it is easily deformed means that under the action of a force the fluid immediately begins to deform.
The main properties of fluids are: density, pressure, viscosity, comprehensibility and flow rate
Fluid, liquids and gases
Within the category of fluids there are differences that allow these fluids to be classified into liquids and gases. The most obvious difference between liquids and gases concerns the volume. While on the one hand liquids always have their own volume, on the other hand gases are not characterized by a well-defined volume. Another difference consists in the fact that liquids are incompressible while gases are easily compressible. The last difference between liquids and gases is that liquids have a higher density than gases. This means that for the same volume, liquids have a greater mass than gases.
Pressure
We have previously listed the main properties of fluids and mentioned pressure among them. In the case of fluids, pressure is the force exerted by the fluid per unit of surface. We can see the mathematical formula below
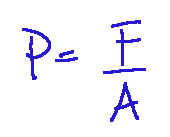
We can give a more technical definition of pressure, saying that a small element of fluid defined by the surface that circumscribes it can therefore exert a force dF on an element of that surface dS. Pressure P is defined as the value of the force per unit of surface, or the ratio described in the formula below.
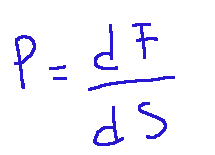
The SI unit of pressure is the Pascal, symbol Pa.
1 Pa =1 N/m^3
Below is a list of the units of pressure used around the world related to the Pascal.
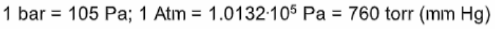
Stevin's Law
When we talk about fluids, we must definitely mention Stevin's Law. Stevin (Simon Stevin) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist and engineer, who lived in the 16th century. He is considered one of the fathers of fluid physics. Ste Eno was a Dutch mathematician, physicist and engineer, who lived in the 16th century. He is considered one of the fathers of fluid physics.
This law expresses the value of pressure exerted by a fluid on a body immersed in it. This occurs as a function of the depth at which the body is located and starting from the value of the gravitational acceleration and the density of the fluid. Basically, this law allows us to calculate the pressure that an incompressible fluid is able to exert on a body as the depth at which the body is located varies. Below we can see how Stevino's law is written in mathematical form.
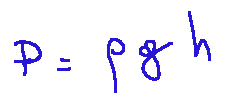
WHERE:
P = pressure at a certain depth,
ρ = density of the fluid,
g = gravitational acceleration,
h = depth in the fluid.
From the formula of Stevino's law it is easy to understand that the pressure is directly proportional to the depth h, as well as to the density of the fluid ρ.
A consequence of this law concerns extended bodies. A body immersed in a fluid will be subject to different pressures on the various parts of its surface. We can therefore say that the pressure exerted on the upper surface is less than that exerted from below on the lower surface.
Atmospheric pressure

image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
What is atmospheric pressure? We can simply say that atmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted by the air on the earth's surface.
Atmospheric pressure written as patm at sea level is 101325 Pascal
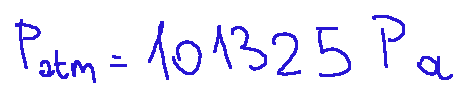
Conclusions
The study of fluids is fundamental in many scientific, technological and industrial fields. We also know that fluids are present in many natural phenomena and practical applications. Fluid mechanics is particularly important in some fields such as aerodynamics, aeronautics, automotive engineering, civil engineering and hydraulic engineering. We must also include the study of fluids in the field of meteorology and climatology, as well as in oceanography and maritime engineering
Question
Did you know that the first person to measure atmospheric pressure was, in 1643, the Italian physicist and mathematician Evangelista Torricelli?

ITALIAN

14-04-2025 - Fisica - I fluidi [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_70)
I fluidi

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione
Quando siamo in ambito fisico e parliamo di Fluidi in generale, dobbiamo tenere presente che parliamo sia di liquidi che di gas. Quindi il termine fluido può riferirsi sia all'acqua che all'aria.
Possiamo dare un’altra definizione per quanto riguarda che cosa significa fluido in fisica. Il fluido in fisica è una sostanza che può scorrere, quindi non ha forma propria e si deforma facilmente. Il fatto che non ha forma propria vuol dire che prende la forma del contenitore, mentre il fatto che si deforma facilmente vuol dire che sotto l’azione di una forza il fluido inizia subito a deformarsi.
Le proprietà principali dei fluidi sono: la densità, la pressione, la viscosità, la comprensibilità e la portata
FLuidi, liquidi e gas
All’interno della categoria dei fluidi esistono delle differenze che permettono di classificare questi fluidi in liquidi e gas. La differenza più evidente tra liquidi e gas riguarda proprio il volume. Se da un lato i liquidi hanno sempre un proprio volume, dall’altro i gas non sono caratterizzati da un volume ben definito. Un’altra differenza consiste nel fatto che i liquidi sono incomprimibili mentre i gas sono facilmente comprimibili. L’ultima differenza che c’è tra liquidi e gas è che i liquidi hanno una densità maggiore di quella dei gas. Questo significa che a parità di volume i liquidi presentano una massa maggiore rispetto ai gas.
La pressione
Prima abbiamo elencato le proprietà principali dei fluidi e abbiamo nominato la pressione tra queste. Nel caso dei fluidi la pressione è la forza esercitata dal fluido per unità di superficie. Possiamo vedere la formula matematica qui sotto riportata
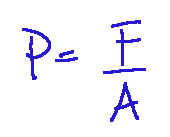
Possiamo dare una definizione più tecnica della pressione, dicendo che un piccolo elemento di fluido definito dalla superficie che lo circoscrive può quindi esercitare una forza dF su un elemento di tale superficie dS. Viene definita pressione P, il valore della forza per unità di superficie, ovvero il rapporto descritto nella formula riportata qui sotto.
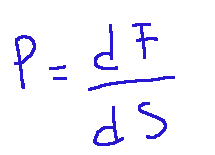
L’unità di misura nel SI della pressione è il Pascal, simbolo Pa.
1 Pa =1 N/m^3
Qui di seguito un elenco delle unità di misura della pressione usate nel mondo rapportate al Pascal.
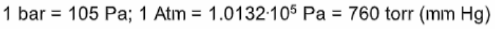
La legge di Stevino
Quando parliamo dei fluidi, dobbiamo sicuramente menzionare la legge di Stevino. Stevino (Simon Stevin) è stato un matematico, fisico e ingegnere olandese, che visse nel XVI secolo. Egli è considerato uno dei padri della fisica dei fluidi. Ste Eno è stato un matematico, fisico e ingegnere olandese, che visse nel XVI secolo. Egli è considerato uno dei padri della fisica dei fluidi.
Questa legge esprime il valore di pressione esercitata da un fluido su un corpo immerso al suo interno.questo avviene in funzione della profondità a cui è situato il corpo e a partire dal valore dell’accelerazione di gravità e dalla densità del fluido.sostanzialmente questa legge permette di calcolare la pressione che un fluido incomprimibile è in grado di esercitare su un corpo al variare della profondità a cui è collocato il corpo. Qui di seguito possiamo vedere come è scritta in forma matematica la legge di Stevino.
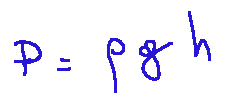
DOVE:
P = pressione a una certa profondità,
ρ = densità del fluido,
g = l’accelerazione gravitazionale,
h = la profondità nel fluido.
Dalla formula della legge di Stevino è facile comprendere che la pressione è direttamente proporzionale alla profondità h, oltre che alla densità del fluido ρ.
Una conseguenza di questa legge riguarda i corpi estesi. Un corpo immerso in un fluido sarà soggetto a pressioni differenti sulle varie parti della sua superficie. Possiamo quindi dire che la pressione che viene esercitata sulla superficie superiore è minore di quella che viene esercitata dal basso sulla superficie inferiore.
Pressione atmosferica

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Che cos’è la pressione atmosferica? Semplicemente possiamo dire che la pressione atmosferica è la pressione esercitata dall’aria sulla superficie terrestre.
La pressione atmosferica scritta come patm al livello del mare vale 101325 Pascal
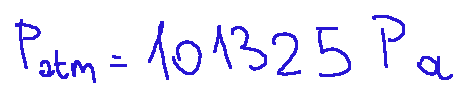
Conclusioni
Lo studio dei fluidi è fondamentale in numerosi campi scientifici, tecnologici e industriali. Inoltre sappiamo che i fluidi sono presenti in moltissimi fenomeni naturali e applicazioni pratiche. La meccanica dei fluidi è particolarmente importante in alcuni ambiti come quello dell’aerodinamica, dell’aeronautica, dell’ingegneria automobilistica, dell’ingegneria civile e dell’ingegneria idraulica. Dobbiamo annoverare anche lo studio dei fluidi nel campo della meteorologia e della climatologia, così come nella oceanografia e nell’ingegneria marittima
Domanda
Lo sapevate che il primo a misurare la pressione atmosferica fu, nel 1643, il fisico e matematico italiano Evangelista Torricelli?
THE END
I remember vividly been thought about this fluid thing in physics. At first it looks quite difficult but glad I learnt it actually
Thanks for stopping by. I think that as long as we study ideal fluids, things can be understood. However, when we enter the field of studying real fluids, the situation becomes quite complicated in my opinion. I think two things are very important in the field of fluid studies: the first is the continuity equation, the other I think is precisely the Bernoulli equation. !PIZZA
Aerodinamica, un argomento che è attuale e NON per le buone notizie
$PIZZA slices delivered:
(1/5) @stefano.massari tipped @consistency
Moon is coming - April 19th, 2025
@stefano.massari, I paid out 0.041 HIVE and 0.009 HBD to reward 1 comments in this discussion thread.
#hive