A beginner's guide to Polygon (MATIC), Ethereum's Layer-2 scaling solution. We review what is Polygon and how to use it for DeFi.
Polygon is a layer-two (L2) scaling solution for Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks.
Using a sidechain on L2, Polygon is designed to enable cheaper, faster and equally secure off-chain Ethereum transactions.
Polygon's ultimate goal is to build a multi-layer sidechain ecosystem, that is fully interconnected.
Something that they see as the internet of Ethereum blockchains.

Originally launched in 2017 as the MATIC network by Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal and Anurag Arjun, Polygon’s native token still bears its original name.
Our guide to Polygon (MATIC) will walk you through the key features of the network and explain what all the fuss is about.
Introduction to Polygon (MATIC)
We introduce the Polygon network and its native MATIC token.
To kick off our guide to Polygon (MATIC), let’s go over the basics of the Polygon network and its native MATIC token.
Let's get started with an introduction to each.
Polygon Network
Polygon is a protocol and a framework for building and connecting Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks.
Built as a layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum, you can think of Polygon as Ethereum’s internet of blockchains.
Polygon leverages the underlying security of the Ethereum network to make it easier for developers to build and users to trust dApps built on the blockchain.
This means that technically if users were scammed on a Polygon based application, it would be possible to reclaim those lost funds by returning to the base Ethereum layer.
MATIC Token
Powering the Polygon ecosystem of dApps, is the MATIC token.
The MATIC token performs multiple functions within this ecosystem, including:
- Paying for transaction fees (gas).
- Securing the network via staking.
- Voting on governance issues.
MATIC token details:
MATIC Circulating Supply: 6,330,554,997 MATIC
MATIC Total Supply: 10,000,000,000 MATIC
MATIC Max Supply: 10,000,000,000 MATIC
How does Polygon (MATIC) work?
We explore the inner workings of the Polygon blockchain and the layers of which the network is comprised.
Polygon is a Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain.
This means that Polygon works by selecting validators in proportion to their MATIC stake.
While it is described an Ethereum side chain, the Polygon blockchain is compromised of its own infrastructure including nodes, token (MATIC) and range of native dApps.
The only difference being that transactions are ultimately processed on the Ethereum mainnet.
For this subsection of our LeoFinance Polygon (MATIC) guide, lets dive down a little deeper on the inner workings of the network.
Polygon is a layer-2 scaling solution
Polygon is a layer-2 scaling solution for the Ethereum blockchain.
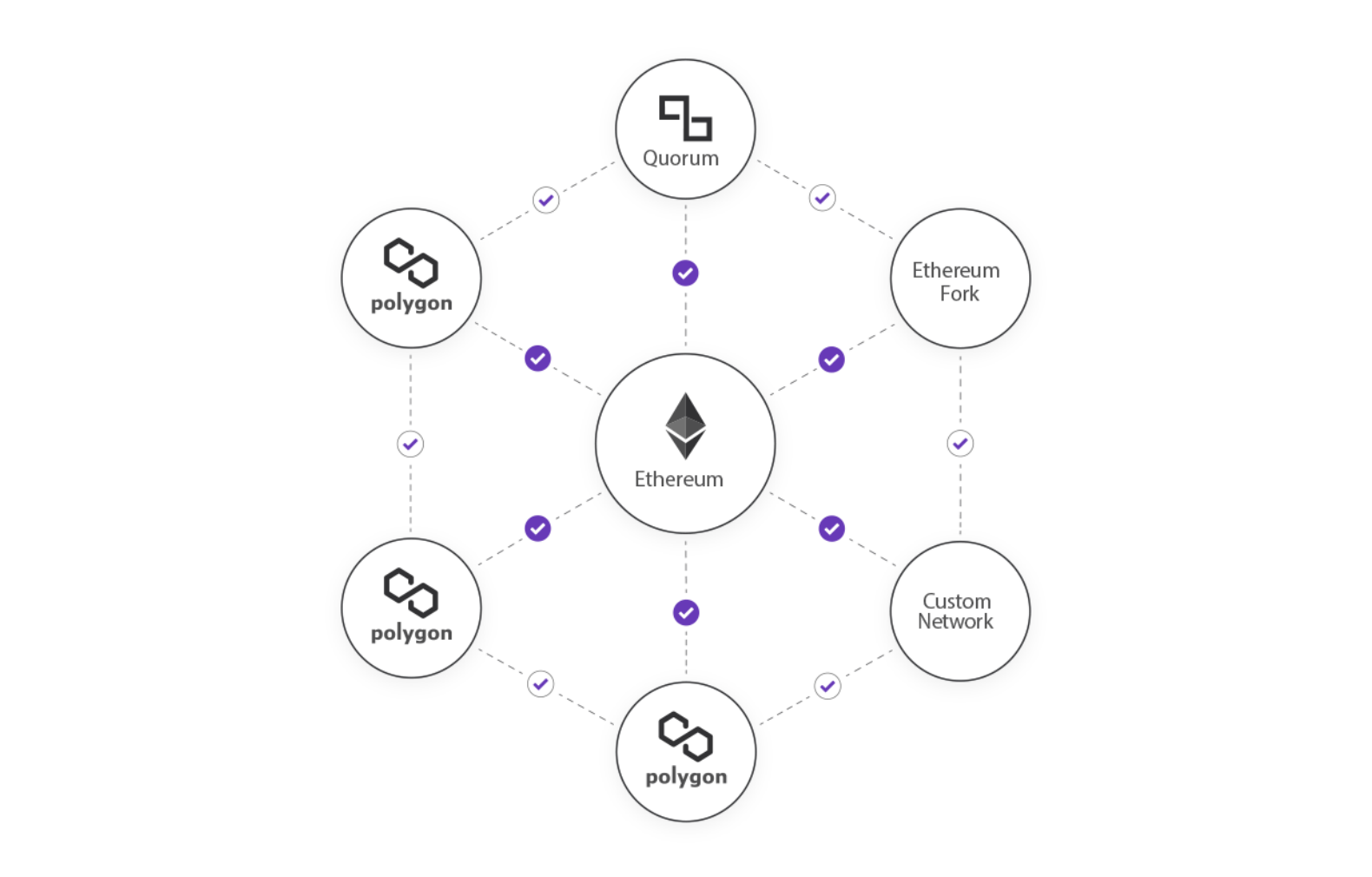
These are sidechains that are built on top of a primary blockchain which is otherwise referred to as layer-1.
In Polygon’s case, this layer-1 blockchain is the Ethereum mainnet.
As a layer-2 scaling solution, Polygon works alongside Ethereum by handling transactions off of the main chain.
Polygon ultimately increases Ethereum’s capabilities by:
- Improving transaction speed.
- Improving the number of transactions per second.
- Lowering gas fees.
4 layers of Polygon
When it comes to network architecture, Polygon is comprised of 4 distinct layers.
Layer 1: Ethereum Layer
Thanks to the use of smart contracts, Polygon chains are able to execute any critical component over the Ethereum network
This means that applications built on Polygon can take advantage of the decentralised security that the Ethreum mainnet can offer.
Layer 2: Security Layer
The second, optional layer provides ‘validators as a service’.
Ultimately the security layer checks all aspects of any Polygon based blockchains and validates transactions if required.
Layer 3: Polygon Networks Layer
Moving onto the third, the mandatory networks layer is utilised by all Polygon based blockchains to allow for interoperability.
It allows Polygon networks to each act independently, while taking advantage of Polygon’s Ethereum layer-2 capabilities.
The network laters is responsible for block production, consensus, and collating transactions.
Layer 4: Execution Layer
The final layer is the mandatory execution layer that interprets and executes transactions included in Polygon’s network chains.
This is achieved by hosting a series of smart contracts that ultimately provide functionality to all dApps built on the Polygon network
Final word on how Polygon (MATIC) works
Ultimately, the Polygon network is an Ethereum sidechain offering value to the vast Ethereum universe of decentralised applications.
Each Ethereum based dApp can be easily converted to an associated Polygon blockchain version.
By taking non-core functions off the Ethereum network and onto layer-2, users gain the best of both worlds by experiencing faster/cheaper transactions on Polygon and all security/decentralisation aspects of Ethereum.
For more a more technical look at how Polygon (MATIC) works, check out the official light-paper.
How to use Polygon (MATIC) for DeFi?
As Ethereum’s main layer-2 scaling solution, using Polygon (MATIC) for DeFi has become extremely popular.
As a protocol and framework for building and connecting Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks, Polygon is perfect for DeFi.
For investors who are currently using Ethereum based DeFi platforms, Polygon offers a simple, fast and low-fee alternative.
Network congestion on Ethereum has driven gas fees to almost unusable levels, especially for smaller DeFi investors.
Enter Polygon.
In this section of our LeoFinance Polygon (MATIC) guide, we explain how to use Polygon for DeFi and show why layer-2 scaling solutions are the future of Ethereum.
Setting up Polygon (MATIC) for DeFi
In order to use Polygon (MATIC) for DeFi, you’re going to have to first move your Ethereum onto the Polygon network.
The easiest way to do this is via the MetaMask wallet and is a lot less overwhelming than it seems at first glance.
Let us walk you through setting up Polygon (MATIC) for DeFi, in 3 simple steps.
1. Connect MetaMask to Polygon
In order to transfer funds from Ethereum, you need to connect your MetaMask wallet to the Polygon network.
After adding the MetaMask Chrome extension, click the “Ethereum Mainnet” text at the top middle of the dropdown and flick to “Custom RPC”.
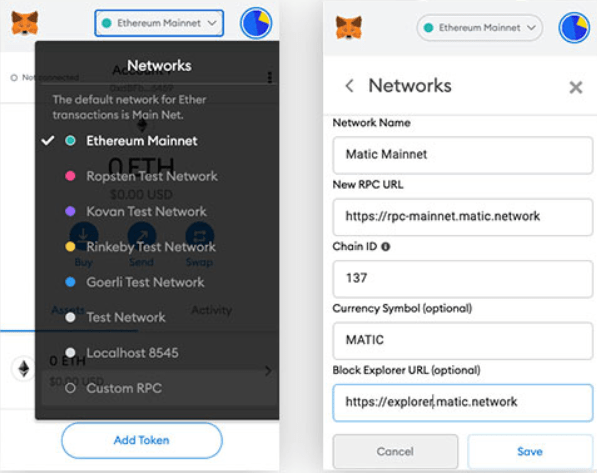
Enter the following details shown in the screenshot above:
- Network Name: Matic Mainnet
- New RPC URL: https://rpc-mainnet.maticvigil.com/
- Chain ID: 137
- Currency Symbol (optional): MATIC
- Block Explorer URL (optional): https://explorer.matic.network/
Once you click save, your MetaMask wallet will now have been switched to the Polygon network.
To switch between Polygon, Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain (if configured), just click the “Matic Mainnet” text at the top middle to bring up the list and switch back as required.
2. Connect the Polygon Web Wallet to Metamask
With all of your funds still sitting in your Ethereum wallet, you need to transfer them onto the Polygon blockchain using the Polygon Web Wallet.

To connect the Polygon Web Wallet, click the MetaMask option and agree to the prompt asking for confirmation of the connection by clicking “Sign”.
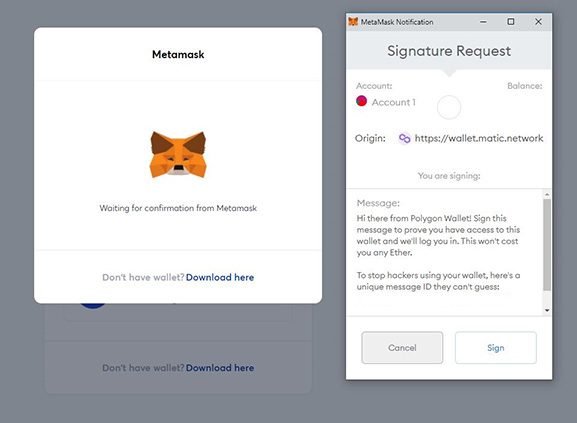
You can now use MetaMask to interact with your Polygon Web wallet.
3. Move funds from Ethereum to Polygon using the Polygon Bridge
Now you’ve connected your Polygon Web Wallet to MetaMask, the following screen will open in your web browser:
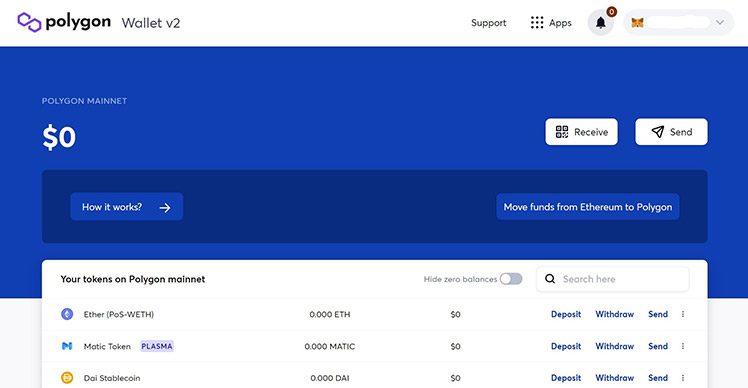
To move your funds from Ethereum to Polygon, simply click the self-explanatory “Move funds from Ethereum to Polygon” button.
This is the Polygon Bridge that allows you to transfer Ethereum tokens onto the Polygon network.
These can be in the form of ETH or any other ERC-20 token sitting in your Ethereum wallet on MetaMask.
On the Polygon Bridge screen, use the dropdown to choose the token you’d like to move to Polygon and enter the amount:
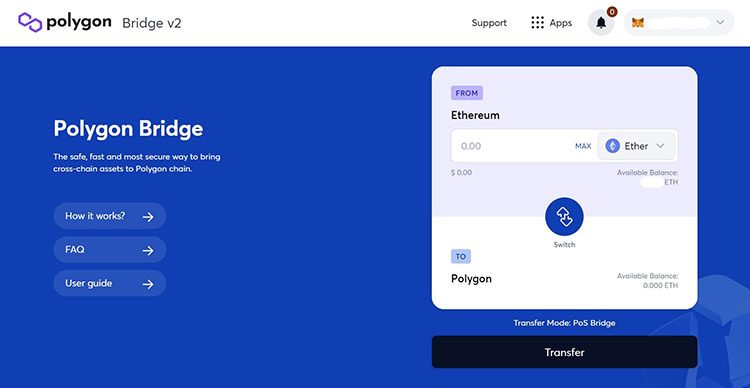
Hit the “Transfer” button, confirm the transaction on your MetaMask popup showing the gas fee on this transaction and let the Polygon Bridge work its magic.
Don’t worry if the transfer takes up to 10 minutes to appear within your Polygon Web Wallet, this is just Ethereum being Ethereum.
Using Polygon (MATIC) DeFi platforms
Now that you have transferred funds to the Polygon blockchain, you can start using Polygon (MATIC) for DeFi.
Actually, you can now use your funds for any application associated with the Polygon blockchain plus any Ethereum based DeFi application.
All of the popular Ethereum based DeFi applications now have an associated Polygon version which you can connect to.
Don't forget to make sure that you’re connecting to the right one.
Some popular Polygon DeFi platforms you can use include:
- SushiSwap
- AAVE
- Curve
- Polycat Finance
Since you’re now using a layer-2 solution in Polygon, you’ll quickly notice that transaction fees are significantly cheaper than if you were still using Ethereum itself.
Just be aware that to transact on the Polygon blockchain, you still have to have a MATIC balance within your wallet to pay the associated (cheaper) gas fees.
Moving funds from Polygon (MATIC) back to Ethereum
The cool thing about using Polygon for DeFi is how simple it is to then move your funds back to Ethereum.
Simply go back to the Polygon Web Wallet and click the “Withdraw” button next to whichever cryptocurrency now sits in your wallet.
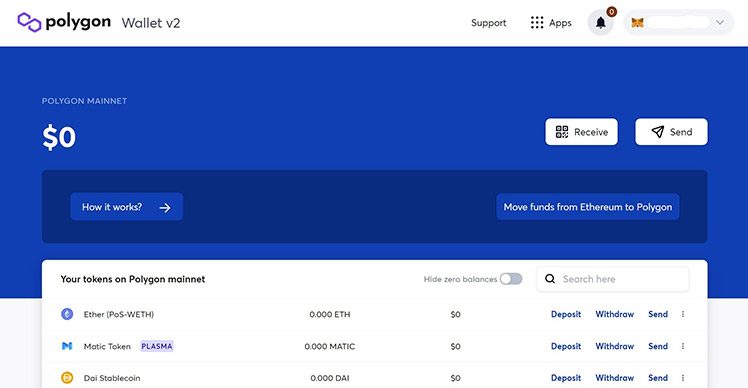
The Polygon Bridge will give you the option to enter how much you’d like to move back to Ethereum before you click “Transfer”.
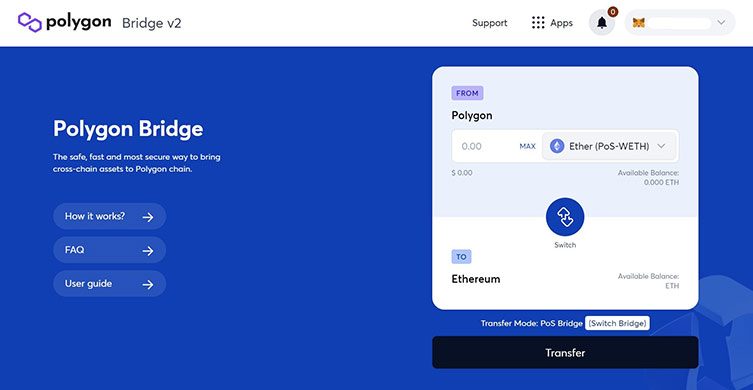
Again, just confirm the transaction on your MetaMask popup showing the gas fee on this transaction and you’re in business.
Using the PoS Bridge will take about an hour to be confirmed by the network, but once it has, you’ll have those funds sitting in your Ethereum wallet once again.
Yep, moving MATIC back to Ethereum after you’ve used an associated Polygon DeFi app, is just as simple.
Note: There are also ETH fees associated with transferring tokens from Ethereum to Polygon and back.
Although once your assets are on the Polygon network, your MATIC fees are minimal.
Last thoughts on using Polygon (MATIC) for DeFi
While a lot of investors are turning to Binance Smart Chain for a cheaper DeFi fix, Polygon is gaining in popularity.
A snapshot of this interest can be seen right here within the LeoFinance community.
We have seen a number of members recently share their own experiences after using #Polygon for DeFi and we’re likely to see many more.
Our community is literally a treasure trove of crypto information just waiting to be discovered.
More on the Polygon (MATIC) wallet
A few extra points on connecting to the Polygon wallet via MetaMask.
We’ve gone over connecting to the Polygon blockchain and the Polygon Web Wallet in the how to use Polygon (MATIC) for DeFi section above.
With that in mind, let’s now go over a few more wallet related points.
The official Polygon Web Wallet
Once obtained, the official version of the Polygon Web Wallet will provide you with super-fast transactions in a simplified environment.
You will find it very easy to interact with the Polygon (MATIC) Network via this particular wallet.
To get the official Polygon Web Wallet:
- Go to https://wallet.matic.network/.
- Connect your existing wallet (Metamask, or by using WalletConnect or Walletlink).
- An ETH Bridge is available for you to easily transfer assets to the Polygon (MATIC) Network.
So is the official Polygon Web Wallet necessary to conduct transactions on the Polygon (MATIC) Network?
"Matic brings you a trustless two-way transaction channel between Matic and Ethereum by introducing the cross-chain bridge with Plasma and PoS security. With this, users can transfer tokens across Polygon without incurring third-party risks and market liquidity limitations.
Matic Network bridge provides a scaling solution that is near-instant, low-cost, and quite flexible. Matic uses a dual-consensus architecture (Plasma + Proof-of-Stake (PoS) platform) to optimise for speed and decentralisation."
For ease of use, and for the simple conversion of BSC assets to the Polygon (MATIC) Network, utilisation of a MetaMask wallet is highly recommended.
The benefits of using MetaMask with your Polygon wallet
Once you have available funds on the Polygon (MATIC) Mainnet, using the Polygon Mainnet option in Metamask allows you to easily manage your MATIC assets and to perform tasks on the Polygon Network with ease.
In whatever application you are using in Polygon, simply connect your MetaMask Wallet (by selecting MATIC Mainnet) and you are ready for action.
An added benefit for Hive users
You can actually HIVE Tokens to purchase MATIC directly.
You will need either the official MATIC Wallet or the MetaMask Wallet to utilise this service.
Again, there is a very easy set of instructions to follow:
- Open your HIVE Blockchain Wallet and select the "Send HIVE" icon to the right of your displayed total of HIVE tokens held.
- In the pop-up window, for recipient, add: "polygonbridge".
- Insert the number of HIVE tokens you wish to be converted to MATIC (note, there is a required minimum of 10 tokens to complete a conversion and transfer).
- In the "Memo" section, copy and paste the destination address for your converted MATIC tokens (i.e. your Metamask Wallet address).
- Hit "Continue" and confirm in your HIVE Keychain.
Within seconds, your MATIC tokens will appear in the destination wallet you chose.
Wallets conclusion
It may seem complicated at first blush, but the steps to create your wallets for access to the Polygon (MATIC) Blockchain is remarkably easy.
Plus, of worthy note, you only have to go through these set-up processes once.
Polygon (MATIC) vs Binance Smart Chain (BSC)
We compare the key differences between Polygon (MATIC) and BSC, before making a call on which one is best.
In this head-to-head comparison, we will discover how the Polygon network is different to Binance Smart Chain.
As we have spoken about throughout this guide, Polygon is a layer-2 solution to Ethereum's scalability, cost and user experience issues.
It's an ecosystem of Ethereum based blockchains, featuring full customisation options.
Another slightly different solution to Ethereum’s scalability issues, is Binance Smart Chain (BSC).
As a fork of Ethereum backed exclusively by Binance, the BSC network quickly became popular but is plagued by centralisation issues.
Let’s now explore the key differences between BSC and Polygon.

6 Differences between Polygon and Binance Smart Chain
1. Innovation
BSC is the modified copy of Ethereum.
It uses the Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA) consensus algorithm, which is a hybrid between Proof of Authority (PoA) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS).
On the other hand, Polygon (Matic Network) is a Layer 2 sidechain of Ethereum, which utilises Plasma framework and POS chains to ensure asset security.
As mentioned above, Polygon is an interoperable, scaling framework for building Ethereum-compatible blockchains.
In the future, they will release ZkRollups, Optimistic Rollups, Standalone Sidechains and Enterprise Sidechains as other scaling solutions.
2. Fees
BSC has much lower gas fees than Ethereum, but it is still a few cents (10-20¢).
The gas fee on the Polygon network however, is almost negligible.
For 1 MATIC, you can do up to 100 basic transactions.
3. Speed
BSC is faster than Ethereum, but transactions take good 3-5 seconds to complete.
Sometimes even longer.
On the Polygon PoS chain, transactions are faster.
Approximately 1 second or less.
On Plasma Chain, they can take up to 7 days.
4. Transactions
In July 2021, BSC is averaging out 3.3 million transactions per day.
For Polygon on the other hand, it's 6.5 million over the same period.
5. Decentralisation
BSC is centralised.
It uses a minimum of 21 nodes to run the chain but all of them are directly or indirectly owned by Binance.
Hence, the DeFi platforms built of BSC are actually CeDeFi.
MATIC does not compromise on decentralisation, while providing higher speeds and low-cost transactions.
6. Network Effect
Binance is one of the biggest brands in the crypto market hence they have a strong network of users and investors.
On the other hand, Polygon is powered by a strong Ethereum developer community.
Polygon is the clear winner
When you consider the points above, Polygon (MATIC) looks like a clear winner.
In theory, the network performs better than BSC without compromising on security and decentralisation of the network.
When you look at the markets, BSC has taken the major share and is doing more transactions than even the Ethereum Mainnet.
Even though it is centralised, BSC hosts a variety of DeFi applications that are user-friendly and easily accessible.
They have comparable TVLs and market caps.
Also, Binance being the biggest crypto exchange in the world has all the resources like developers and funds to create the market some amazing products.
Ethereum congestion and scalability issues drive the adoption for other blockchain projects like Polygon, Polkadot, ADA or Cosmos.
The scalability of blockchains is a never-ending project so we will no doubt see more than Polygon (MATIC) and Binance Smart Chain (BSC) innovating in this space.
Polygon (MATIC) vs Ethereum (ETH)
We compare the key differences between Polygon (MATIC) and the main chain in Ethereum.
In this head-to-head comparison, we will discover how Polygon is different from the Ethereum Blockchain.
The fact that Polygon is a layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum makes this comparison a little less straightforward, but worth looking at nonetheless.
Polygon facilitates the creation of an entire ecosystem of Ethereum based blockchains featuring full customisation and is one solution to Ethereum's scalability and user experience issues.
As you’ll discover when you get deeper into this guide, Polygon has multiple pros and cons when compared to the main Ethereum chain.
Let's explore some of the key differences between the two.

6 differences between Polygon and Ethereum
1. Scaling
Ethereum is facing scaling issues and Polygon provides a developer-friendly framework to scale projects with Ethereum based sidechains without compromising security and decentralization.
The main Ethereum chain is transitioning from PoW to a PoS consensus model, which has massive throughput and speed at a much cheaper rate per transaction.
This whole process will take years to complete and its after-effects are still unknown.
On the other hand, Polygon currently provides two scaling protocols which are already live and others are under development.
2. Fees
On Ethereum, you might have to pay a few dollars to complete your transactions.
On Polygon however, you can do 100 basic transactions with just 1 MATIC.
That’s just $0.89 cents at the time of writing.
3. Speed
Polygon is much faster than Ethereum.
It takes a second or less to complete one transaction on Polygon, whereas on Ethereum it can take up to a few minutes.
Sometimes on Ethereum, you’re even forced to pay higher gas fees to force it to go through.
4. Transactions
Ethereum is averaging out 1.2 million transactions per day in July 2021.
On the other hand, for Polygon, it's 6.5 million transactions for the same period.
5. Network Effect
Ethereum has the biggest developer community associated with it since they introduced the smart contract capabilities early on.
Its scaling issues allowed others to create their own scaling solutions like Polygon, Cosmos, Polkadot, Binance Smart Chain, etc.
Polygon takes advantage of Ethereum's network effect and actually compliments the main chain by creating Ethereum's internet of blockchains.
6. Dependency
While it makes sense for Polygon to create its ecosystem around Ethereum since it’s going to be the biggest gateway to web 3.0 in the future, you cannot ignore the dependency.
Polygon’s success is relying solely on the scalability issues of Ethereum, which may or may not be mitigated by Ethereum 2.0 in the future.
Only time will tell.
The final verdict on Polygon vs Ethereum
Polygon provides a full scaling framework to create EVM-compatible blockchains using Ethereum as a base layer for security and decentralisation.
Currently, it provides a Plasma framework and POS chains.
In the future, they will release ZkRollups, Optimistic Rollups, Optimistic Rollups, Standalone Sidechains & Enterprise Sidechains as other scaling solutions.
Ethereum's scaling however, is a never-ending project.
For now, Polygon is one of the most promising contenders to win Ethereum's scaling race.
The number of transactions is growing and the fee paid per transaction is much lower as compared to other blockchains.
It's becoming the platform of choice for developers to build their apps at a low cost and provide a better user experience.
Even the existing dApps on Ethereum can easily transition to the Polygon network and scale themselves.
The price of the MATIC Token has even jumped from $0.02 (1st Jan 2021) to $0.88 (22nd Jul 2021).
It could easily join Ethereum in the top 10 coins by market cap in the future, due to its growing interest.
Putting all this together, we can recommend that both Ethereum and Polygon be considered good long-term investments.
What gives Polygon (MATIC) value?
We investigate the core attributes and capabilities that give Polygon (MATIC) value.
Much of the value inherent in Polygon and therefore its native MATIC token, is derived from the growth of Ethereum.
As Polygon can do the same technical things as Ethereum except faster and cheaper, the public's perception of the blockchain as an alternative to Ethereum has grown exponentially.
Polygon is an efficient problem-solving blockchain
Due to this structure, Polygon has been able to tap into some of the hottest areas of cryptocurrency on the internet.
These include:
- DeFi (Decentralized finance).
- DApps (Decentralized applications).
- DAO's (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations).
- NFT's (Non-Fungible Tokens).
Beyond offering solutions within these popular areas of the cryptocurrency space, Polygon offers 3 other significant value-enhancing features.
These extra 3 key features being:
1. Polygon is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine: This makes Polygon useful for those who develop apps on Ethereum and program in Solidity.
2. Polygon’s security model is optional: Therefore, there is no need to sacrifice flexibility for the sake of additional security if not needed.
3. Polygon is extremely flexible: In fact, its flexible enough to incorporate different scalability solutions beyond Plasma chains, including optimistic and ZK-rollups".
Polygon the collaborators
In terms of adding value to the Polygon network and ultimately the MATIC token, we’ve seen several large collaborations recently announced.
These collaborations include:
- M-Setu: A partnership with the consulting portion of Infosys, Ltd. This partnership aims to allow its client businesses to cross-operate on the Ethereum blockchain, through utilisation of a created open-source bridge.
- Trace Networks: A collaboration that aims to create the go-to place for retailers to bring the NFT's they make on their products, to both existing and potential customers.
- Google Cloud: On May 29, 2021, Polygon announced its completion of integrating Polygon assets into Google Cloud's BigQuery Project.
These collaborations have all been huge value adds for Polygon.
Celebrities creating hype for Polygon (MATIC)
The final aspect giving value to Polygon (MATIC) is celebrity endorsements and investments.
Leading the charge is billionaire Mark Cuban.
It is presently unknown how much Cuban has invested in Polygon (MATIC), but it would be an understatement to say he is merely 'bullish' on the subject.
For example, on Cuban's own website, he states:
"Polygon is the first well-structured, easy-to-use platform for Ethereum scaling and infrastructure development".
Cuban offers feedback on marketing and facilitates integrations into other projects he invests in including lazy.com, a platform to extend NFTs and personal galleries.
Cuban's celebrity backing of Polygon alone has obviously directed a lot of internet traffic, hype and token demand in its direction.
Final thoughts on what gives Polygon (MATIC) value
On Polygon’s official website, the value of Polygon can be summarised using their own words:
Ethereum's Internet of Blockchains.
Polygon is a protocol and a framework for building and connecting Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks.
Aggregating scalable solutions on Ethereum and supporting a multi-chain Ethereum ecosystem.
Polygon (MATIC) pros and cons
A pros and cons list for Polygon (MATIC), Ethereum’s layer-2 scaling solution.
In this section of our Polygon (MATIC) guide, we’re going to look at some of the network’s major pros and cons.
After considering all of the points below, we will then try to answer whether you should invest in Polygon in 2021, or let this one slide.
Let's get started.
Pros of Polygon (MATIC)
1. Scaling Framework
There are so many projects out there that are mitigating scaling issues of Ethereum (such as Polkadot, Cosmos, etc).
However, none of them provides a solution to create those scaling blockchains and the ability to connect them.
Polygon differs by offering a framework that can be used by developers to create their own scaling solutions.
This unique feature provides flexibility and interoperability and avoids developmental challenges.
2. Decentralization
Unlike Binance Smart Chain (BSC) for example, Polygon is decentralized.
This elevates the trust factor of the network over its competitors, while still providing much higher transaction speeds and lower fees.
As a clearly superior alternative, we currently see numerous Ethereum and BSC based apps moving over to the Polygon network.
3. Ethereum's Network Effect
As there are so many people involved in its ecosystem all over the world, Ethereum's community is huge.
As a decentralized execution platform, Polygon provides a simple and quick transition for any dApp that is already built on Ethereum.
Thanks to Polygon, developers can benefit from the Ethereum network effect, while still creating their own sovereign blockchain connected to the network.
4. Quick Adoption
DeFi giants like Aave, PolyMarket, SushiSwap, and Curve have quickly adopted the Polygon Network.
Best of all, the list of popular applications using Polygon continues to grow.
The primary drivers of this quick adoption by numerous projects being Polygon’s cheaper gas fees and faster block speed.
5. Security
Polygon’s layer-2 solution relies on Ethereum for security.
Through its framework, it provides "security as a service" and an alternative to creating independent networks that can each choose their own protocols.
6. Developer Friendly
Polygon is made for developers, by the developers.
The team behind Polygon all have solid credentials in software development.
They are fully committed to the Ethereum ecosystem and therefore have created a solution in Polygon that is designed to easily onboard the current Ethereum dev community.
7. Celebrity Endorsements
Overall the reputation of Polygon is increasing due to several endorsements that came along the way.
Polygon has been praised numerous times by the Founder of Ethereum, Vitalik Buterin and has also recently been added to the portfolio of Mark Cuban.
Polygon even received funds and support from the Binance Launchpad program.
Cons of Polygon (MATIC)
1. Ethereum Dependent
As the settlement layer, Ethereum is the epicentre of Polygon's ecosystem.
For this reason, Polygon is fully Ethereum dependent.
It makes sense because Ethereum is setting out to become the premier base layer of Web 3.0 and in the long run, plans to dominate the blockchain space.
But with questions around Ethereum’s ability to scale remaining, one cannot ignore this dependency.
2. Under Development
Right now, Polygon provides Matic Plasma and Matic POS Chains as their two scaling solutions.
Other than that, Polygon Framework is available through SDK which provides developers with enough documentation to get started.
Other scaling solutions like ZK Rollups, Optimistic Rollups, Validum Chains, Sidechains, and Enterprise Chains are all in various developmental stages.
We don't know when they are going to go live.
3. Matic Plasma Chains
Matic plasma chains are not versatile and can only be used for limited functions.
POS Chains are preferred because they provide flexibility and a better user experience when compared to Matic Plasma.
4. MATIC Token Demand
Right now MATIC is required to become a validator, for governance and for paying transaction fees.
But it’s looking like ZK Rollups’ solutions will not use MATIC at all.
Transactions fees are already so cheap, hence you don't need a big stack of MATIC tokens to transact as required.
5. Competition
Other scaling solutions like Polkadot, Solana, Optimism and Cosmos are also slowly gaining momentum.
They too are all using Ethereum or other blockchains to provide a better user experience overall.
Over time we might see better solutions coming up and developer talent moving where the action is.
6. Upcoming Release of Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum 2.0 is expected to complete by early 2022, taking Ethereum from a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus model, to Proof of Stake (PoS).
This release will scale the Ethereum network and could solve the high gas fees and network congestion we see on the Ethereum main chain.
This might reduce the popularity of layer-2 solutions like Polygon and therefore limit its relevance over time.
Should I Buy Polygon (MATIC) in 2021?
While buying Polygon (MATIC) is ultimately up to you, we go over a few considerations.
While we could offer our own opinion on whether you should be buying Polygon (MATIC) in 2021, we’re going to leave this to one of the greatest investors of our generation.
Let’s take a look at what Mark Cuban thinks about Polygon.
Mark Cuban thinks you should buy Polygon (MATIC)
If a billionaire like Mark Cuban is buying Polygon, then who are we to argue?
Mark’s thoughts are that aside from Bitcoin and Ethereum, the Polygon network is “destroying everybody else.”
In his eyes, Bitcoin and Ethereum certainly aren't going anywhere.
But when you take a look at other altcoins, the advantages described in this Polygon guide makes it more likely to be the one that comes out on top.
Especially when crypto adoption goes to the next level and the crypto market shakes out.
Mark Cuban even lists Polygon under the companies section of his website.
In this section, he describes Polygon as the first well-structured, easy-to-use platform for Ethereum scaling and infrastructure development.
That usability can explain why Mark Cuban is buying Polygon and why you could consider following his lead.
Final Thoughts on buying Polygon in 2021
While Mark Cuban’s current notoriety is due to his friendly spats with fellow billionaire Elon Musk regarding Bitcoin and Dogecoin, you can’t knock him for actually putting his money where his mouth is by investing heavily in Polygon (MATIC.)
Alongside Cuban’s enthusiasm for Polygon, we’re also excited about the mobile app SmartDeFi which wants to do for cryptocurrencies what RobinHood did for stocks.
That is increasing mainstream accessibility to crypto markets.
For us, the fact that SmartDefi chose Polygon as its network of choice is extremely exciting.
Not to mention we continue to see other DeFi protocols accepting MATIC, and even various high profile cryptocurrency indexes including the token as an asset worth tracking.
Thanks to an increase in usage by protocols, developers, and networks, Polygon was able to do something most altcoins rarely if ever do: Rally while Bitcoin fell.
As a sidechain of Ethereum which aims to alleviate the high gas fees and the congestion experienced on Ethereum, Polygon is fast becoming a viable solution of choice.
Just as Ethereum is a strong buy, the network’s layer-2 solution in Polygon looks like it could be a strong buy as well.
LeoFinance Crypto Guides.
Why not leave a comment below and share your thoughts on our guide to Polygon (MATIC) crypto? All comments that add something to the discussion will be upvoted.
This Polygon (MATIC) crypto guide is exclusive to leofinance.io.
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta
Because this blog is a very good content, I did reblog to note and learn Polygon.
!PIZZA
@crypto-guides! I sent you a slice of $PIZZA on behalf of @tin.aung.soe.
Learn more about $PIZZA Token at hive.pizza (5/10)
Great write-up! I learned so much about Polygon from this, I feel like I have a much better understanding of the layer-2 ETH solution. The fact that Polygon can connect ANY ETH or ERC-20-based tokens with each other, really is a game-changer!
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta