
This question has been asked by every futurist research lab at many of the largest banks, central banks, financial institutions, think tanks, consulting firms and government committees around the world.
R3CEV, a consortium effort financed by the world's largest bank is busy for answering this question. Goldman Sachs, McKinsey Consulting, and Consumer Research have all written excellent reports on this question. The governments of the UK, US Senate, Canada, Australia and the EU have all raised questions in this regard.
Much of this research highlights, There are four main areas of change:
Infrastructure For Cross-Border Transactions
The digital revolution has completely changed the media, as we all know. This also has an impact on the financial industry. Of course, financial institutions use computers. They grew for databases in the 1970s and 1980s, they created web pages in the 1990s and they migrated to mobile apps in the new millennium.
But the digital revolution has not revolutionized cross-border transactions. Western Union remains a big name, doing the same business they have always owned. Banks continue to use the complex infrastructure for simple transactions, such as sending money abroad.
Blockchain technology allows institutions to make direct financial links between each other, correspondent banking. R3's main product to date, Corda, operates for correspondent banking. Corda is a play on words that combines 'deal' (deal) and 'cable' (the straightest line between two points in a circle). In Corda's case, the circle consisted of banks that would use the shared ledger for important transactions, contracts and documents.
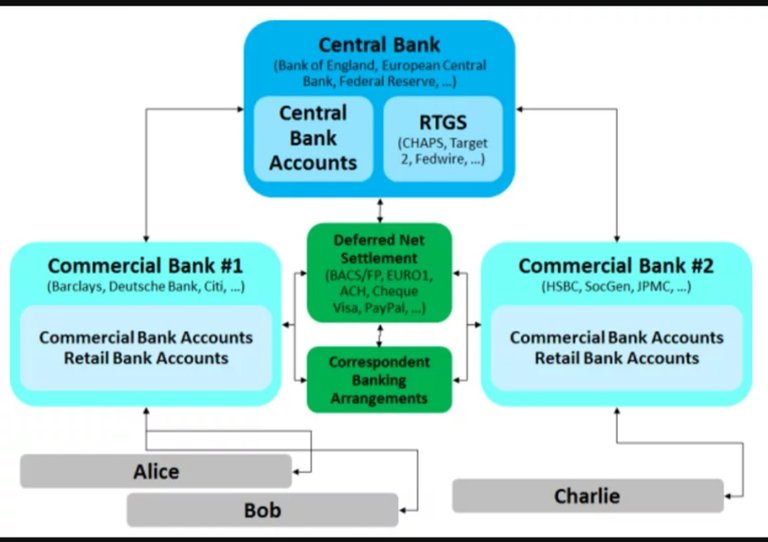
Financial institutions can compete using this common database to track execution, clearing, and settlement of transactions without the need to involve a central database or management system. In short, banks will be able to formalize and secure digital relationships among themselves in ways that were not possible before.
In the above representation, it means that correspondent banking agreements and RTGS can be shortened.
Transactions can take place directly between two parties on a frictionless P2P basis. Ripple, a licensed blockchain, was created to solve many of these problems.
Digital Assets is a Class
Bitcoin creates something unique: digital property. Before bitcoin, "digital" was not synonymous with scarcity. Anything that is digital can be copied with the click of a button. A glimpse of the music industry and album sales tells this story convincingly.
But bitcoin did something new: it created a digital code that couldn't be copied.

So, for the first time since bits and bytes were invented, there was a way to have something digital that couldn't be copied. It gives a digital code value. To this day, bitcoin's value is based on its blockchain capacity to prevent double spends and the creation of fake coins.
Governance and Markets
This capability, however, goes beyond just recording transactions. The Nasdaq, for example, was one of the first to build a platform that would allow private companies to issue and trade stocks using blockchain.
Other developers code pre-programmable financial instruments to perform corporate action and business logic.
In 2016, a blockchain project called The DAO, which runs on the ethereum blockchain, was launched with the aim of emulating the crowdfunding market. The percentage of your contribution to the fund represents the percentage of votes in how the total funds will be spent.
Reporting and Regulatory Compliance
Blockchain function as a record system that is completely transparent and accessible to regulators. Can also be coded to authorize transactions that comply with regulatory reporting.
For example, banks have heavy reporting obligations to institutions such as FinCEN. Whenever they authorize a transaction of more than $ 10,000, they must report the information to FinCEN, which stores it for use as an anti-money laundering database.
Clearing and Settlement
With paper world trading, the time frame for clearing and settling a transaction is commonly referred to as a 'T + 3' - that is, three days after the trade (T), the transaction is completed.
With blockchain technology, the entire trading life cycle - execution, clearing and settlement - occurs at the trading stage. With digital assets, trading is settlement, and the cryptographic keys and digital holdings they control can reduce post-trade latency and counterparty risk.
Accounting and Auditing
Whereas most databases are snapshots of a moment in time, blockchain databases are built from their own transaction history. They are databases with context, history itself, a stand-alone record system.
The implications for auditing and accounting are enormous.
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta
This is the place, from where you copied this article:
https://www.slideshare.net/DharmaMortha/how-could-blockchain-technology-change-finance
And you want now rewards?
For your hard work of copy-paste, and changing a few words?
Enjoy my DOWNVOTES
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta
Congratulations @cryptopedia666! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDo not miss the last post from @hivebuzz: