
Summary of the article:
- Introduction: Introduces the topic, objective and questions of the text.
- Blockchain: Disruptive technology for the financial sector Explains what blockchain is, how it works, what applications it has and what advantages and challenges it presents for the financial sector.
- Artificial intelligence: a tool to optimize the decentralized financial system. Explains what artificial intelligence is, how it works, what applications it has and how it can be combined with blockchain to improve the decentralized financial system.
- How to design and implement a decentralized financial system in a fictitious or real country: Proposes a methodology to design and implement a decentralized financial system in a fictitious or real country, based on four phases: context analysis, model design, system implementation and system evaluation.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the main ideas of the text, highlights the importance and impact of the proposal and raises the need for further research, regulation and education on the subject.
Resumen del artículo:
- Introducción: Presenta el tema, el objetivo y las preguntas del texto.
- Blockchain: Tecnología disruptiva para el sector financiero Explica qué es blockchain, cómo funciona, qué aplicaciones tiene y qué ventajas y retos presenta para el sector financiero.
- Inteligencia artificial: una herramienta para optimizar el sistema financiero descentralizado. Explica qué es la inteligencia artificial, cómo funciona, qué aplicaciones tiene y cómo puede combinarse con blockchain para mejorar el sistema financiero descentralizado.
- Cómo diseñar e implementar un sistema financiero descentralizado en un país ficticio o real: Propone una metodología para diseñar e implementar un sistema financiero descentralizado en un país ficticio o real, basada en cuatro fases: análisis del contexto, diseño del modelo, implementación del sistema y evaluación del sistema.
- Conclusión: Resume las ideas principales del texto, destaca la importancia y el impacto de la propuesta y plantea la necesidad de seguir investigando, regulando y educando sobre el tema.
Introduction
Financial systems are the set of institutions, markets, instruments and rules that facilitate economic transactions between agents in a society. These systems have a great influence on the economic, social and political development of countries, since they affect aspects such as savings, investment, consumption, income distribution, price stability, legal security and financial inclusion.
However, traditional financial systems, based on the intermediation of centralized entities such as central banks, commercial banks, governments or regulatory agencies, present a series of problems and limitations that hinder their efficiency and transparency. Some of these problems are:
- Lack of access to financial services for a significant part of the world's population, especially in developing countries, due to high costs, bureaucratic barriers or lack of infrastructure.
- Vulnerability to financial crises, caused by excessive indebtedness, speculation, corruption, mismanagement or lack of supervision of financial institutions.
- The loss of monetary and fiscal sovereignty of countries in the face of supranational organizations or private entities that impose their conditions or interests.
- Lack of transparency and accountability of financial entities, which hide or manipulate information on their activities, profits, risks or social and environmental impacts.
- Inefficient and slow payment and settlement processes, involving high commissions, delays, errors or fraud.
Against this backdrop, there is a need to look for alternatives to create more democratic, efficient and transparent financial systems. One of these alternatives is the use of blockchain technology and artificial intelligence, which offer new possibilities for designing and implementing decentralized financial systems, based on the direct and voluntary participation of economic agents, without the need for intermediaries or central authorities.
What is blockchain, what is artificial intelligence, how can they be combined to create a decentralized financial system, and what are the advantages and challenges of this proposal? These are some of the questions we will try to answer in this text.

Introduccion
Los sistemas financieros son el conjunto de instituciones, mercados, instrumentos y normas que facilitan las transacciones económicas entre los agentes de una sociedad. Estos sistemas tienen una gran influencia en el desarrollo económico, social y político de los países, ya que afectan a aspectos como el ahorro, la inversión, el consumo, la distribución de la renta, la estabilidad de precios, la seguridad jurídica o la inclusión financiera.
.
Sin embargo, los sistemas financieros tradicionales, basados en la intermediación de entidades centralizadas como bancos centrales, bancos comerciales, gobiernos o agencias reguladoras, presentan una serie de problemas y limitaciones que dificultan su eficiencia y transparencia. Algunos de estos problemas son:
.
- La falta de acceso a los servicios financieros de una parte importante de la población mundial, especialmente en los países en desarrollo, debido a los altos costes, las barreras burocráticas o la falta de infraestructura.
- La vulnerabilidad a las crisis financieras, provocadas por el exceso de endeudamiento, la especulación, la corrupción, la mala gestión o la falta de supervisión de las entidades financieras.
- La pérdida de soberanía monetaria y fiscal de los países frente a organismos supranacionales o entidades privadas que imponen sus condiciones o intereses.
- La falta de transparencia y rendición de cuentas de las entidades financieras, que ocultan o manipulan información sobre sus actividades, beneficios, riesgos o impactos sociales y ambientales.
- La ineficiencia y lentitud de los procesos de pago y liquidación, que implican altas comisiones, retrasos, errores o fraudes.
.
Ante este panorama, surge la necesidad de buscar alternativas que permitan crear sistemas financieros más democráticos, eficientes y transparentes. Una de estas alternativas es el uso de la tecnología blockchain y la inteligencia artificial, que ofrecen nuevas posibilidades para diseñar e implementar sistemas financieros descentralizados, basados en la participación directa y voluntaria de los agentes económicos, sin necesidad de intermediarios ni autoridades centrales.
.
¿Qué es el blockchain? ¿Qué es la inteligencia artificial? ¿Cómo pueden combinarse para crear un sistema financiero descentralizado? ¿Qué ventajas y desafíos presenta esta propuesta? Estas son algunas de las preguntas que intentaremos responder en este texto.
Blockchain: a disruptive technology for the financial sector
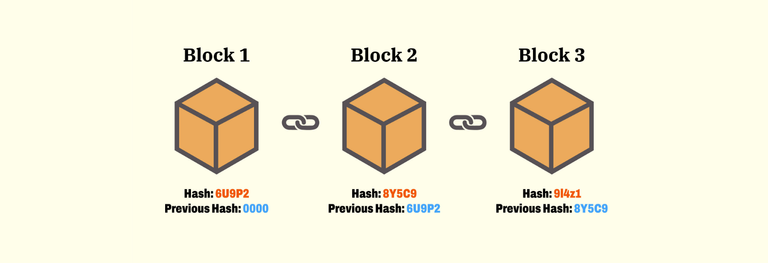
The blockchain is a technology that allows storing and transmitting information in a secure, verifiable and distributed way. It is a database shared by a network of nodes or participants that record and validate the transactions made between them, without the need for intermediaries or central authorities. Each transaction is grouped in a block that is linked to the previous one by means of a cryptographic code, forming an immutable and transparent chain.
The blockchain originated in 2008, when an individual or group under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published the article "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System", describing the functioning of the first decentralized financial system based on this technology: bitcoin. Bitcoin is a digital currency or cryptocurrency that is created and transferred using a computer protocol that guarantees its scarcity, security and anonymity. Since then, other cryptocurrencies based on the blockchain have emerged, such as ethereum, litecoin or ripple.
The blockchain not only allows the creation of digital currencies, but also other types of financial assets or smart contracts. Financial assets are digital representations of value that can be exchanged or transferred between system participants. For example, digital tokens or tokens representing stocks, bonds, currencies, commodities or property rights can be created. Smart contracts are computer programs that are automatically executed when predefined conditions are met by the parties, without the need for intermediaries or central authorities. For example, smart contracts can be created to regulate the payment of rent, the shipment of goods, the fulfillment of a bet or the distribution of profits.
The blockchain offers a number of advantages for the financial sector, such as:
- Reducing transaction costs by eliminating intermediaries and the fees they charge for their services.
- Improving the speed and efficiency of payment and settlement processes by reducing waiting times, errors and fraud.
- Improved security and trust by ensuring the integrity, veracity and traceability of information through the use of cryptography and distributed consensus.
- Improved financial inclusion and participation, by facilitating access to financial services for people or entities that do not have them or are excluded by the traditional system.
- Improved transparency and accountability, by enabling public and audited access to information about financial transactions and assets.
However, blockchain also presents a number of challenges and limitations for the financial sector, such as:
- The lack of regulation and oversight, which generates legal uncertainty, legal and tax risks, and makes it difficult to protect the rights and interests of consumers and investors.
- Lack of scalability and sustainability, which limits the capacity and performance of the network to process a large volume of transactions, and which generates high energy consumption and a high ecological footprint.
- Lack of interoperability and standardization, which hinders communication and integration between different blockchain-based platforms or systems, and prevents taking advantage of synergies and economies of scale.
- Lack of education and awareness, which prevents greater dissemination and adoption of the blockchain by economic agents, and which generates resistance or distrust on the part of traditional players in the financial sector.
Blockchain: una tecnología disruptiva para el sector financiero
El blockchain o cadena de bloques es una tecnología que permite almacenar y transmitir información de forma segura, verificable y distribuida. Se trata de una base de datos compartida por una red de nodos o participantes que registran y validan las transacciones que se realizan entre ellos, sin necesidad de intermediarios ni autoridades centrales. Cada transacción se agrupa en un bloque que se enlaza con el anterior mediante un código criptográfico, formando una cadena inmutable y transparente.
.
El blockchain tiene su origen en el año 2008, cuando un individuo o grupo bajo el seudónimo de Satoshi Nakamoto publicó el artículo “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”, donde describía el funcionamiento del primer sistema financiero descentralizado basado en esta tecnología: el bitcoin. El bitcoin es una moneda digital o criptomoneda que se crea y se transfiere mediante un protocolo informático que garantiza su escasez, su seguridad y su anonimato. Desde entonces, han surgido otras criptomonedas basadas en el blockchain, como el ethereum, el litecoin o el ripple.
.
El blockchain no solo permite crear monedas digitales, sino también otros tipos de activos financieros o contratos inteligentes. Los activos financieros son representaciones digitales de valor que pueden ser intercambiados o transferidos entre los participantes del sistema. Por ejemplo, se pueden crear tokens o fichas digitales que representen acciones, bonos, divisas, materias primas o derechos de propiedad. Los contratos inteligentes son programas informáticos que se ejecutan automáticamente cuando se cumplen unas condiciones preestablecidas por las partes, sin necesidad de intermediarios ni autoridades centrales. Por ejemplo, se pueden crear contratos inteligentes que regulen el pago de un alquiler, el envío de una mercancía, el cumplimiento de una apuesta o el reparto de beneficios.
.El blockchain ofrece una serie de ventajas para el sector financiero, como:
- Reducción de los costes de transacción al eliminar intermediarios y las comisiones que cobran por sus servicios.
- Mejora de la velocidad y la eficiencia de los procesos de pago y liquidación al reducir los tiempos de espera, los errores y el fraude.
- Mejora de la seguridad y la confianza, garantizando la integridad, veracidad y trazabilidad de la información mediante el uso de la criptografía y el consenso distribuido.
- Mejora de la inclusión y la participación financieras, facilitando el acceso a los servicios financieros a personas o entidades que carecen de ellos o están excluidas por el sistema tradicional.
- Mejora de la transparencia y la rendición de cuentas, al permitir el acceso público y auditado a la información sobre transacciones y activos financieros.
.Sin embargo, blockchain también presenta una serie de retos y limitaciones para el sector financiero, tales como:
- La falta de regulación y supervisión, que genera inseguridad jurídica, riesgos legales y fiscales, y dificulta la protección de los derechos e intereses de consumidores e inversores.
- Falta de escalabilidad y sostenibilidad, que limita la capacidad y el rendimiento de la red para procesar un gran volumen de transacciones, y que genera un elevado consumo energético y una alta huella ecológica.
- Falta de interoperabilidad y estandarización, que dificulta la comunicación e integración entre diferentes plataformas o sistemas basados en blockchain, e impide aprovechar sinergias y economías de escala.
- Falta de educación y concienciación, que impide una mayor difusión y adopción del blockchain por parte de los agentes económicos, y que genera resistencia o desconfianza por parte de los actores tradicionales del sector financiero.
Artificial intelligence: a tool to optimize the decentralized financial system
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a scientific discipline that studies how to create systems or machines capable of performing tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, communicating or solving problems. AI is based on the use of algorithms or mathematical rules that allow processing large amounts of data or information to extract knowledge or make decisions.
AI has multiple applications in different fields, such as medicine, education, industry or entertainment. In the financial field, AI can provide value in aspects such as:
- Financial analysis: AI can help analyze historical or real-time data about markets, companies, assets or consumers, to identify financial trends, patterns, opportunities or risks.
- Financial advice: AI can help provide personalized or automated financial advisory services to clients or investors based on their profiles, preferences or financial needs.
- Financial trading: AI can help execute financial transactions quickly, efficiently and profitably, using intelligent strategies or algorithms that adapt to market conditions.
- Financial management: AI can help optimize internal or external processes related to financial management, such as accounting, auditing, compliance or fraud prevention.
AI can be combined with blockchain to create a more advanced and competitive decentralized financial system. Some ways in which AI can improve the decentralized financial system are:
- Consensus optimization: AI can help improve the distributed consensus mechanism used to validate transactions on the blockchain by using techniques such as machine learning or deep learning to adjust the consensus parameters or criteria according to the characteristics of the network, nodes or transactions to increase the efficiency, security and scalability of the system.
- Optimization of smart contracts: AI can help improve the design, execution and evaluation of smart contracts used to automate financial transactions on the blockchain, through the use of techniques such as natural language processing or automated reasoning, which enable the creation of more expressive, flexible and robust smart contracts that adapt to changing conditions or circumstances in the environment.
- Optimization of financial assets: AI can help to improve the creation, management and exchange of financial assets represented on the blockchain, through the use of techniques such as computer vision or pattern recognition, which enable the creation of more diverse, innovative and personalized financial assets that match the preferences or needs of economic agents.
- Optimization of financial services: AI can help to improve the supply, demand and quality of financial services provided in the blockchain, through the use of techniques such as expert systems or intelligent agents, which make it possible to create more sophisticated, accessible and transparent financial services, aimed at meeting the expectations or requirements of customers or investors.
The combination of AI and blockchain offers a number of advantages for the decentralized financial system, such as:
- The improvement of collective intelligence: the combination of AI and blockchain allows creating a more intelligent and collaborative decentralized financial system, where economic agents can share information, knowledge and resources, to make better financial decisions.
- The improvement of financial innovation: the combination of AI and blockchain allows the creation of a more innovative and competitive decentralized financial system, where economic agents can explore new financial possibilities and opportunities, to generate more economic and social value.
- Improved financial adaptation: the combination of AI and blockchain enables the creation of a more adaptive and resilient decentralized financial system, where economic agents can adjust to changing conditions or circumstances in the environment, to reduce financial risks and leverage competitive advantages.
However, the combination of AI and blockchain also presents a number of challenges and limitations for the decentralized financial system, such as:
- Technical complexity: the combination of AI and blockchain implies a higher technical complexity to design and implement a decentralized financial system, which requires a high level of knowledge, expertise and resources from the system developers or providers.
- Ethical responsibility: the combination of AI and blockchain implies a greater ethical responsibility to regulate and supervise a decentralized financial system, ensuring respect for ethical principles such as fairness, transparency, privacy or security by the users or beneficiaries of the system.
- Democratic governance: the combination of AI and blockchain implies greater democratic governance to manage and coordinate a decentralized financial system, ensuring the effective, equitable and inclusive participation of all economic agents involved in the system.

Inteligencia artificial: una herramienta para optimizar el sistema financiero descentralizado
La inteligencia artificial (IA) es una disciplina científica que estudia cómo crear sistemas o máquinas capaces de realizar tareas que normalmente requieren inteligencia humana, como aprender, razonar, comunicarse o resolver problemas. La IA se basa en el uso de algoritmos o reglas matemáticas que permiten procesar grandes cantidades de datos o información para extraer conocimiento o tomar decisiones.
.La IA tiene múltiples aplicaciones en distintos campos, como la medicina, la educación, la industria o el entretenimiento. En el ámbito financiero, la IA puede aportar valor en aspectos como:
- Análisis financiero: La IA puede ayudar a analizar datos históricos o en tiempo real sobre mercados, empresas, activos o consumidores, para identificar tendencias, patrones, oportunidades o riesgos financieros.
- Asesoramiento financiero: La IA puede ayudar a proporcionar servicios de asesoramiento financiero personalizados o automatizados a clientes o inversores en función de sus perfiles, preferencias o necesidades financieras.
- Operaciones financieras: La IA puede ayudar a ejecutar transacciones financieras de forma rápida, eficiente y rentable, utilizando estrategias o algoritmos inteligentes que se adaptan a las condiciones del mercado.
- Gestión financiera: La IA puede ayudar a optimizar los procesos internos o externos relacionados con la gestión financiera, como la contabilidad, la auditoría, el cumplimiento o la prevención del fraude.
La IA puede combinarse con blockchain para crear un sistema financiero descentralizado más avanzado y competitivo. Algunas formas en las que la IA puede mejorar el sistema financiero descentralizado son:
- La optimización del consenso: la IA puede ayudar a mejorar el mecanismo de consenso distribuido que se usa para validar las transacciones en el blockchain, mediante el uso de técnicas como el aprendizaje automático (machine learning) o el aprendizaje profundo (deep learning), que permiten ajustar los parámetros o criterios del consenso según las características de la red, los nodos o las transacciones, para aumentar la eficiencia, la seguridad y la escalabilidad del sistema.
- La optimización de los contratos inteligentes: la IA puede ayudar a mejorar el diseño, la ejecución y la evaluación de los contratos inteligentes que se usan para automatizar las operaciones financieras en el blockchain, mediante el uso de técnicas como el procesamiento del lenguaje natural (natural language processing) o el razonamiento automático (automated reasoning), que permiten crear contratos inteligentes más expresivos, flexibles y robustos, que se adapten a las condiciones o circunstancias cambiantes del entorno.
- La optimización de los activos financieros: la IA puede ayudar a mejorar la creación, la gestión y el intercambio de los activos financieros que se representan en el blockchain, mediante el uso de técnicas como la visión artificial (computer vision) o el reconocimiento de patrones (pattern recognition), que permiten crear activos financieros más diversos, innovadores y personalizados, que se ajusten a las preferencias o necesidades de los agentes económicos.
- La optimización de los servicios financieros: la IA puede ayudar a mejorar la oferta, la demanda y la calidad de los servicios financieros que se prestan en el blockchain, mediante el uso de técnicas como los sistemas expertos (expert systems) o los agentes inteligentes (intelligent agents), que permiten crear servicios financieros más sofisticados, accesibles y transparentes, que se orienten a satisfacer las expectativas o requerimientos de los clientes o inversores.
La combinación de la IA y el blockchain ofrece una serie de ventajas para el sistema financiero descentralizado, como:
- La mejora de la inteligencia colectiva: la combinación de la IA y el blockchain permite crear un sistema financiero descentralizado más inteligente y colaborativo, donde los agentes económicos pueden compartir información, conocimiento y recursos, para tomar mejores decisiones financieras.
- La mejora de la innovación financiera: la combinación de la IA y el blockchain permite crear un sistema financiero descentralizado más innovador y competitivo, donde los agentes económicos pueden explorar nuevas posibilidades y oportunidades financieras, para generar más valor económico y social.
- La mejora de la adaptación financiera: la combinación de la IA y el blockchain permite crear un sistema financiero descentralizado más adaptable y resiliente, donde los agentes económicos pueden ajustarse a las condiciones o circunstancias cambiantes del entorno, para reducir los riesgos financieros y aprovechar las ventajas competitivas.
Sin embargo, la combinación de la IA y el blockchain también presenta una serie de desafíos y limitaciones para el sistema financiero descentralizado, como:
- La complejidad técnica: la combinación de la IA y el blockchain implica una mayor complejidad técnica para diseñar e implementar un sistema financiero descentralizado, que requiere un alto nivel de conocimiento, experiencia y recursos por parte de los desarrolladores o proveedores del sistema.
- La responsabilidad ética: la combinación de la IA y el blockchain implica una mayor responsabilidad ética para regular y supervisar un sistema financiero descentralizado, que garantice el respeto a los principios éticos como la equidad, la transparencia, la privacidad o la seguridad por parte de los usuarios o beneficiarios del sistema.
- La gobernabilidad democrática: la combinación de la IA y el blockchain implica una mayor gobernabilidad democrática para gestionar y coordinar un sistema financiero descentralizado, que asegure la participación efectiva, equitativa e inclusiva de todos los agentes económicos implicados en el sistema.
How to design and implement a decentralized financial system in a fictitious or real country
To design and implement a decentralized financial system in a fictitious or real country, a series of steps or phases must be followed:
Context analysis: a diagnosis must be made of the economic, social and political context of the country where the decentralized financial system is to be implemented, identifying the needs, problems, opportunities and relevant actors in the financial sector.
Model design: the conceptual and technical model of the decentralized financial system must be defined, specifying the objectives, characteristics, functions and components of the system. These components are:
-) The blockchain platform: the blockchain platform to be used to create and manage the decentralized financial system must be chosen, taking into account aspects such as the type of blockchain (public, private or hybrid), the consensus mechanism (proof of work, proof of participation, etc.), the communication protocol (TCP/IP, UDP, etc.), the programming language (Solidity, Python, etc.) or the technological infrastructure (cloud, local, etc.).
-) The digital currency: the digital currency to be used as a medium of exchange or store of value in the decentralized financial system must be created, taking into account aspects such as the name, symbol, unit, issuance, distribution, supply or demand of the currency.
-) Financial assets: the financial assets to be represented on the blockchain and exchanged or transferred in the decentralized financial system must be created, taking into account aspects such as the type, quantity, value, liquidity or volatility of the assets.
-) Smart contracts: the smart contracts that are to be used to automate financial transactions on the blockchain and that are to be executed in the decentralized financial system must be created, taking into account aspects such as conditions, actions, events or consequences of the contracts.
-) Financial services: the financial services to be provided on the blockchain and offered in the decentralized financial system must be created, taking into account aspects such as the type, quality, price or accessibility of the services.Implementation of the system: the decentralized financial system must be put into operation in the country where it is to be implemented, carrying out the necessary actions for its operation and dissemination. These actions are:
-) Installation and configuration of the system: the decentralized financial system must be installed and configured in the chosen technological infrastructure, ensuring its compatibility, security and performance.
-) System integration and connection: the decentralized financial system must be integrated and connected to other systems or platforms existing in the country or in the world, ensuring their interoperability, standardization and scalability.
-) Promotion and dissemination of the system: the decentralized financial system must be promoted and disseminated among potential economic agents in the country or the world, ensuring their education, awareness and adoption.Evaluation of the system: the impact and results of the decentralized financial system in the country where it has been implemented must be evaluated, following up and monitoring its operation and performance. These indicators are:
-) The efficiency and transparency of the system: the efficiency and transparency of the decentralized financial system must be measured, analyzing aspects such as cost, speed, security or traceability of transactions or financial assets.
-) The financial inclusion and participation of the system: the financial inclusion and participation of the decentralized financial system should be measured, analyzing aspects such as access, availability or quality of financial services.
-) Economic and social development of the system: the economic and social development of the decentralized financial system should be measured, analyzing aspects such as economic growth, income distribution or social and environmental impact.

Cómo diseñar e implantar un sistema financiero descentralizado en un país ficticio o real
Para diseñar e implantar un sistema financiero descentralizado en un país ficticio o real, hay que seguir una serie de pasos o fases:
- Análisis del contexto: se debe realizar un diagnóstico del contexto económico, social y político del país donde se va a implantar el sistema financiero descentralizado, identificando las necesidades, problemas, oportunidades y actores relevantes del sector financiero.
- Diseño del modelo: se debe definir el modelo conceptual y técnico del sistema financiero descentralizado, especificando los objetivos, características, funciones y componentes del sistema. Estos componentes son:
-) La plataforma blockchain: se debe elegir la plataforma blockchain que se utilizará para crear y gestionar el sistema financiero descentralizado, teniendo en cuenta aspectos como el tipo de blockchain (pública, privada o híbrida), el mecanismo de consenso (prueba de trabajo, prueba de participación, etc.), el protocolo de comunicación (TCP/IP, UDP, etc.), el lenguaje de programación (Solidity, Python, etc.) o la infraestructura tecnológica (nube, local, etc.).
-) La moneda digital: se debe crear la moneda digital que se utilizará como medio de cambio o depósito de valor en el sistema financiero descentralizado, teniendo en cuenta aspectos como el nombre, símbolo, unidad, emisión, distribución, oferta o demanda de la moneda.
-) Activos financieros: deben crearse los activos financieros que se representarán en la blockchain y se intercambiarán o transferirán en el sistema financiero descentralizado, teniendo en cuenta aspectos como el tipo, la cantidad, el valor, la liquidez o la volatilidad de los activos.
-) Contratos inteligentes: deben crearse los contratos inteligentes que se utilizarán para automatizar las transacciones financieras en la cadena de bloques y que se ejecutarán en el sistema financiero descentralizado, teniendo en cuenta aspectos como las condiciones, acciones, eventos o consecuencias de los contratos.
-) Servicios financieros: deben crearse los servicios financieros que se prestarán en la blockchain y que se ofrecerán en el sistema financiero descentralizado, teniendo en cuenta aspectos como el tipo, la calidad, el precio o la accesibilidad de los servicios.- Implantación del sistema: el sistema financiero descentralizado debe ponerse en funcionamiento en el país donde se vaya a implantar, llevando a cabo las acciones necesarias para su funcionamiento y difusión. Estas acciones son:
-) Instalación y configuración del sistema: el sistema financiero descentralizado debe ser instalado y configurado en la infraestructura tecnológica elegida, garantizando su compatibilidad, seguridad y desempeño.
-) Integración y conexión del sistema: el sistema financiero descentralizado debe integrarse y conectarse a otros sistemas o plataformas existentes en el país o en el mundo, asegurando su interoperabilidad, estandarización y escalabilidad.
-) Promoción y difusión del sistema: el sistema financiero descentralizado debe ser promovido y difundido entre los potenciales agentes económicos del país o del mundo, asegurando su educación, concienciación y adopción.- Evaluación del sistema: se debe evaluar el impacto y los resultados del sistema financiero descentralizado en el país donde se ha implantado, realizando un seguimiento y control de su funcionamiento y rendimiento. Estos indicadores son:
-) La eficiencia y transparencia del sistema: se debe medir la eficiencia y transparencia del sistema financiero descentralizado, analizando aspectos como el coste, la rapidez, la seguridad o la trazabilidad de las transacciones o activos financieros.
-) La inclusión y participación financiera del sistema: se debe medir la inclusión y participación financiera del sistema financiero descentralizado, analizando aspectos como el acceso, la disponibilidad o la calidad de los servicios financieros.
-) El desarrollo económico y social del sistema: debe medirse el desarrollo económico y social del sistema financiero descentralizado, analizando aspectos como el crecimiento económico, la distribución de la renta o el impacto social y medioambiental.
How to control inflation with blockchain and artificial intelligence
One of the most important problems affecting the financial system is inflation, which is defined as a generalized and sustained increase in the prices of goods and services over a given period of time. Inflation reduces the purchasing power of the currency and negatively affects economic growth, income distribution and financial stability.
Inflation is usually related to the supply and demand for money, as well as to the expectations or confidence of economic agents. When there is more supply than demand for money, the value of money decreases and prices increase. When there is more demand than supply of money, the value of money increases and prices decrease. When there are abrupt or unpredictable changes in the value of money, economic instability or uncertainty is generated.
The use of blockchain technology and artificial intelligence can offer a solution to control inflation by creating a decentralized financial system based on a digital currency that guarantees its scarcity, security and anonymity, and dynamically adjusts to market conditions.
The blockchain-based digital currency is created and transferred using a computer protocol that limits its total supply to a fixed or predefined amount, thus avoiding uncontrolled issuance or devaluation of the currency by monetary authorities. In addition, the protocol guarantees the security and anonymity of transactions, through the use of cryptography and distributed consensus.
Artificial intelligence based on the blockchain is responsible for monitoring and dynamically adjusting the speed of transactions, according to the demand and supply of the currency, to maintain its stable value and avoid fluctuations or volatility. Transaction velocity refers to the number of transactions that can be processed per unit of time in the system. When there is more demand than supply of the currency, the velocity of transactions increases, which implies a greater circulation or turnover of the currency, and therefore, greater economic activity. When there is more supply than demand for the currency, the velocity of transactions decreases, which implies a lower circulation or turnover of the currency, and therefore, a lower economic activity.
Artificial intelligence can use a reinforcement learning algorithm to adapt the speed of transactions according to the performance of the system. The algorithm is rewarded or punished according to the outcome of its actions, and thus learns to optimize the speed of transactions. For example, if the system is congested or saturated by excess demand or supply, the algorithm reduces the speed of transactions to avoid crashes or delays. If the system is underutilized or underutilized due to a lack of demand or supply, the algorithm increases the speed of transactions to encourage activity or movement.
In this way, a balance is achieved between supply and demand for the currency, as well as stability and predictability in its value, which allows inflation and its negative effects on the financial system to be controlled.

Cómo controlar la inflación con Blockchain e inteligencia artificial.
Uno de los problemas más importantes que afectan al sistema financiero es la inflación, que se define como el aumento generalizado y sostenido de los precios de los bienes y servicios durante un período de tiempo determinado. La inflación reduce el poder adquisitivo de la moneda y afecta negativamente al crecimiento económico, a la distribución de la renta y a la estabilidad financiera.
.
La inflación suele estar relacionada con la oferta y la demanda de dinero, así como con las expectativas o la confianza de los agentes económicos. Cuando hay más oferta que demanda de dinero, el valor del dinero disminuye y los precios aumentan. Cuando hay más demanda que oferta de dinero, el valor del dinero aumenta y los precios disminuyen. Cuando hay cambios bruscos o impredecibles en el valor del dinero, se genera una inestabilidad o una incertidumbre económica.
.
El uso de la tecnología blockchain y la inteligencia artificial puede ofrecer una solución para controlar la inflación, al crear un sistema financiero descentralizado basado en una moneda digital que garantice su escasez, su seguridad y su anonimato, y que se ajuste dinámicamente a las condiciones del mercado.
.
La moneda digital basada en el blockchain se crea y se transfiere mediante un protocolo informático que limita su oferta total a una cantidad fija o predefinida, evitando así la emisión descontrolada o la devaluación de la moneda por parte de las autoridades monetarias. Además, el protocolo garantiza la seguridad y el anonimato de las transacciones, mediante el uso de la criptografía y el consenso distribuido.
.
La inteligencia artificial basada en el blockchain se encarga de monitorizar y ajustar dinámicamente la velocidad de las transacciones, según la demanda y la oferta de la moneda, para mantener su valor estable y evitar fluctuaciones o volatilidades. La velocidad de las transacciones se refiere al número de transacciones que se pueden procesar por unidad de tiempo en el sistema. Cuando hay más demanda que oferta de la moneda, la velocidad de las transacciones aumenta, lo que implica una mayor circulación o rotación de la moneda, y por tanto, una mayor actividad económica. Cuando hay más oferta que demanda de la moneda, la velocidad de las transacciones disminuye, lo que implica una menor circulación o rotación de la moneda, y por tanto, una menor actividad económica.
.
La inteligencia artificial puede usar un algoritmo de aprendizaje por refuerzo para adaptar la velocidad de las transacciones según el rendimiento del sistema. El algoritmo recibe una recompensa o un castigo según el resultado de sus acciones, y así aprende a optimizar la velocidad de las transacciones. Por ejemplo, si el sistema está congestionado o saturado por un exceso de demanda u oferta, el algoritmo reduce la velocidad de las transacciones para evitar colapsos o retrasos. Si el sistema está desaprovechado o infrautilizado por una falta de demanda u oferta, el algoritmo aumenta la velocidad de las transacciones para incentivar la actividad o el movimiento.
.
De esta forma, se consigue un equilibrio entre la oferta y la demanda de la moneda, así como una estabilidad y una previsibilidad en su valor, lo que permite controlar la inflación y sus efectos negativos sobre el sistema financiero.
Advantages and disadvantages of creating a decentralized financial system using Blockchain technology and artificial intelligence:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Reduction of transaction costs | Lack of education and awareness |
| Improved speed and efficiency of payment and settlement processes | Technical complexity |
| Improved safety and confidence | Ethical responsibility |
| Improving financial inclusion and participation | none |
| Improving transparency and accountability | none |
| Improving collective intelligence | none |
| Improving financial innovation | none |
Ventajas y desventajas de crear un sistema financiero descentralizado utilizando la tecnología Blockchain y la inteligencia artificial:
Ventajas Desventajas Reducción de los costes de transacción Falta de educación y concienciación Mejora de la velocidad y la eficiencia de los procesos de pago y liquidación Complejidad técnica Mejora de la seguridad y la confianza Responsabilidad ética Mejora de la inclusión y la participación financiera ninguna Mejora de la transparencia y la rendición de cuentas ninguna Mejora de la inteligencia colectiva ninguna Mejora de la innovación financiera ninguna
Conclusion
In this text we have seen how it is possible to create a decentralized financial system using blockchain technology and artificial intelligence. We have reviewed the history of centralized financial systems and their problems, explained how blockchain and artificial intelligence can offer a more efficient and transparent alternative, and proposed how a decentralized financial system could be designed and implemented in a fictitious or real country.
The use of blockchain technology and artificial intelligence to create a decentralized financial system presents a number of advantages and challenges that must be considered rigorously and responsibly. It is an innovative and disruptive proposal that can radically transform the financial sector and have a major impact on the economic and social development of countries. Therefore, further research, regulation and education on this proposal is required, as well as greater collaboration and participation of all economic agents involved.
Thank you for reading 📜
Conclusión
En este texto hemos visto cómo es posible crear un sistema financiero descentralizado utilizando la tecnología blockchain y la inteligencia artificial. Hemos repasado la historia de los sistemas financieros centralizados y sus problemas, hemos explicado cómo blockchain y la inteligencia artificial pueden ofrecer una alternativa más eficiente y transparente, y hemos propuesto cómo podría diseñarse e implantarse un sistema financiero descentralizado en un país ficticio o real.
.
El uso de la tecnología blockchain y la inteligencia artificial para crear un sistema financiero descentralizado presenta una serie de ventajas y retos que deben ser considerados con rigor y responsabilidad. Se trata de una propuesta innovadora y disruptiva que puede transformar radicalmente el sector financiero y tener un gran impacto en el desarrollo económico y social de los países. Por ello, es necesaria una mayor investigación, regulación y educación sobre esta propuesta, así como una mayor colaboración y participación de todos los agentes económicos implicados.
.
Gracias por leer 📜
Congratulations @mrwiki! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 300 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCheck out our last posts:
There is reasonable evidence that this article is machine-generated. Posting such content is considered fraud. Fraud is discouraged by the community and may result in the account being Blacklisted.
Guide: Why and How People Abuse and Defraud
If you believe this comment is in error, please contact us in #appeals in Discord.